PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Course A terminal branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It travels posteriorly, passing through the space between the lumbosacral trunk and the anterior ramus of spinal nerve S1. It exits the pelvic cavity by passing through the greater sciatic foramen. On leaving the greater sciatic foramen it divides into a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Dorsal surface of the ischial spine. Insertion: Blends with the more superior fibres of the tendon of the obturator internus and attaches with the tendon to the medial border of the greater trochanter of the femur. Key Relations: Lies superior to the obturator internus muscle. Functions Working with gemellus inferior and obturator internus,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
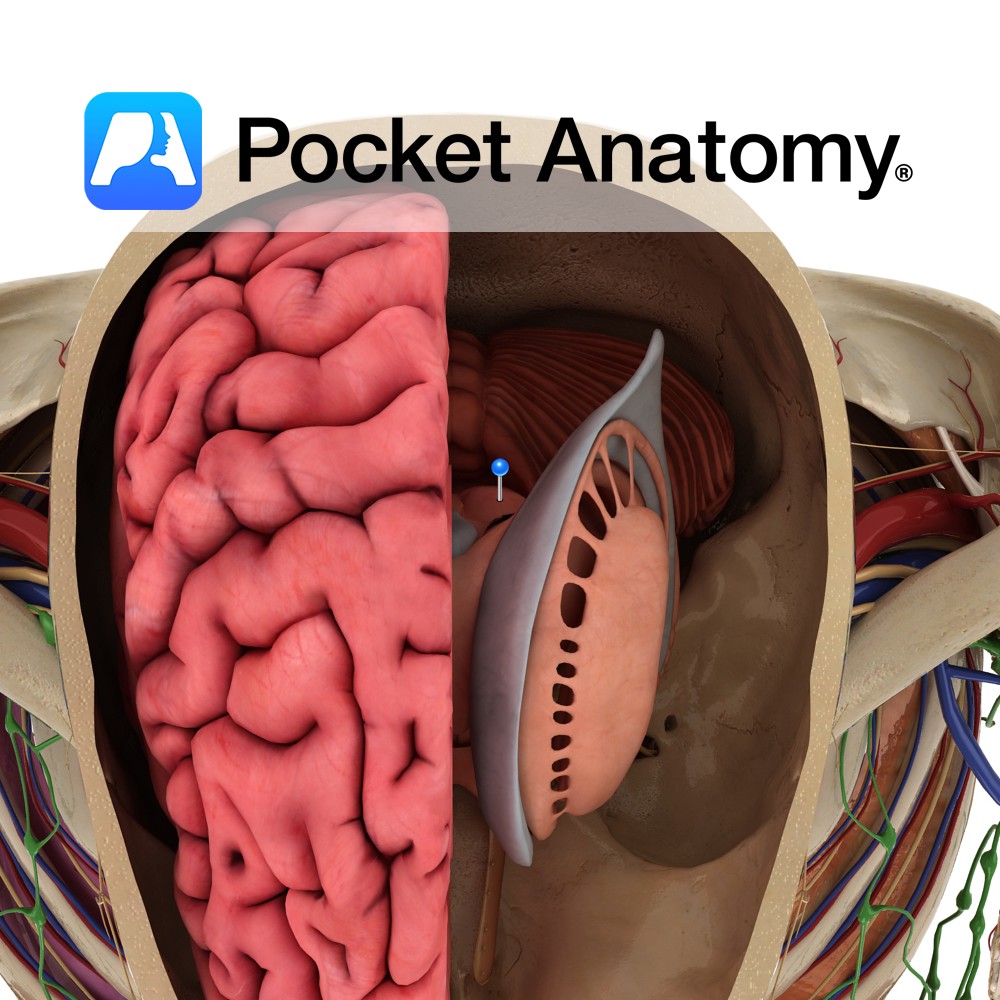
Anatomy Paired structure that forms a superficial elevation on the dorsal side of the rostral midbrain. It is located within the tectum of the midbrain. The superior and inferior colliculi are collectively known as the corpora quadrigemina. Blood Supply: Supplied by branches of the posterior cerebral arteries. Functions Tectospinal fibers arise from the superior colliculus.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
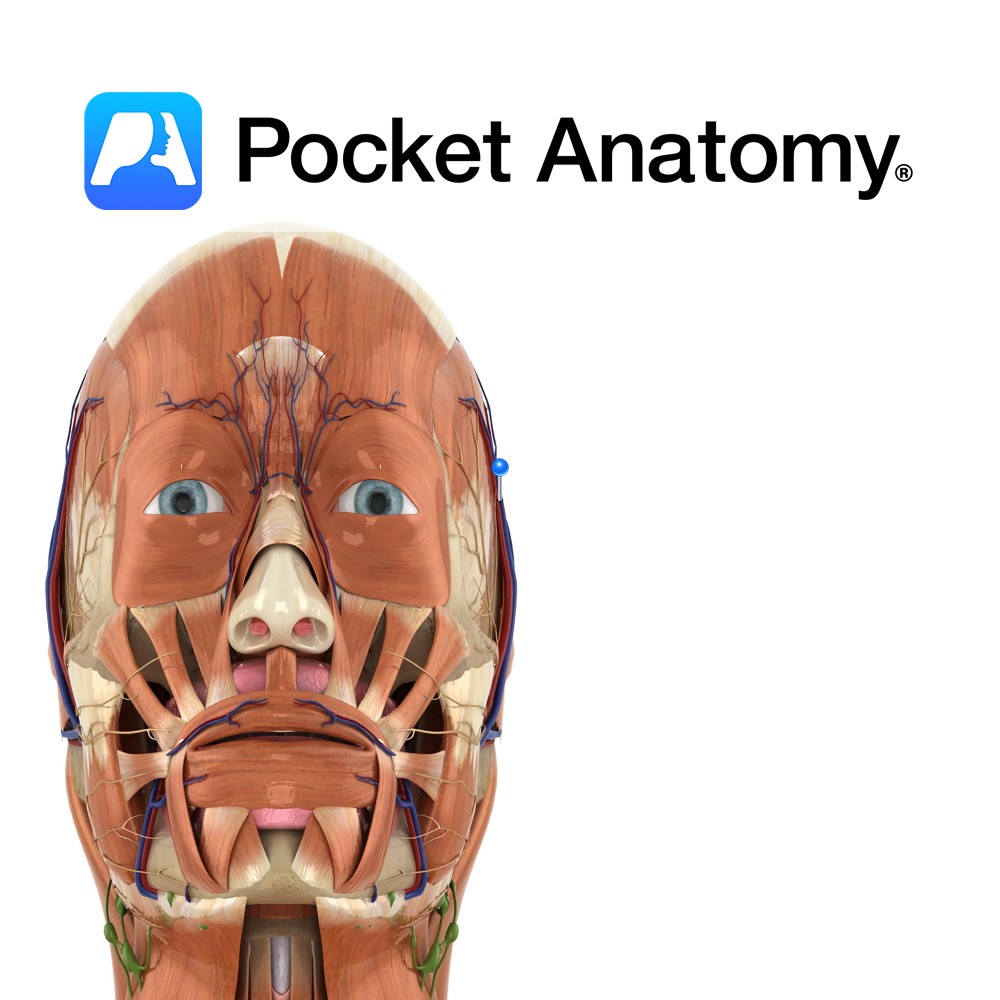
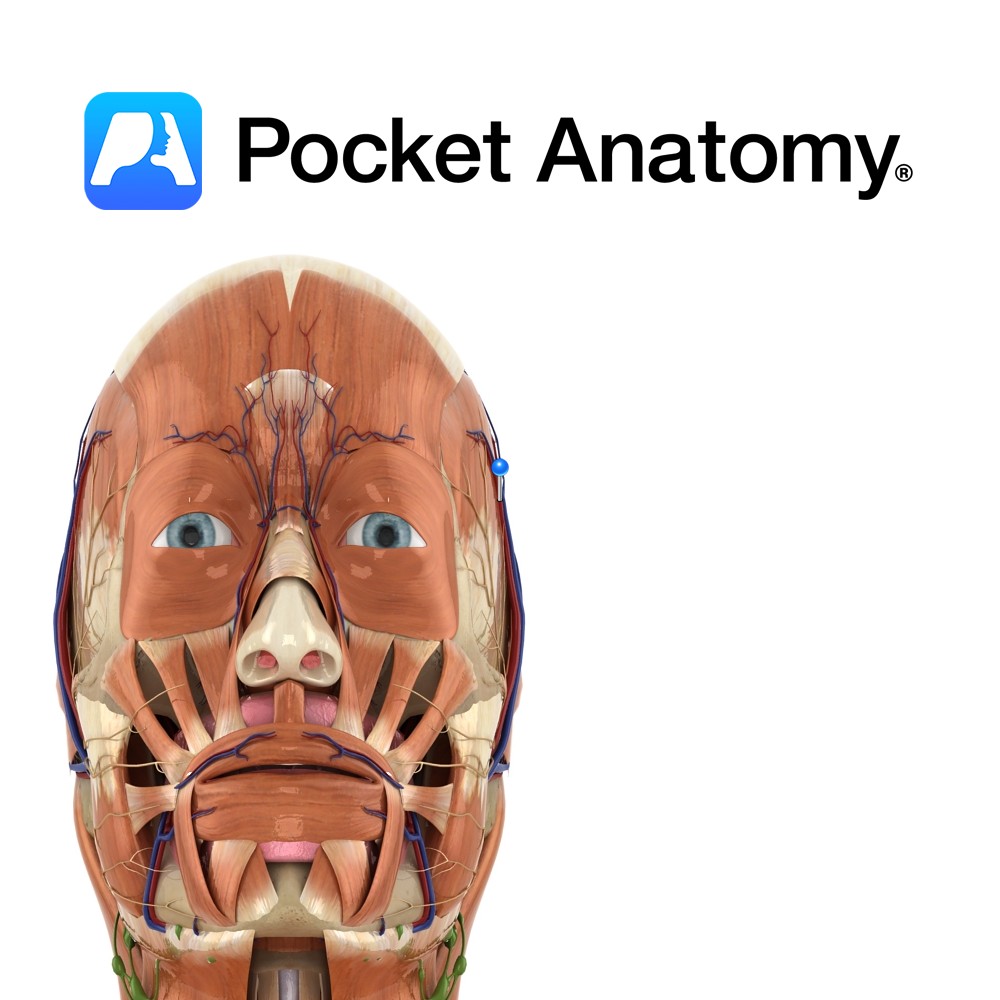
Anatomy Course Begins in a venous plexus on the side of the scalp. It travels through the connective tissue layer of the scalp, to just above the parotid gland, where it unites with the maxillary vein to form the retromandibular vein. Drain Drains the superficial temporal aspect of the scalp. Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the external carotid artery. It is a terminal branch of the external carotid and is said to begin in the parotid gland. It ascends anterior to the ear and divides into branches that travel in the connective tissue layer of the scalp. Supply Supplies most of the scalp. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
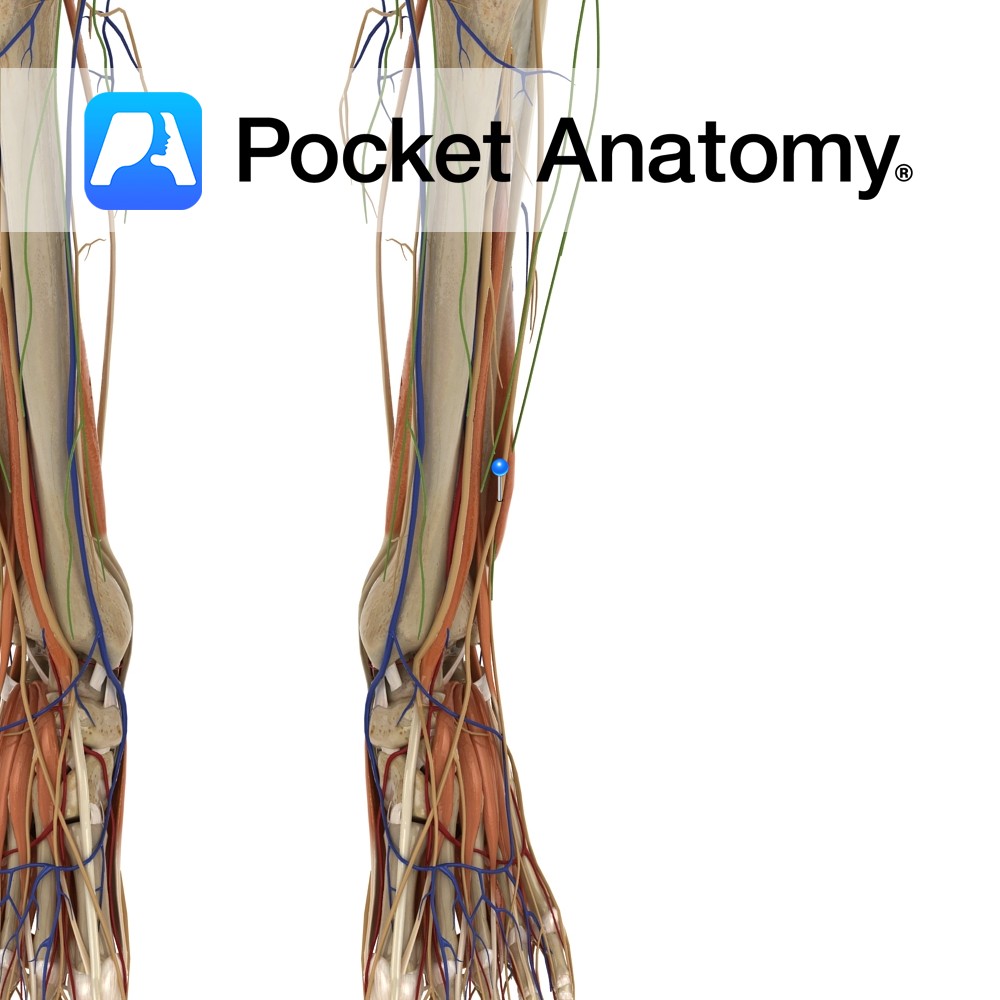
Anatomy Course Branches from the common peroneal nerve just below the knee joint on the anterolateral side of the leg. It descends towards the foot passing between the peroneus longus and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It then becomes more superficial, piercing through the deep fascia approximately half-way down the leg. It ends in branches which
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
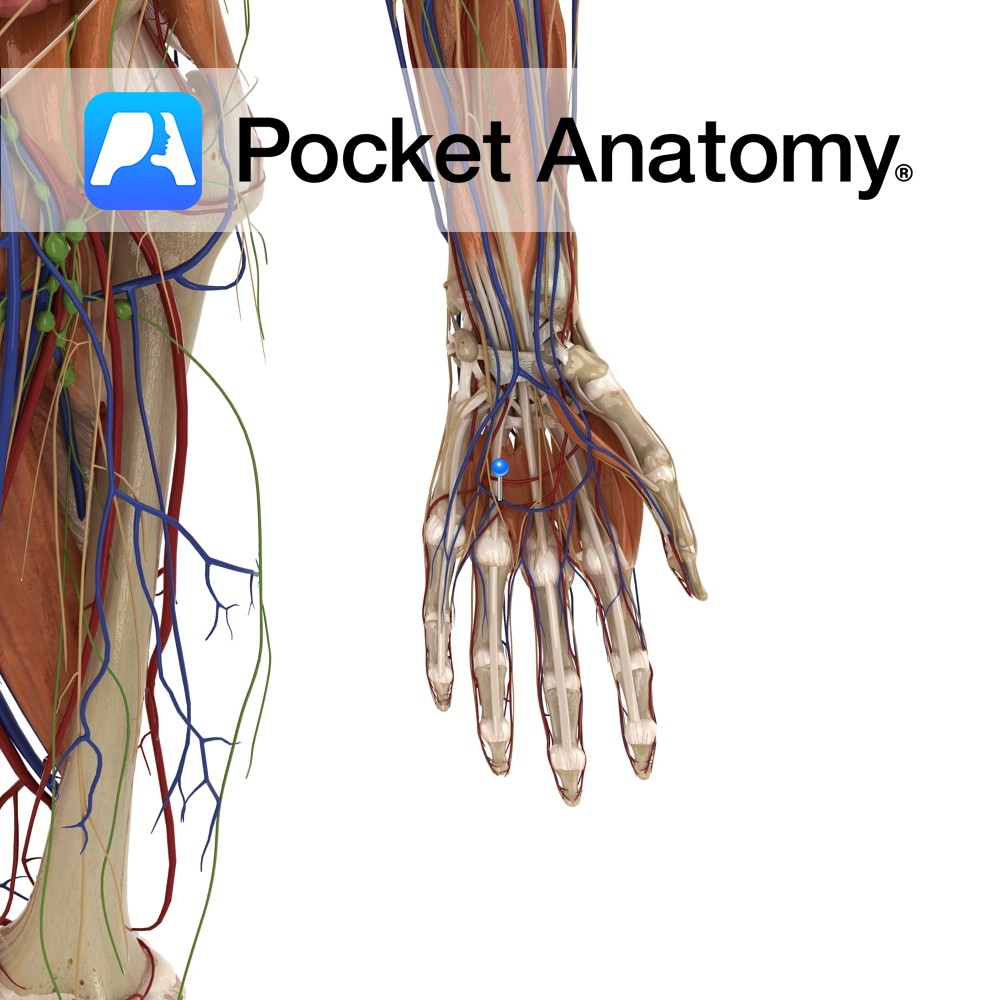
Anatomy Course Receives blood from the palmar digital veins. It forms an arch around the palm and drains into the radial and ulnar veins of the forearm. Drain Drains the superficial aspect of the palm. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
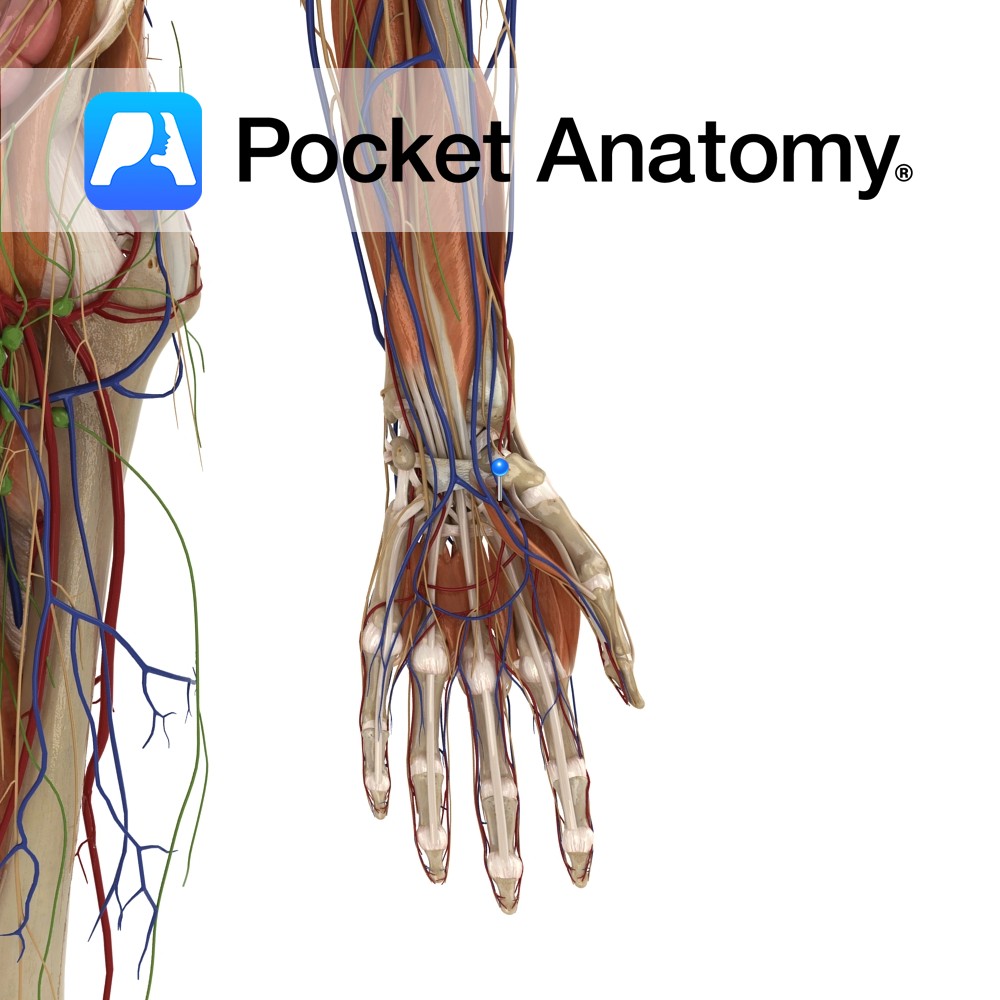
Anatomy Course Contributes to the superficial palmar arterial arch, even though the ulnar artery is the main supply. It branches from the radial artery just before the radial artery curves under the lateral side of the wrist. The artery passes between the thenar muscles close to their origin, travelling beneath adductor pollicis brevis and above
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
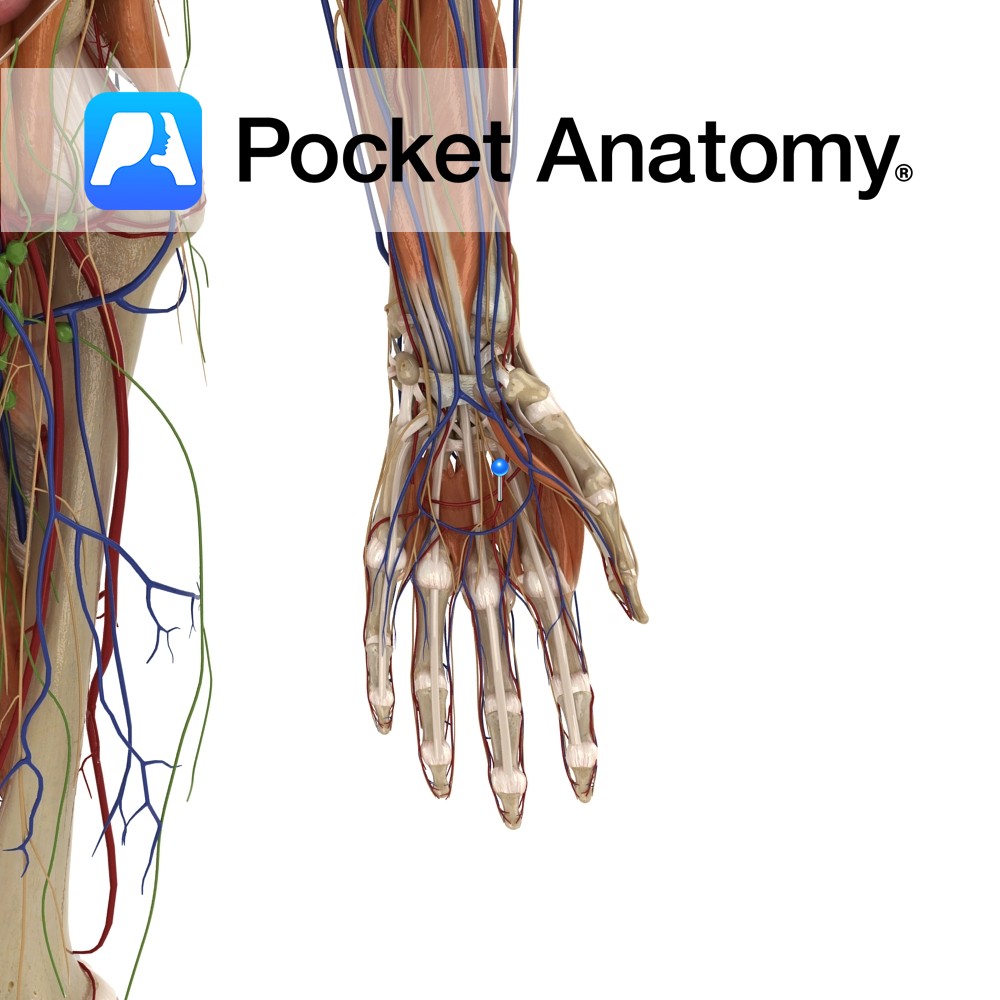
Anatomy Course Mainly contributed to by the ulnar artery, though it connects both ulnar and radial arteries, as it anastomoses with the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery. It runs across the palm in the plane, just deep to the palmar aponeurosis and lies on the flexor tendons of the digits. Supply Supplies blood
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
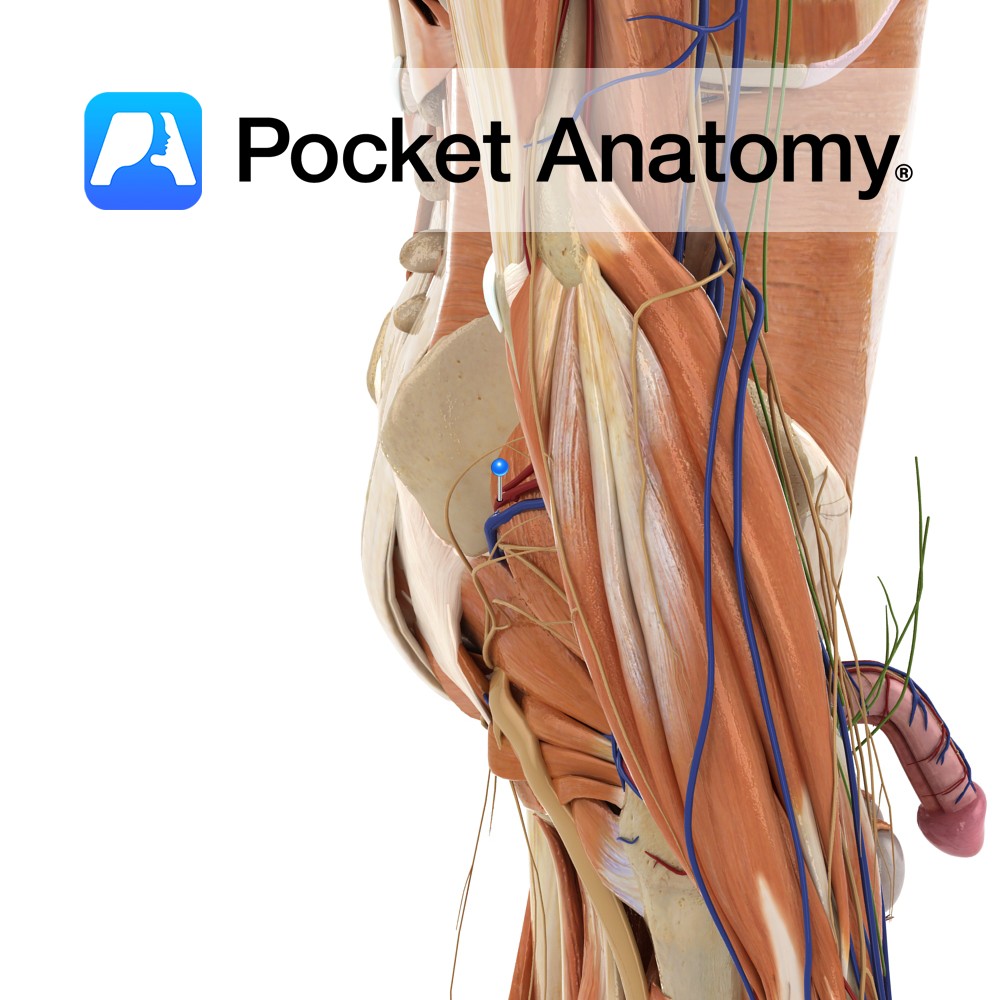
Anatomy Course The popliteal vein becomes known as the femoral vein after the adductor canal. It runs superiorly until it ends at the inferiorly to the inguinal ligament, where it then drains into the external iliac vein. Properly known as the femoral vein, though used by some specialists (e.g. radiologists) to differentiate the femoral vein
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins