PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
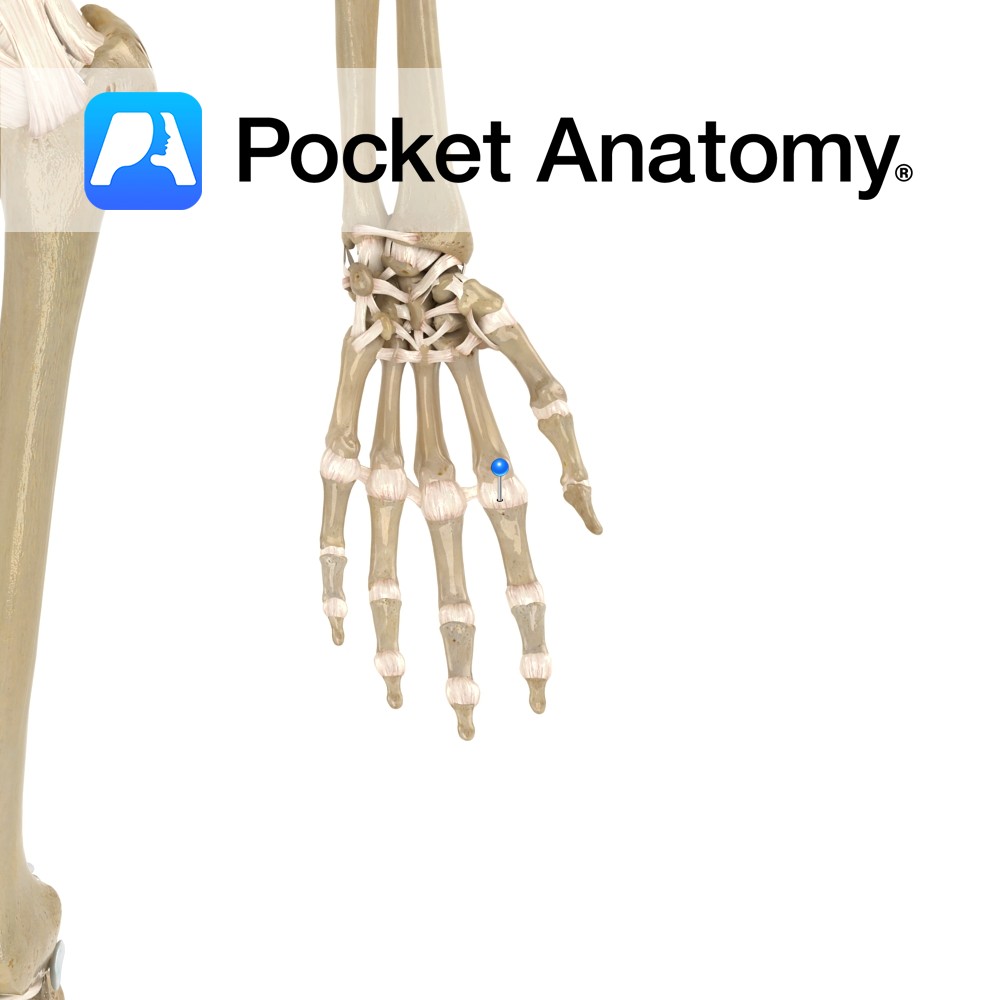
Anatomy The metacarpophalangeal ligaments attach from the distal heads of metacarpals two to five on the radial and ulnar surfaces, then attaching to the base of the corresponding phalangeals. Functions To reinforce laterally the metacarpophalangeal joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course All the colic veins follow their corresponding arteries and eventually empty into the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. Drain Left colic drains the descending colon, the right colic drains the ascending colon and the middle colic drains the transverse colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branch of either the superior mesenteric artery or the ileocolic artery (inconsistent). Along its path it crosses anteriorly to the gonadal vessels, right ureters and the psoas major muscle. Supply Supplies both the ascending and transverse colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branch of the inferior mesenteric artery, which travels retroperitoneally and divides into ascending and descending branches. Supply Supplies the descending and transverse colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
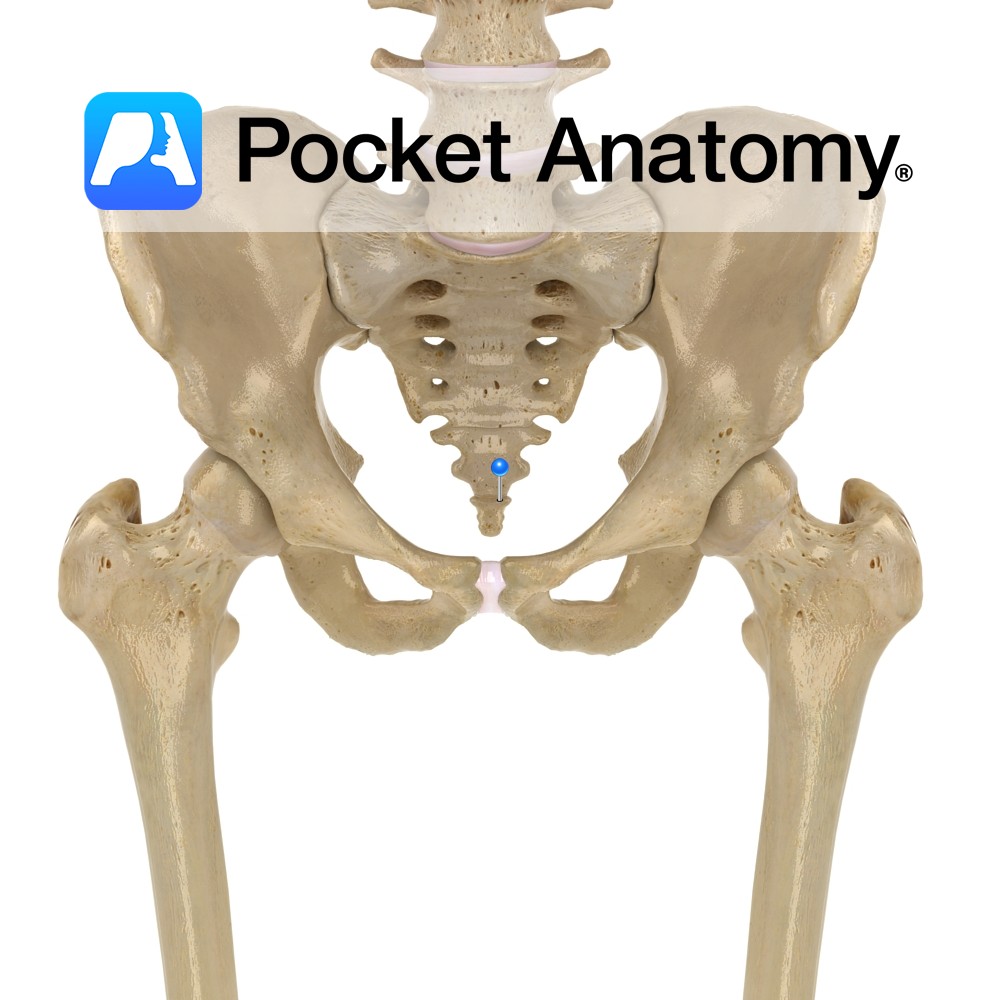
Anatomy Tailbone. Lowest section of spine, made up of 3-5 small vertebrae, often fused. Transition top to bottom of coccyx, from rudimentary to absent pedicles, laminae, transverse and spinous processes. Clinical Articulates with Sacrum above; limited movement. Vignette From Greek for cuckoo, as viewed from side, resembles its beak. Vestigial tail. Interested in taking our
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Ischial spine and the pelvic surface of the sacrospinous ligament. Insertion: Lateral margin of the coccyx and related border of the sacrum. Key Relations: -Coccygeus overlies the sacrospinous ligament. -Contributes to the formation of the posterior part of the pelvic diaphragm in association with the levator ani muscles- iliococcygeus (for more information see
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
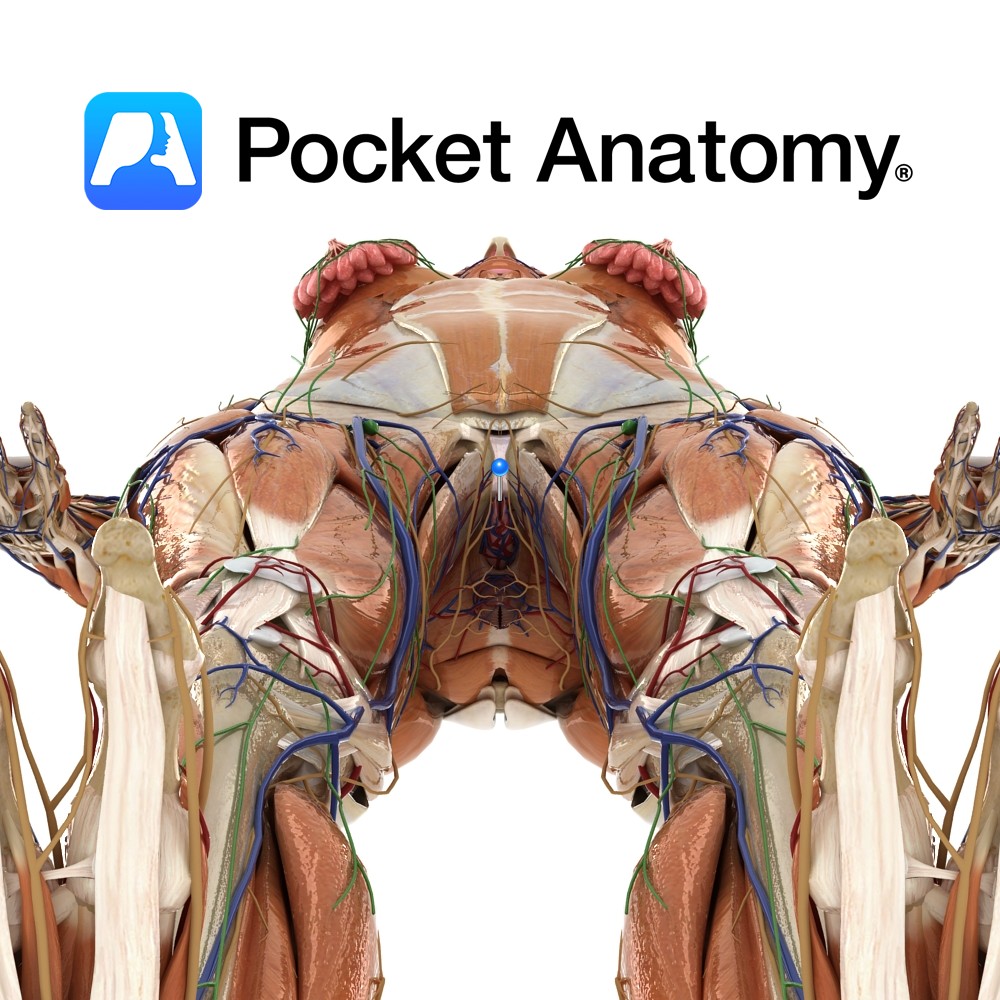
Anatomy Complex 3D/multiplanar structure, the pea-sized glans and shaft (variably hooded by the labia minora and curtained by the upper/anterior junction/commissure of the labia majora) the only distinctly visible surface element. There is also an internal portion of the shaft and a much bigger associated cluster of tissue, some clearly distinguishable anatomically/histologically (such as paired
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
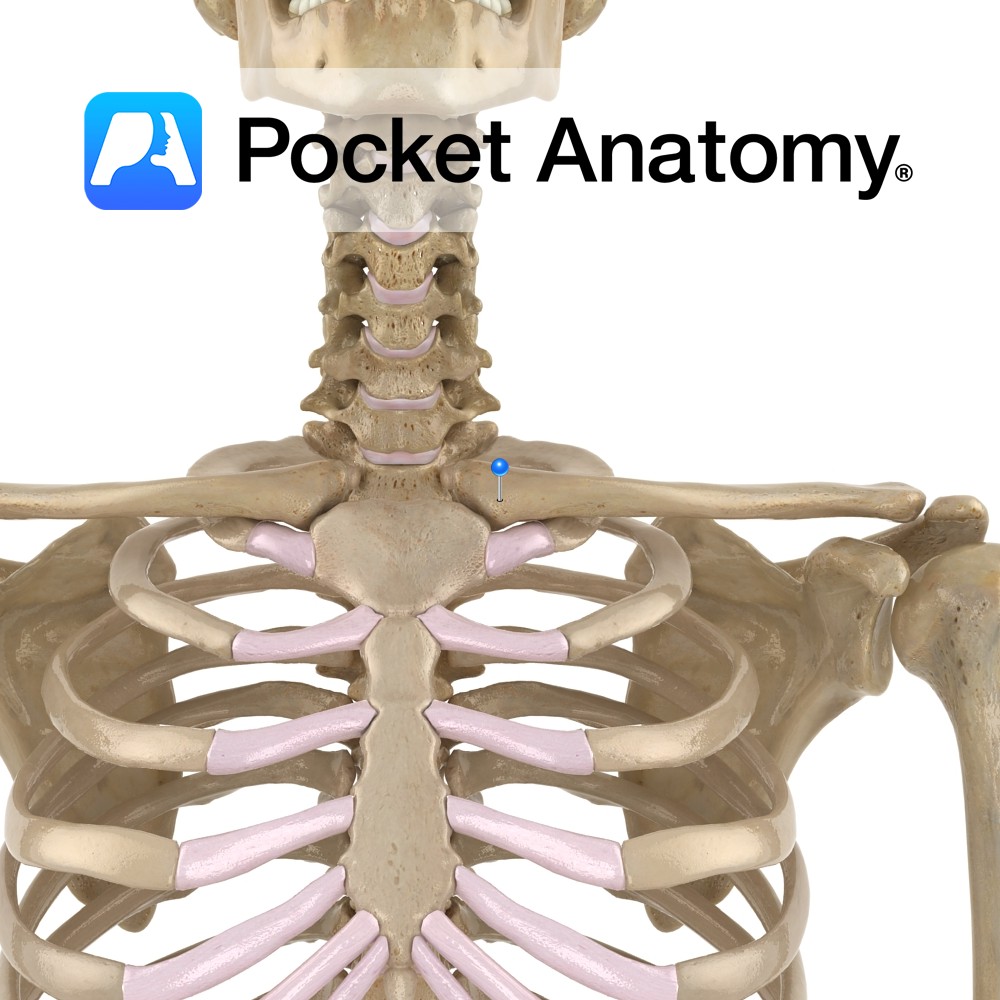
Anatomy Medial end of clavicle (which is a long flat bone, elongated s-shape, convex at medial end, concave at lateral) articulates with manubrium of sternum. Clinical The only horizontal long bone (though ordinarily, no marrow), the clavicle acts as a strut, holding scapula in place and free to move on thoracic wall, which in turn
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
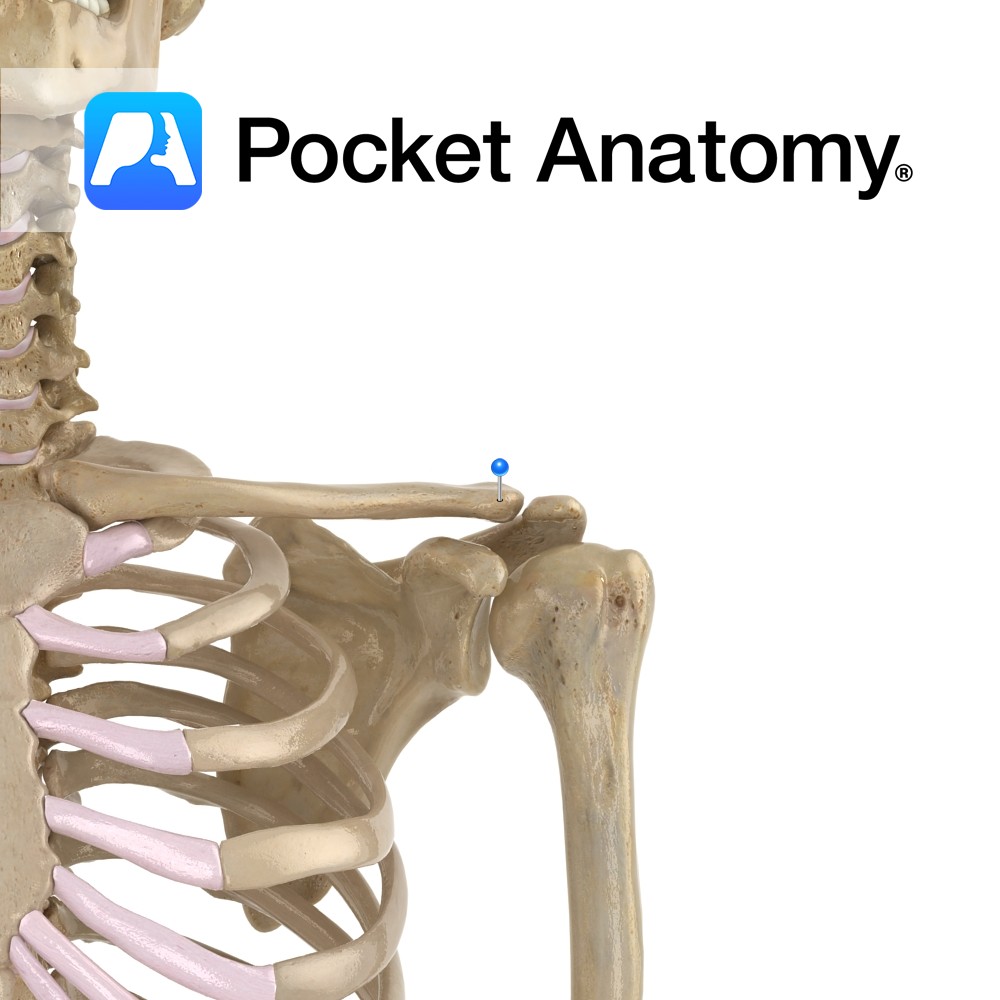
Anatomy Lateral end of clavicle (which is a long flat bone, elongated s-shape, convex at medial end, concave at lateral) articulates with acromial process of scapula. Connected to coracoid process below by coracoclavicular ligament. Clinical Clavicula (Latin); little key. First bone to begin ossification (5-6 weeks in embryo), one of last to finish (21-25 years).
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
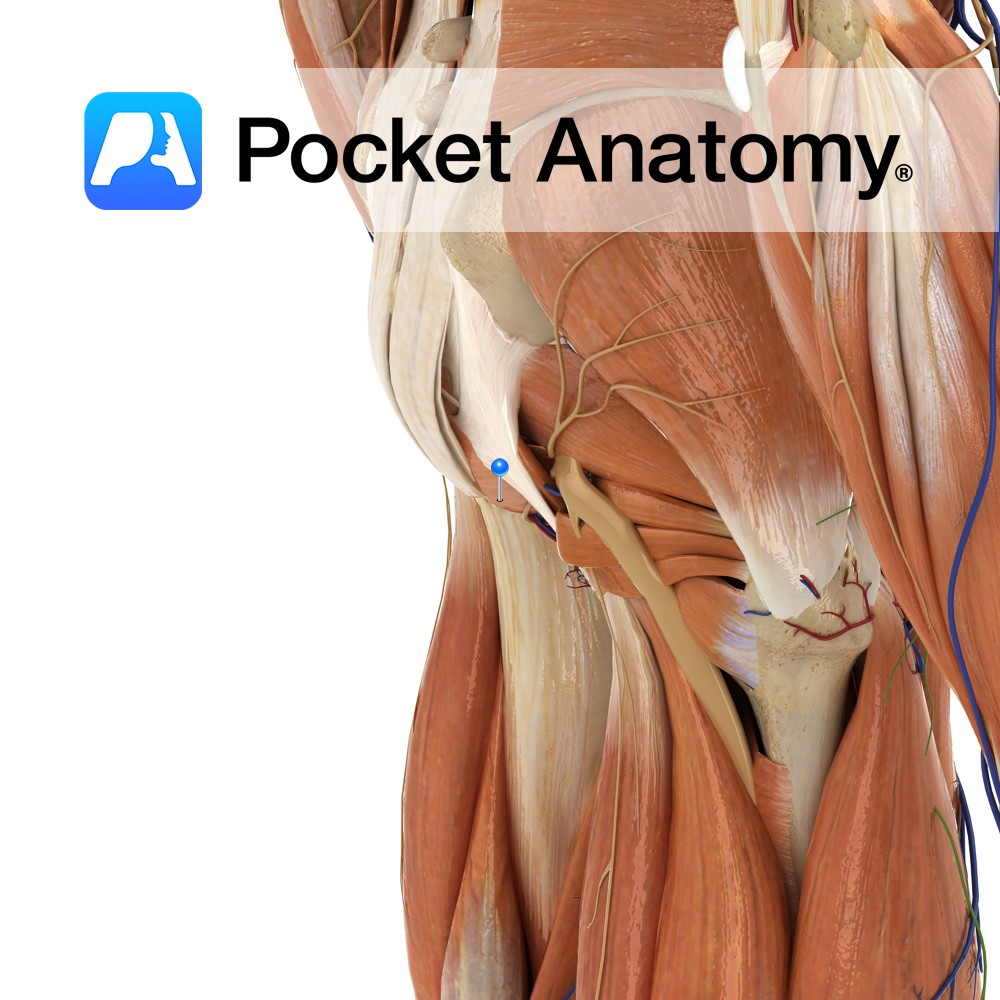
Anatomy Course Arises from the third division axillary artery at the inferior border of the subscapularis muscle. In association with the axillary nerve it travels through the quadrangular space. Supply Supplies the glenohumeral joint and the neck of the humerus. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)