PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
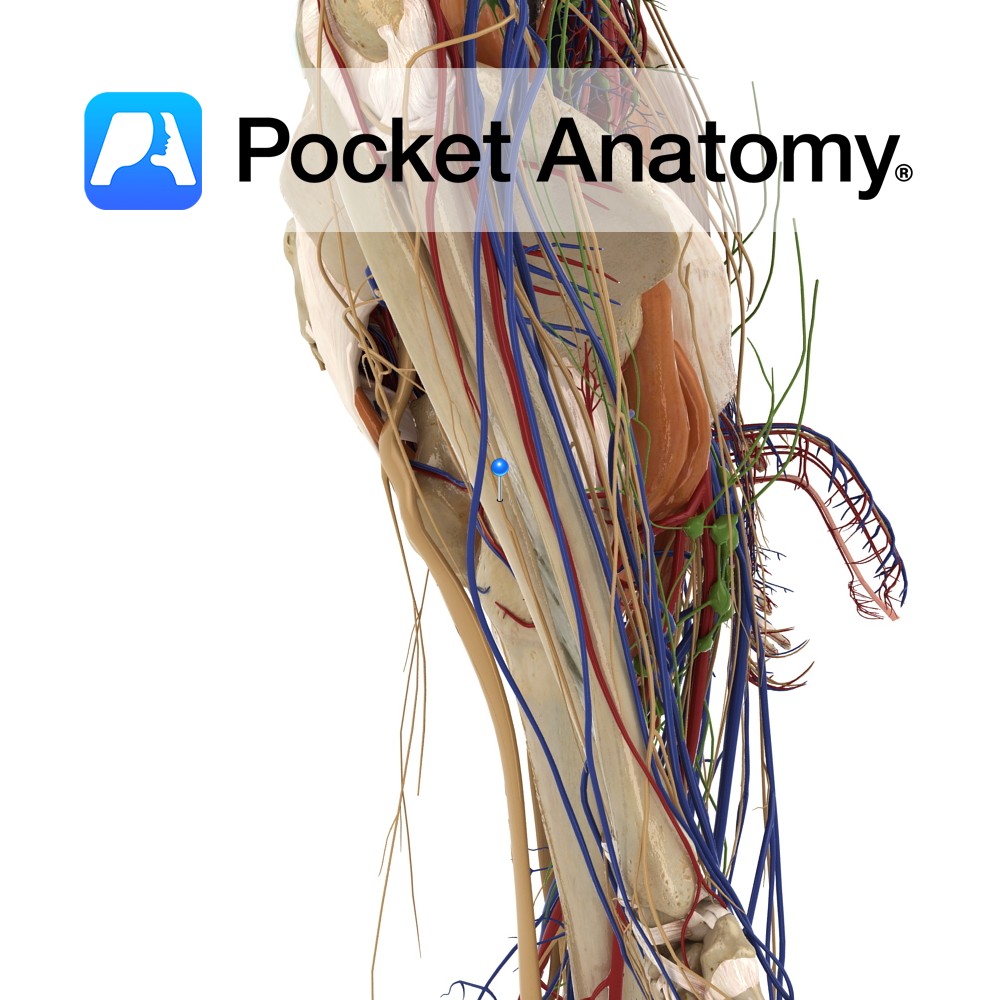
Anatomy Course Branches off the lateral aspect of the femoral artery in the femoral triangle. It then descends between the pectineus and the adductor longus. Supply Supplies the majority of the thigh. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
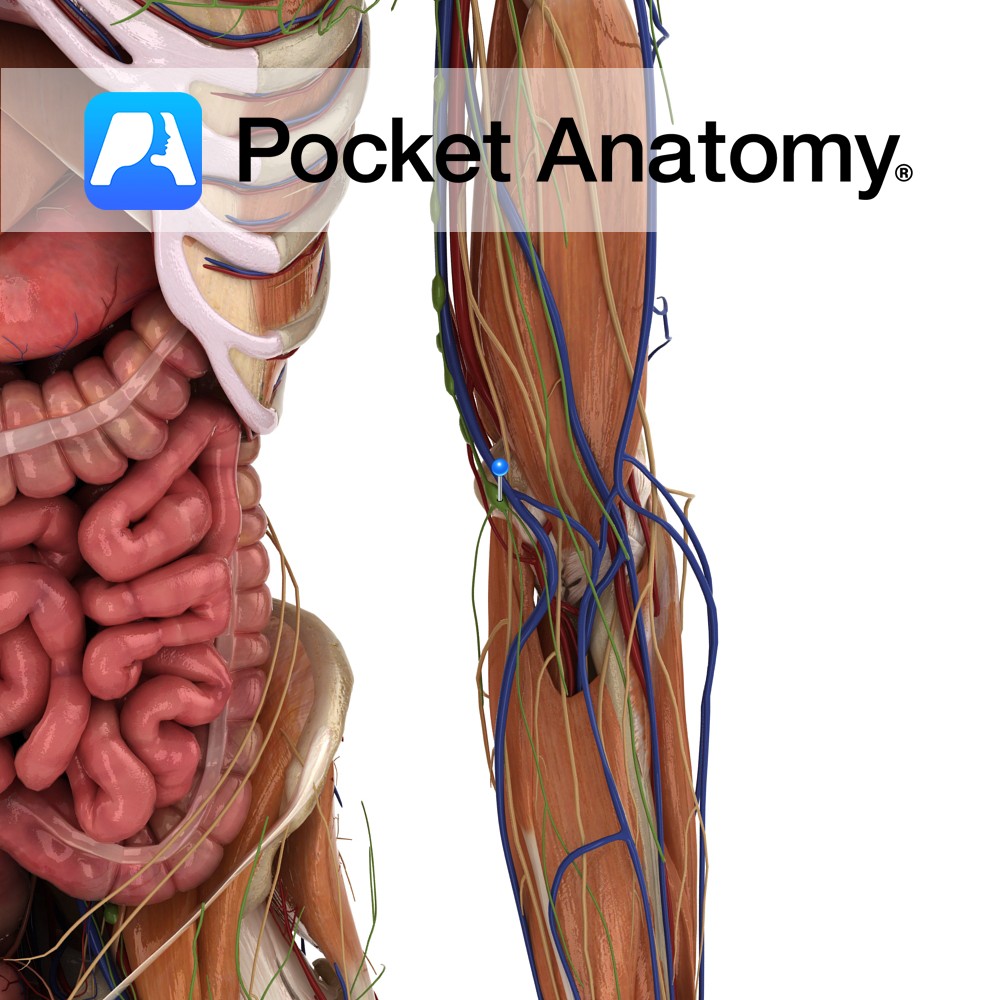
Anatomy Course As the name suggests it is a branch of the radial nerve which travels posteriorly to lateral aspect of the radius in between the supinator muscle. It continues a downwards path until it reaches approximately the middle of the forearm, where it continues as the posterior interosseous nerve. Supply Motor innervation to the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
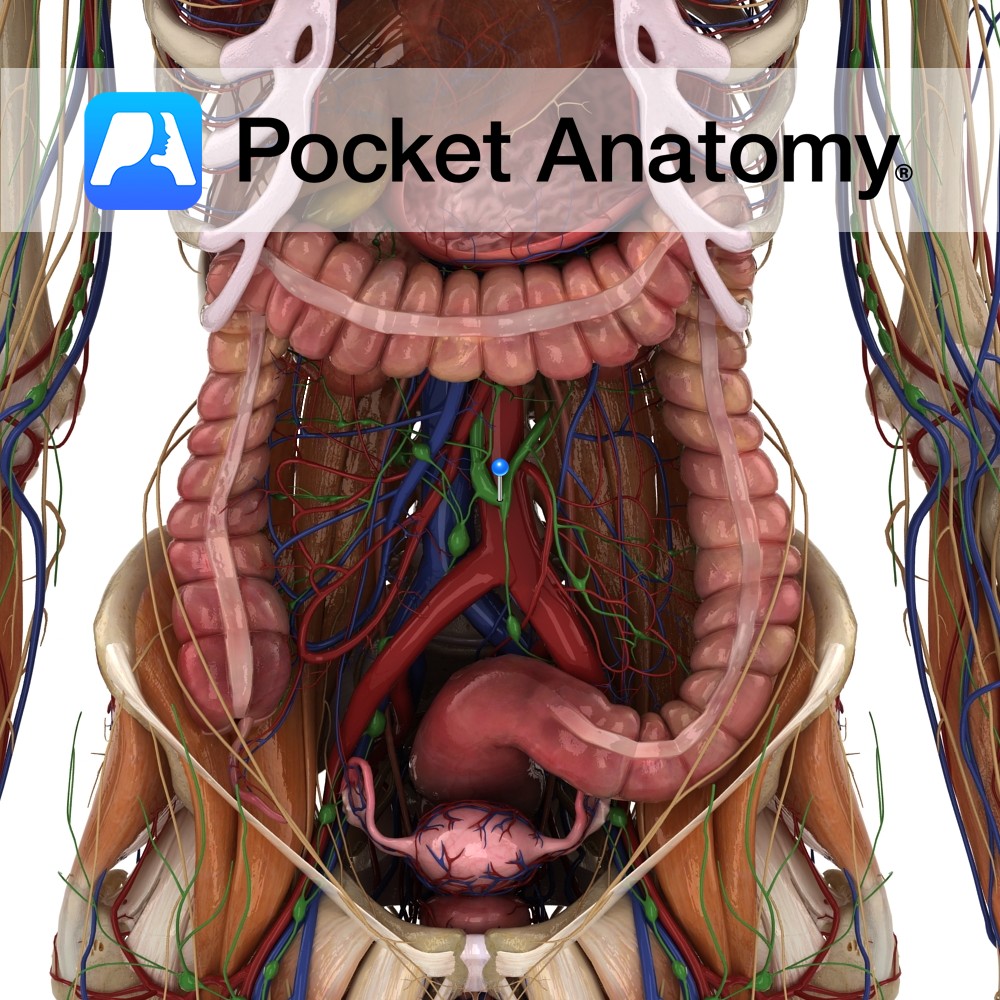
Anatomy Also known as Cisterna Chyli, a sac (constituting the start of the Thoracic Duct) receiving lymph from both Lumbar Trunks and the Intestinal Trunk. Physiology The lymphatic ducts of the small intestine begin in the villi as specialised capillaries called Lacteals. Lacteals take up lymph and also absorbed fats, the milky combination then called
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
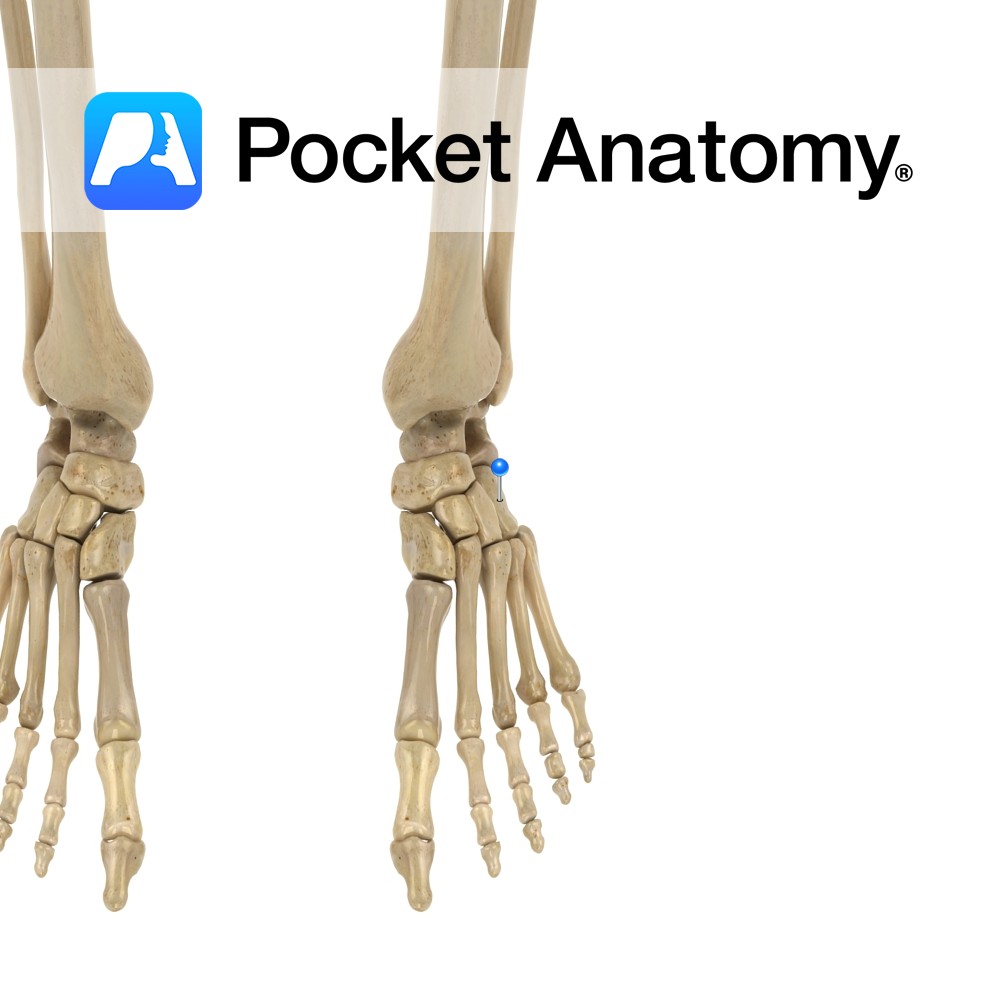
Anatomy Tarsal bone. Articulates proximally/back with calcaneus, forward with 4th and 5th (laterally) metatarsals, in/medially with lateral (3rd) cuneiform and sometimes the navicular. Cuboid + navicular + 3 cuneiforms = midfoot (form arches of foot). Clinical Damage to nearby muscles, ligaments, joints, can lead to partial dislocation (subluxation) cuboid, with lateral foot pain and weakness
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Also known as epitrochlear nodes, near the elbow, above epicondyle. There are superficial and deep sets of cubital nodes, receiving afferent drainage of forearm and the hand, efferents thence passing up to superficial and deep Axillary lymph nodes. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
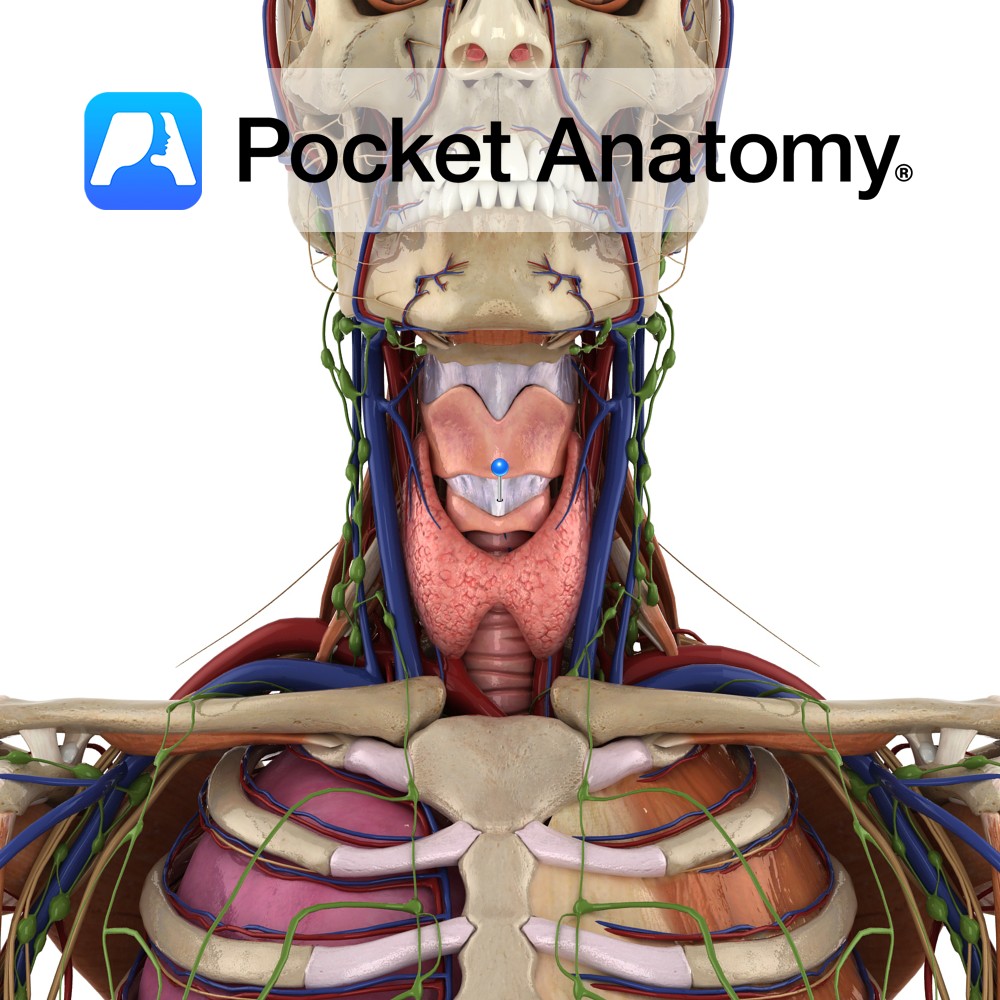
Anatomy A thickening of the median portion of the anterior cricothyroid membrane. It begins as a broad band attaching to the anterior superior aspect of the cricoid cartilage and narrows as it ascends to attach to the lower aspect of the thyroid cartilage. Functions Binds the cricoid and thyroid cartilage while limiting the anterior posterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
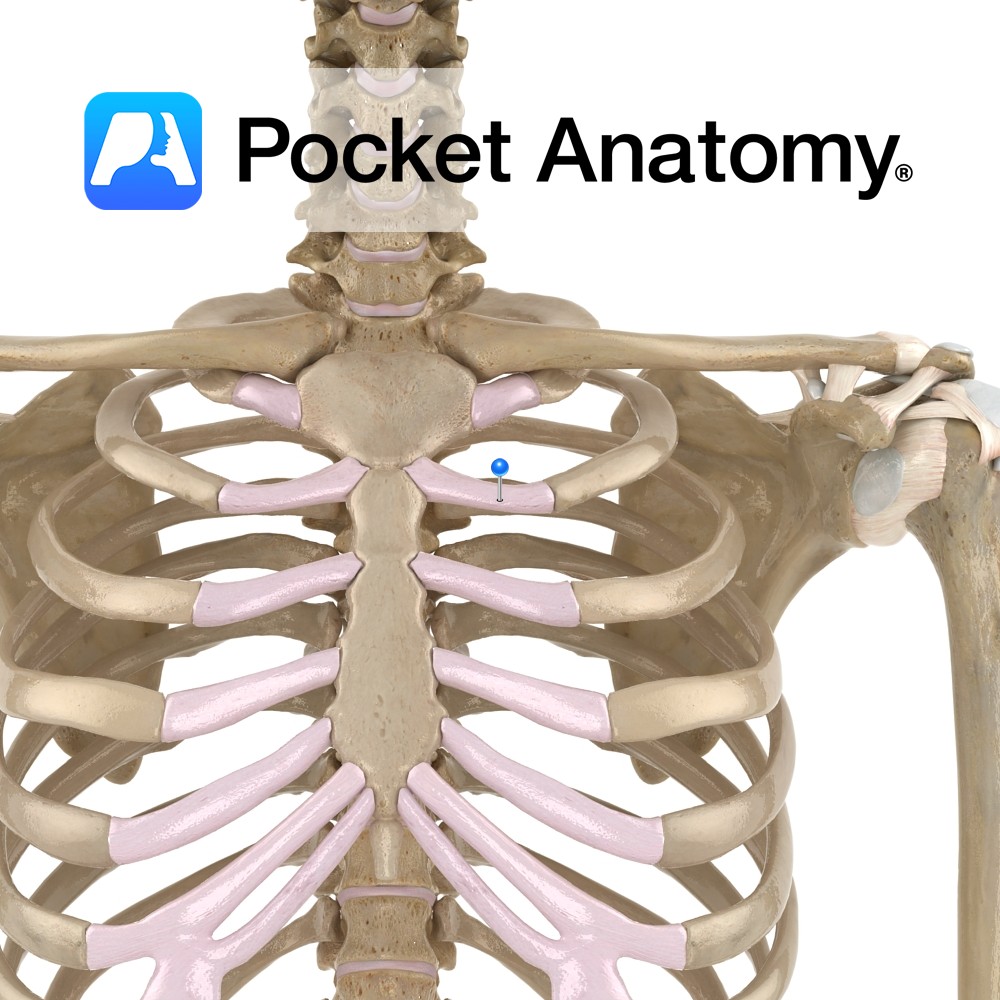
Anatomy Cartilaginous forward/anterior/sternal prolongations of the ribs, articulating with the sternum, giving the thorax elasticity with strength. Clinical Hyaline cartilage is found on articular surfaces of synovial joints (as a thin covering layer with a smooth surface), providing resilience. Also found in nasal septum, larynx, trachea and bronchi, where it provides elasticity. Costal cartilage has
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
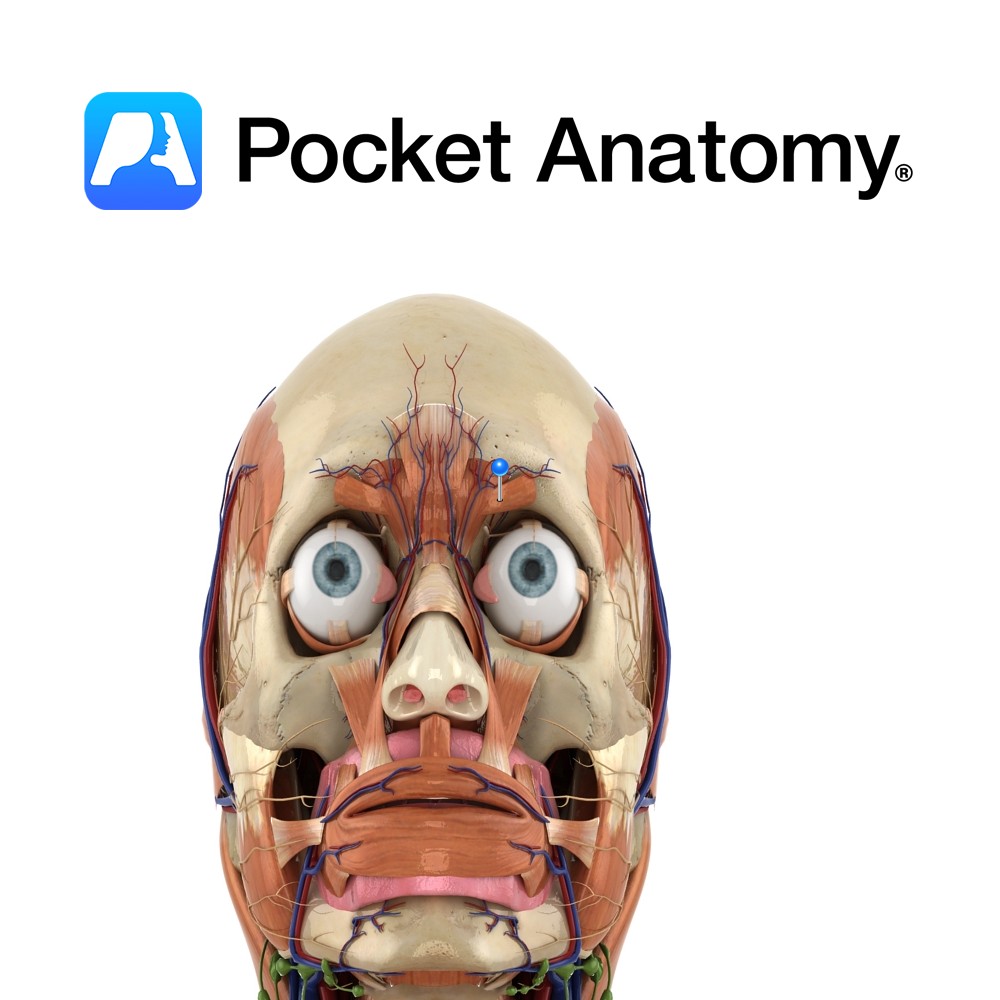
Anatomy Origin: Medial end of superciliary arch. Insertion: Skin of medial half of eyebrow. Key Relations: Lies deep to orbicularis oculi and the eyebrows. Functions Draws eyebrows medially and downwards. e.g. when frowning.. Supply Nerve Supply: Temporal branch of the facial nerve (CN 7). Blood Supply: Opthalmic artery. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
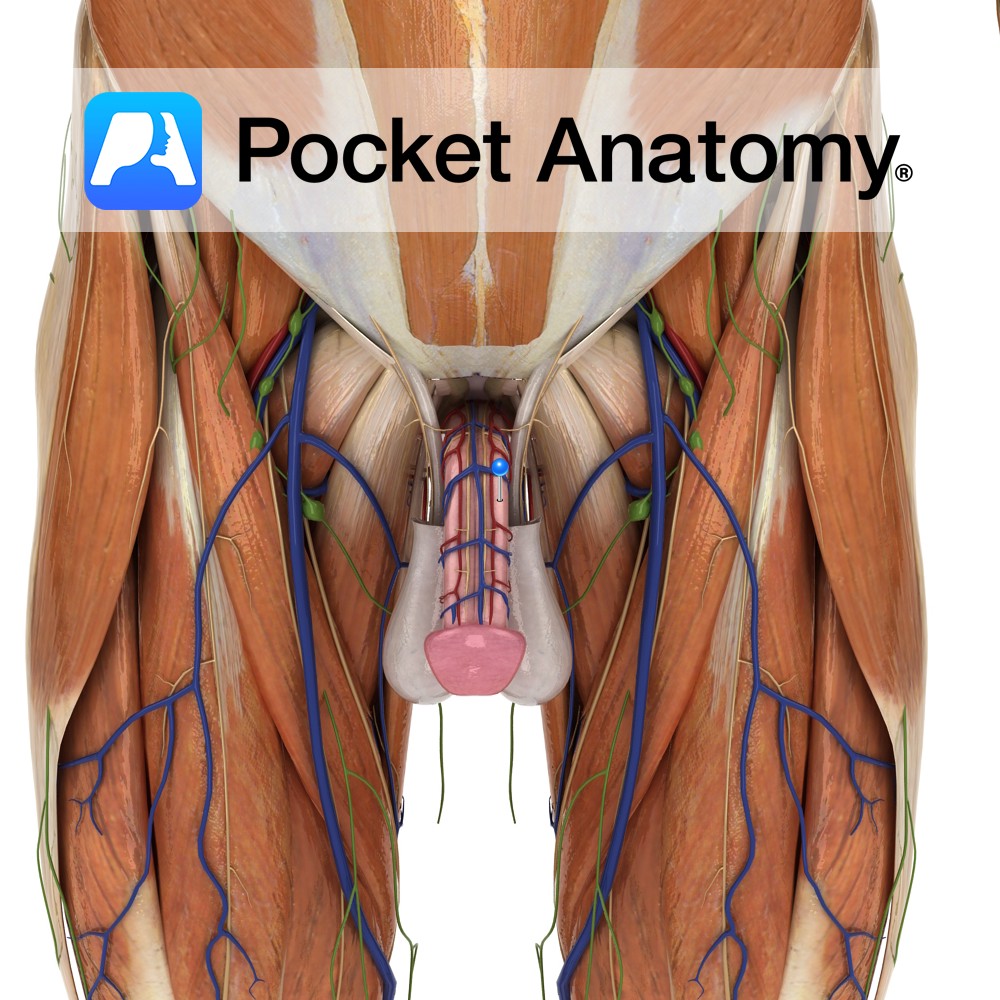
Anatomy There are 3 cylindrical strips of expandable/inflatable/erectile tissue along length of penis; 2 corpus cavernosum side by side and dorsal to 1 (smaller) corpus spongiosum (central and ventral, expanded at proximal end into bulb and distal into glans, and through which urethra courses). Corpus cavernosum starts at pubic bone, left and right end by
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
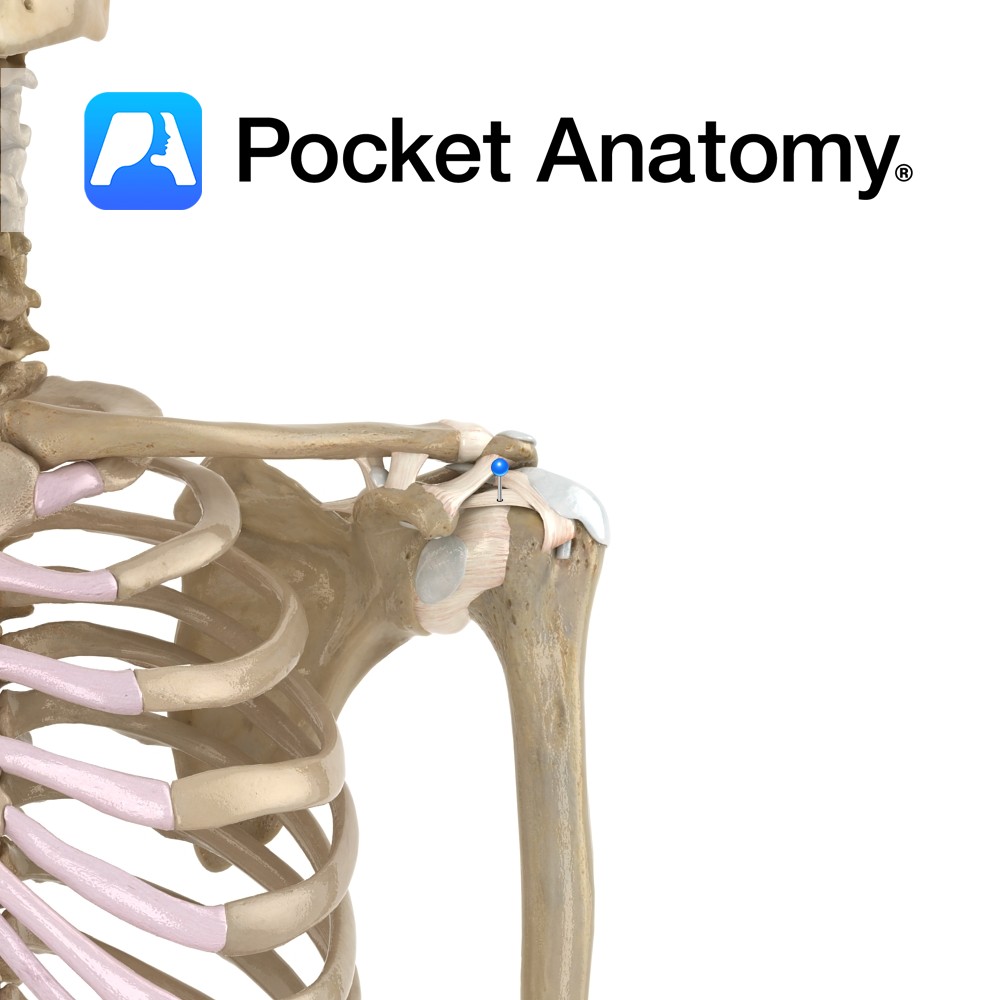
Anatomy The coracohumeral ligament attaches from the lateral surface of the coracoid process to blend with the supraspinatus tendon, and attach to the superior surface of the greater tuberosity of the humerus. Functions Helps to keep the head of the humerus in contact with glenoid fossa of the scapula. Provides support and stability to the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)