PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
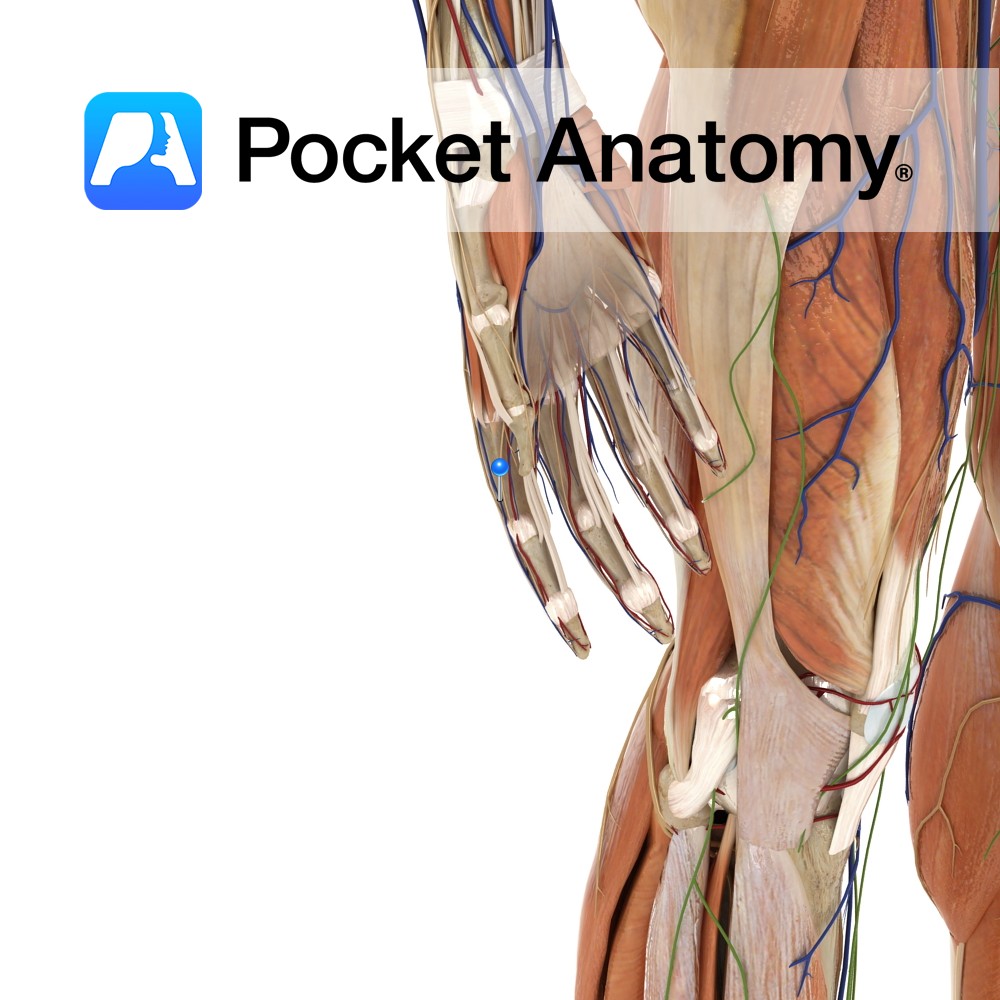
Anatomy Origin: Bipennate muscles that arise by two heads from adjacent sides of posterior aspect of the metacarpals. Insertion: Extensor hood and base of proximal phalanges of the index, middle and ring fingers. (It is the middle digit that has two dorsal interossei inserting onto it.) Key relations: The radial artery (after passing between the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
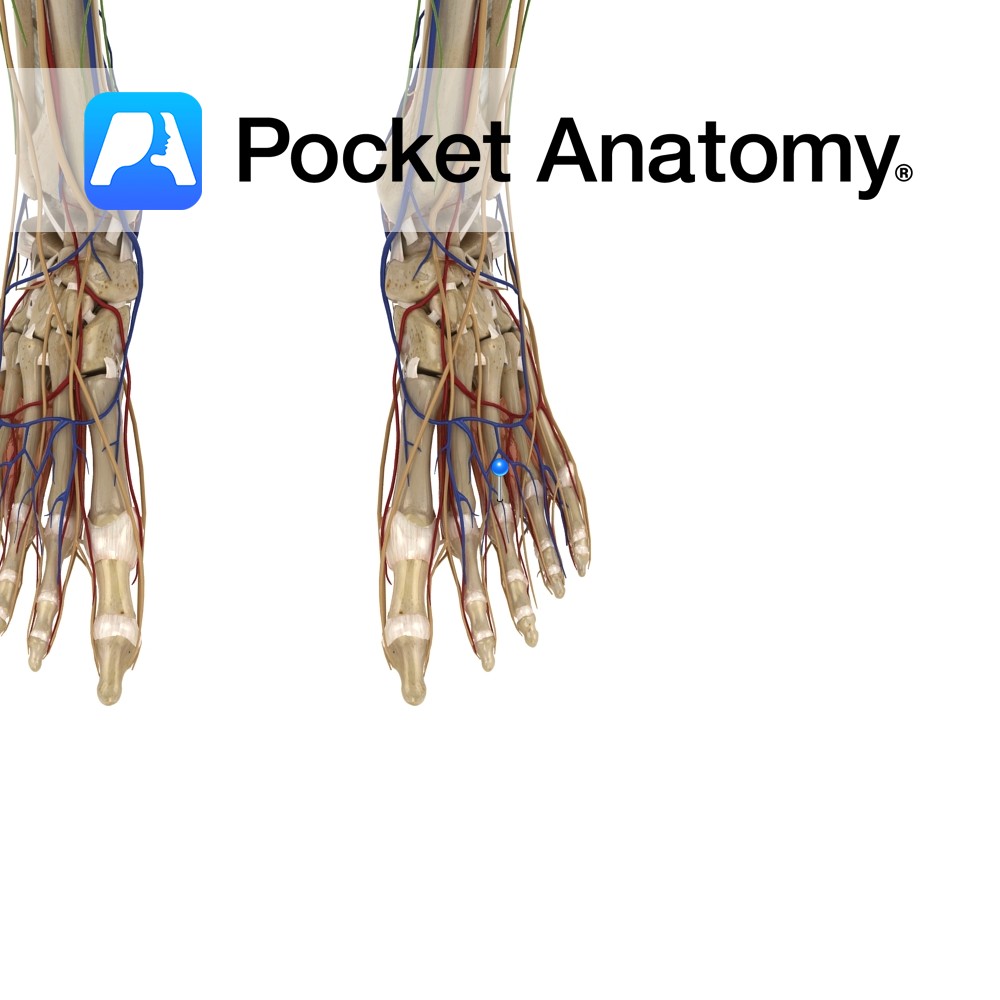
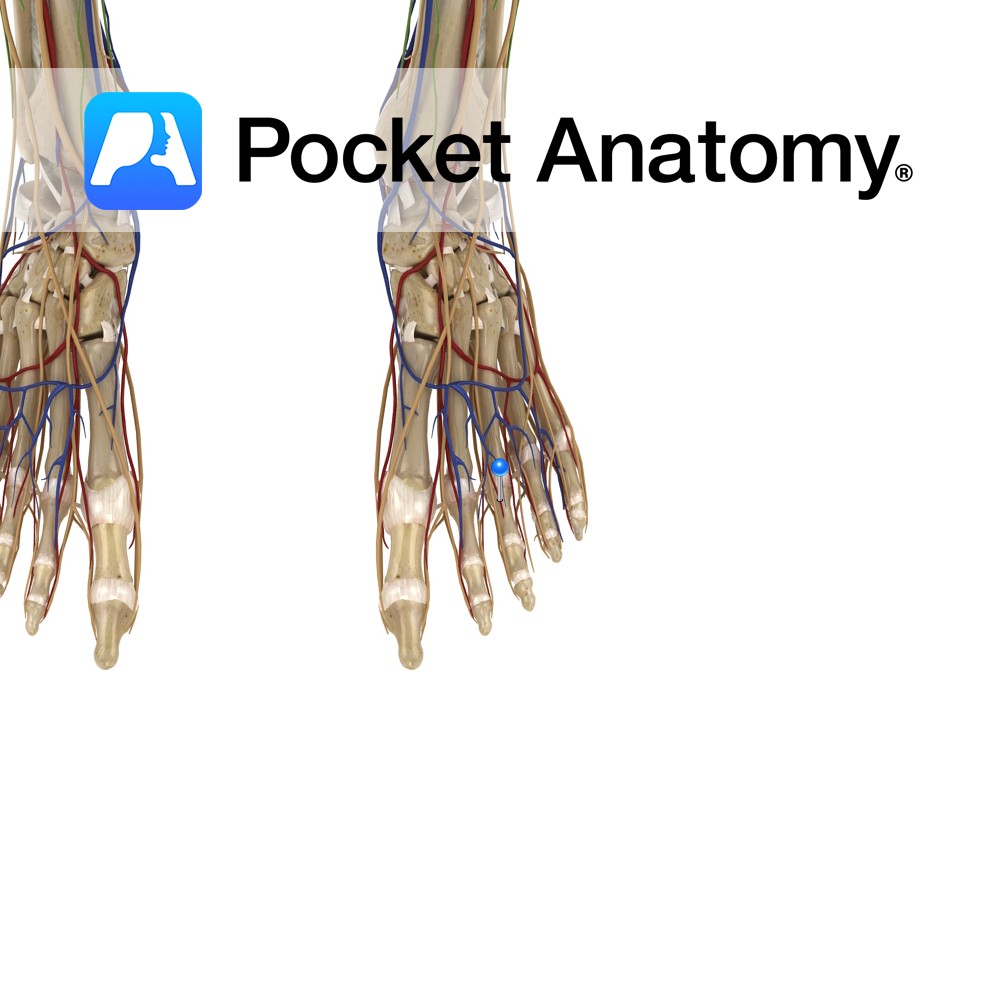
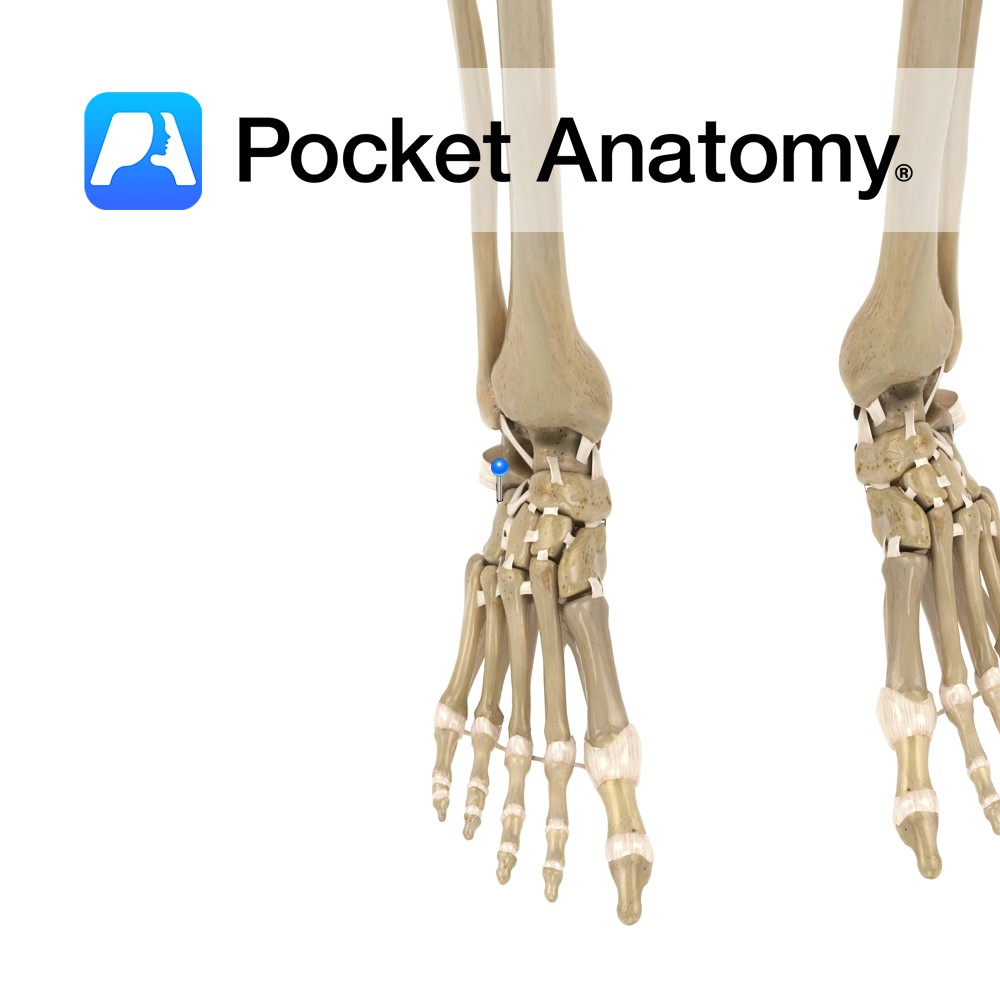
Anatomy Origin: Sides of the adjacent metatarsals. Insertion: Bases of proximal phalanges of 2nd, 3rd and 4th toes and dorsal expansions of the extensor digitorum longus tendons. Key relations: The dorsal interossei lie dorsal to the plantar interossei and together they form the fourth layer of the plantar muscles of the foot. Also, see view
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course On the dorsum of the foot they receive the intercapitular veins. They travel briefly to join the plantar cutaneous venous arch. Drain Drains the dorsal surface of the digits of the foot. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begin at the sides of the digits beside their counterpart arteries and drain into the dorsal metacarpal venous network on the back of the hand. Drain Drains the digits of the hand. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branches of the superficial radial nerve near its termination. Supply Lateral aspect of the middle finger as well as the medial aspect of the index finger. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branches of the dorsal metacarpal arteries. They enter the distal portions of the digits on the posterior surface of the phalanges. Anastamoses exist between them and the proper palmar digital arteries. The arteries are dorsal to the digital nerves. Supply Supply the lateral, medial and dorsal aspects of the digits. Interested in taking
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
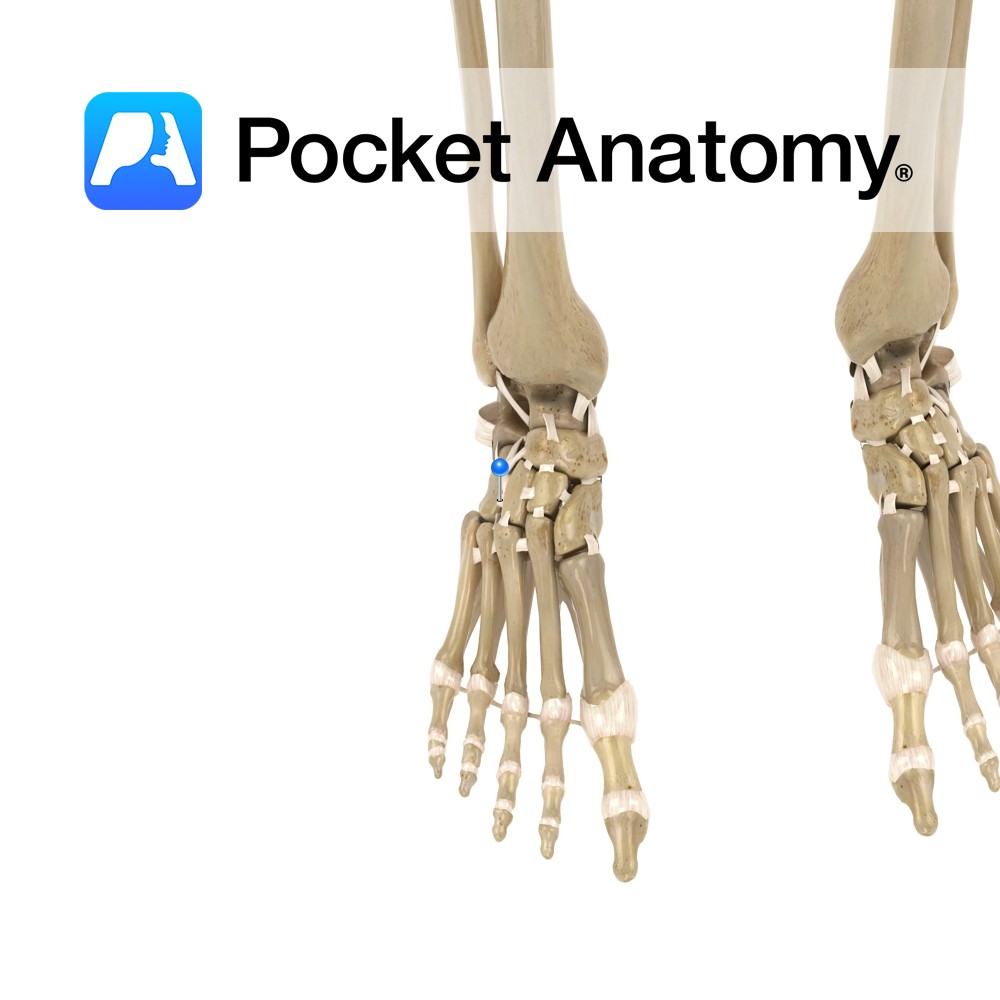
Anatomy Attaches from the dorsal margin of the cuboid bone to the lateral dorsal margin of the lateral cuneiform bone of the foot. Functions One of the dorsal ligaments of the foot. It stabilizes the dorsal surface of the foot. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
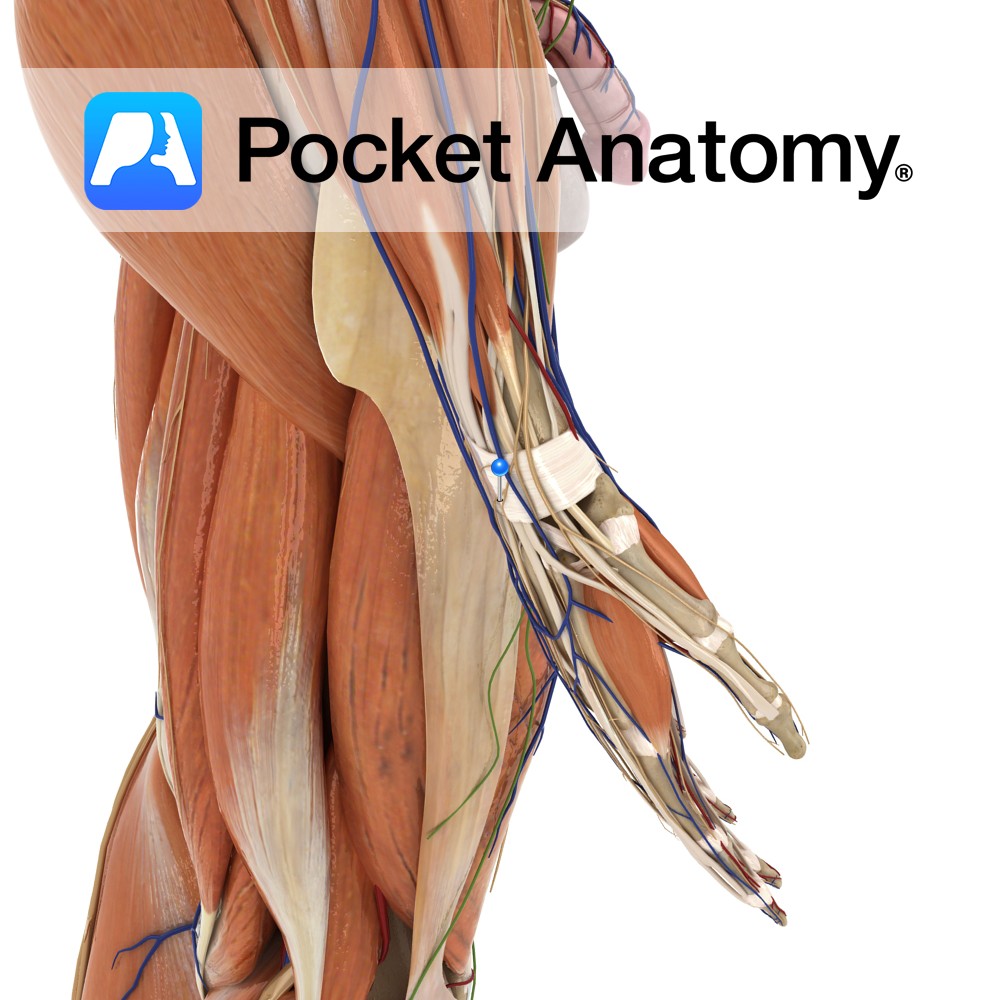
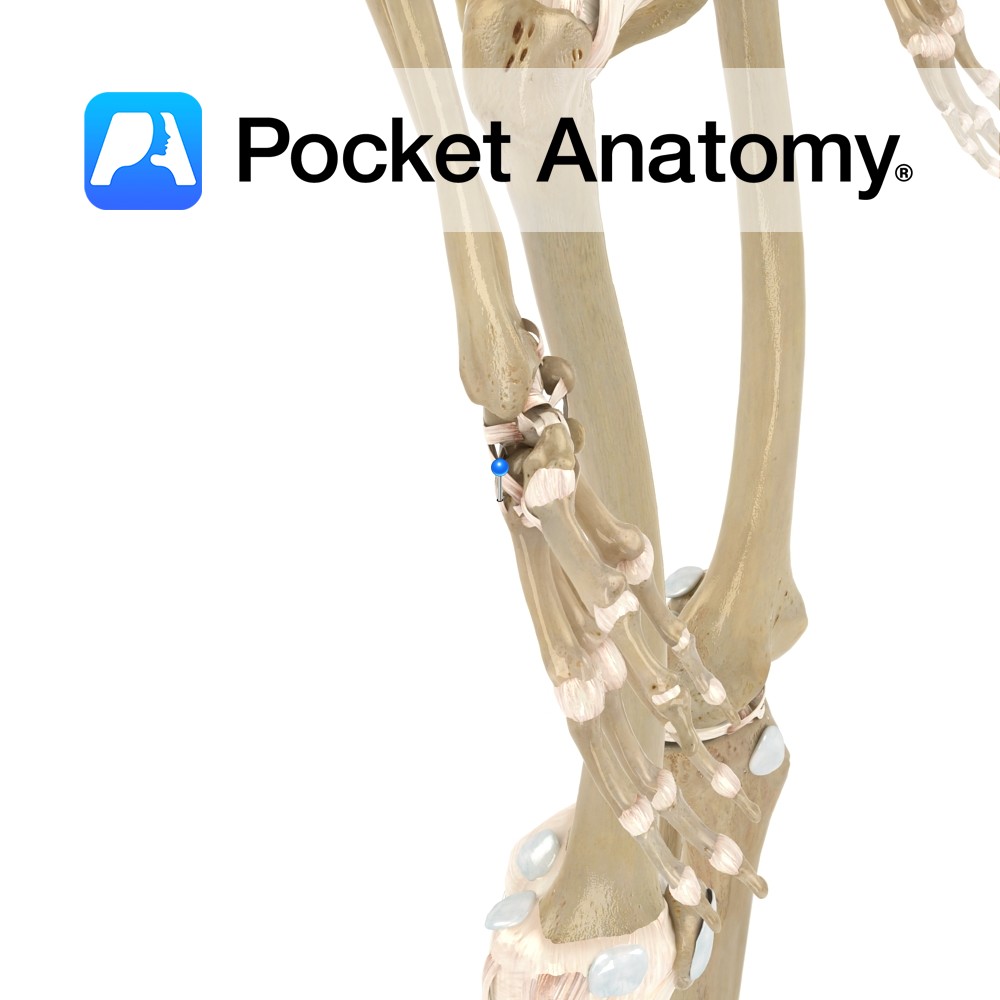
Anatomy Strongest and most distinct carpometacarpal ligaments connecting the carpal and metacarpal bones on their dorsal surface of the hand. The second metacarpal bone receives two fibrous bands from the trapezoid and trapezium bone. The third metacarpal receives two bands, one each from the trapezium and capitate bones. The fourth two, one each from the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy A thin but broad fibrous bundle, which passes between the adjacent surfaces of the calcaneus and cuboid, on the dorsal surface of the joint. Functions Provides support to the subtalar joint between the calcaneus and cuboid. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
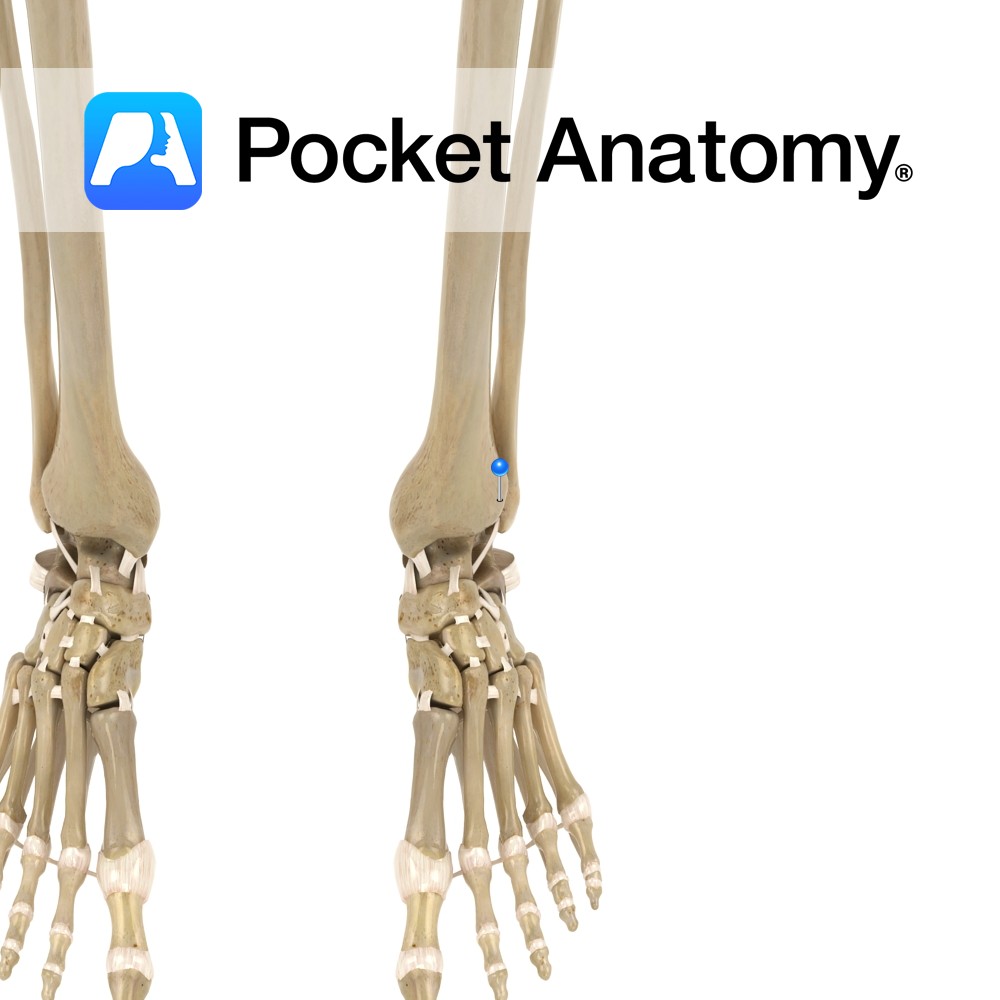
Motion The distal tibiofibular joint is a syndemosis type fibrous joint. The medial surface of the inferior end of the fibula articulates with the fibular notch on the lateral side of the tibia. It allows very little movement but slight movement accommodates the talus during dorsiflexion of the foot. Stability Ligaments stabilizing the joint include:
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)