PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Course Originates from the anterior side of the external carotid artery, where it then rises superiorly through the deep structures of the neck until it reaches the mandible. It then curves around the inferior border of mandible, anterior to the master muscle. From there it undergoes a tortuous path superomedially, where it becomes the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
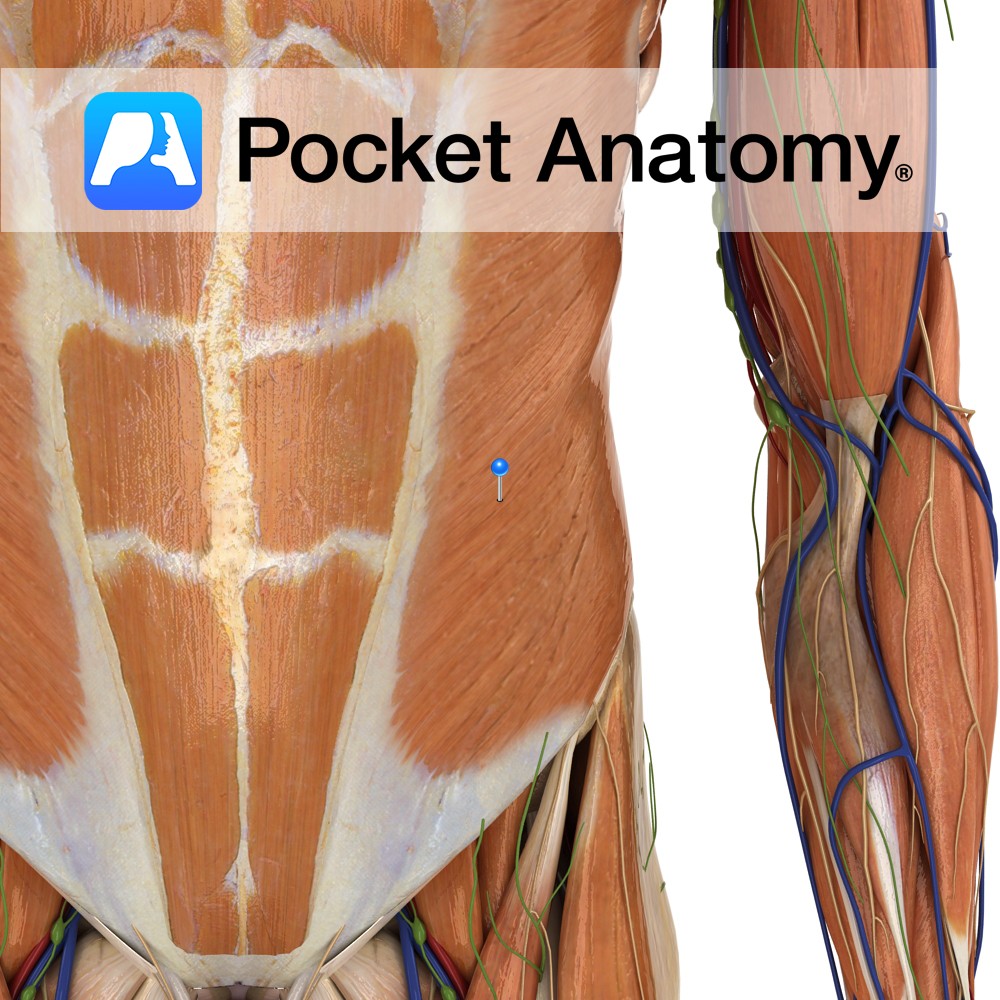
Anatomy Origin: Muscular digitations from the external inferior borders of the 5th to 12th ribs. Insertion: Via aponeurosis to the linea alba and the lateral lip of the iliac crest. Key relations: -Largest and most superficial of the three flat abdominal muscles. -Helpful to visualise the directions of the fibres as a putting your hands
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
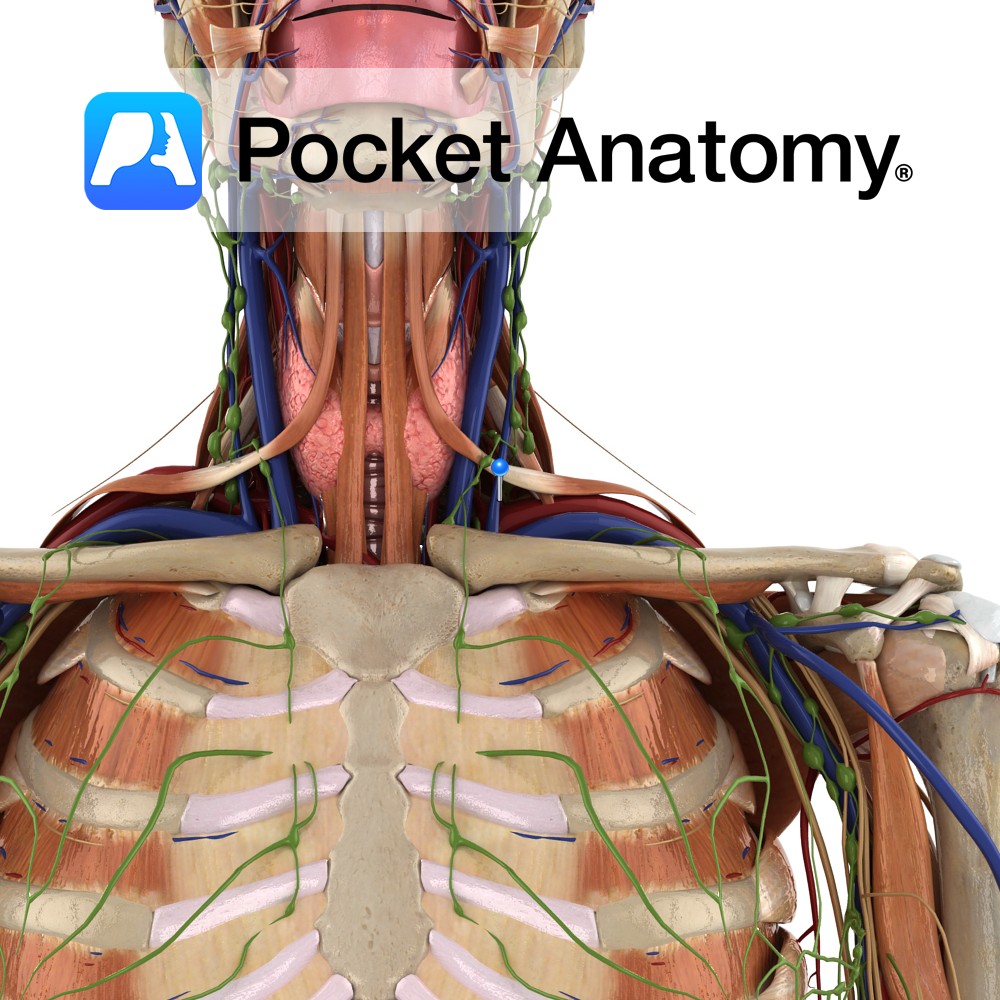
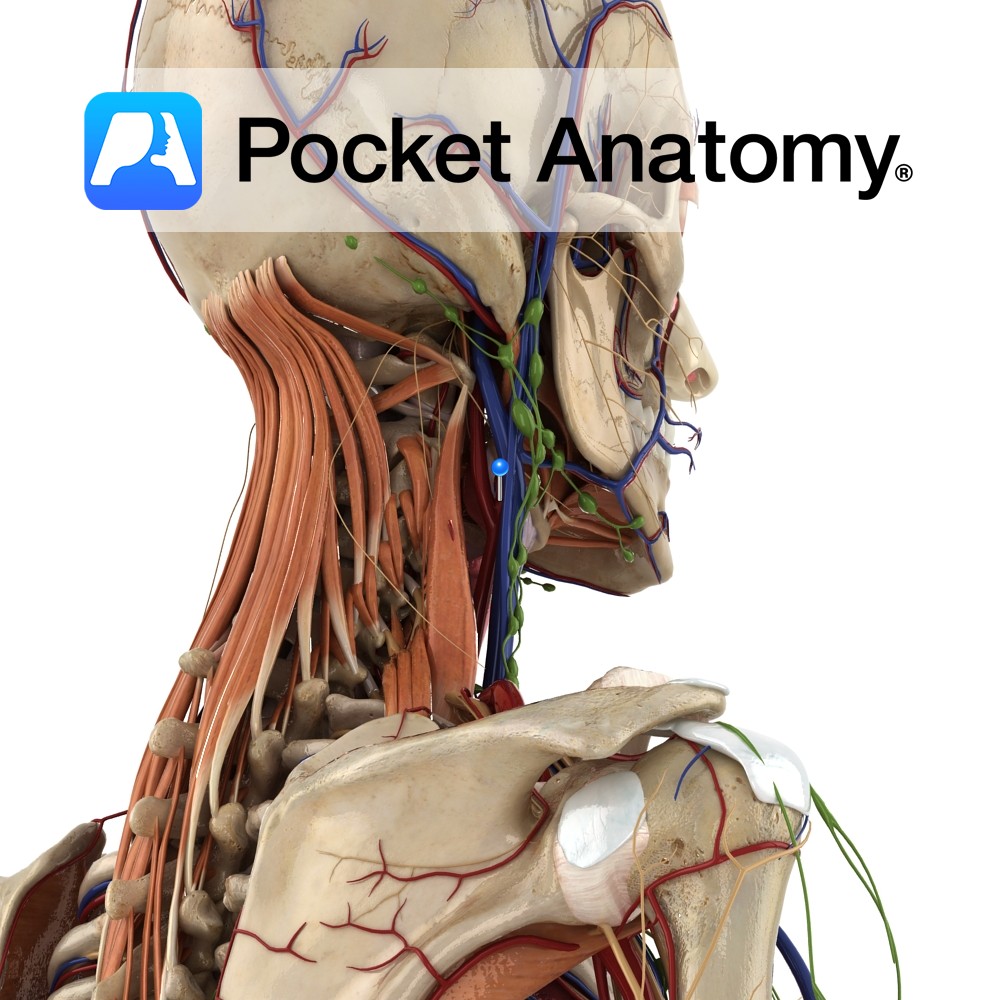
Anatomy Course Begins with the fusion of the posterior auricular vein and a portion of the retromandibular vein in the parotid gland. As it descends from the head it perforates the deep fascia until it eventually joins the subclavian vein, lateral to the internal jugular vein. Drain Drains the blood exterior to the cranium. Interested
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
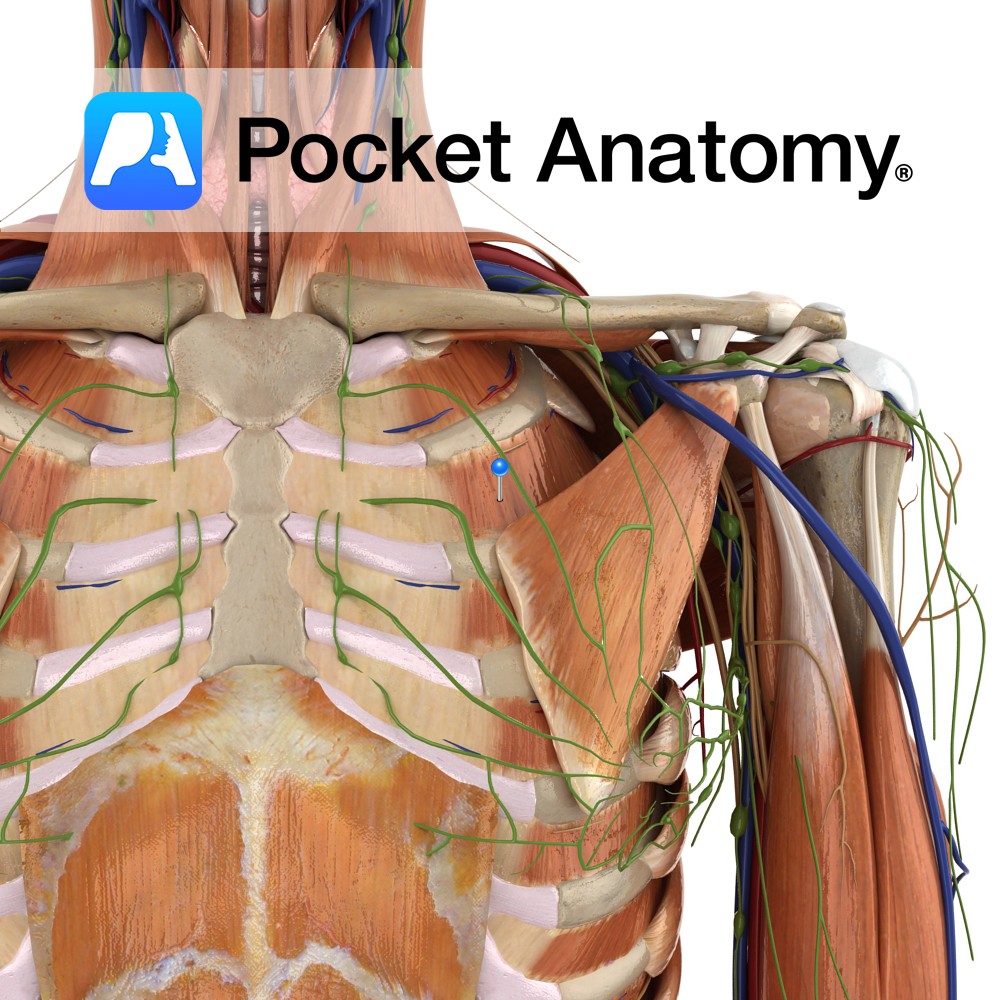
Anatomy Origin: Inferior margin of the rib above i.e. ribs 1 to 11. Insertion: Superior surface of the rib below i.e. ribs 2 to 12. Key relations: -Muscle fibres run obliquely anteroinferiorly. -Most superficial intercostal muscle. Functions -Moves ribs superiorly during inspiration, thereby expanding the thoracic cavity. -Maintains intercostals spaces during inspiration and expiration. Supply
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
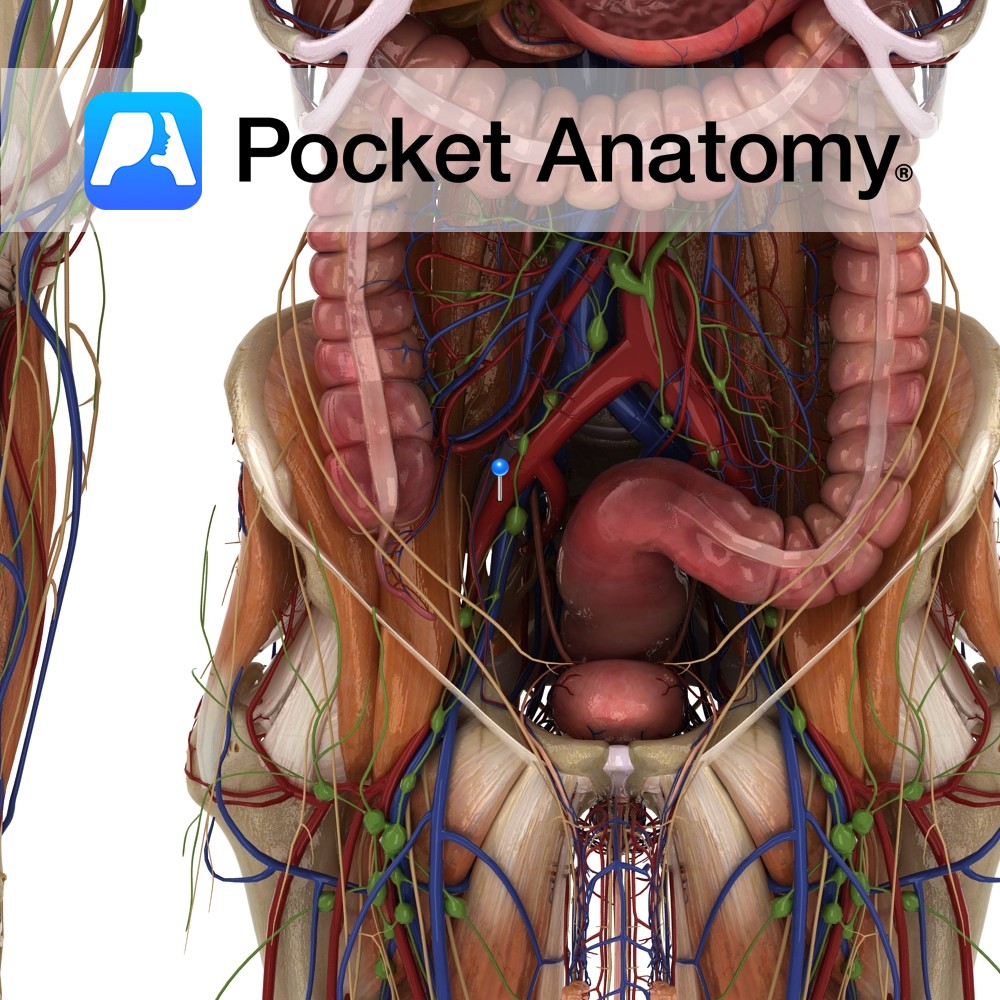
Anatomy Course Continuation of the femoral vein after it travels beneath the inguinal ligament. Travels briefly with its counterpart artery until it joins with the internal iliac vein and becomes the common iliac vein. Drain Drains the deep veins of the leg. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
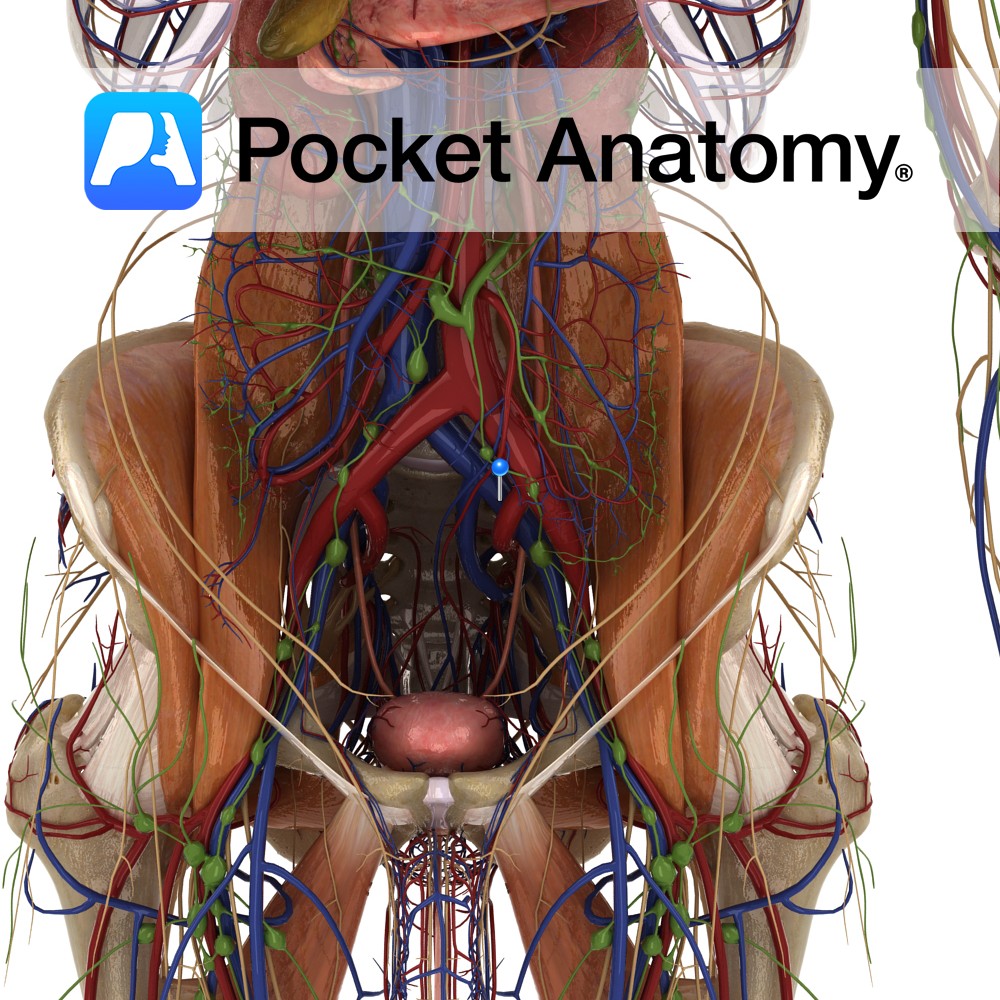
Anatomy Course Arises after the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. It descends on the psoas muscle until it passes underneath the inguinal ligament, where it is referred to as the femoral artery. Supply Major source for the lower limb. Clinical In renal transplants, the surgeon often attaches the renal artery of the donor’s kidney
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
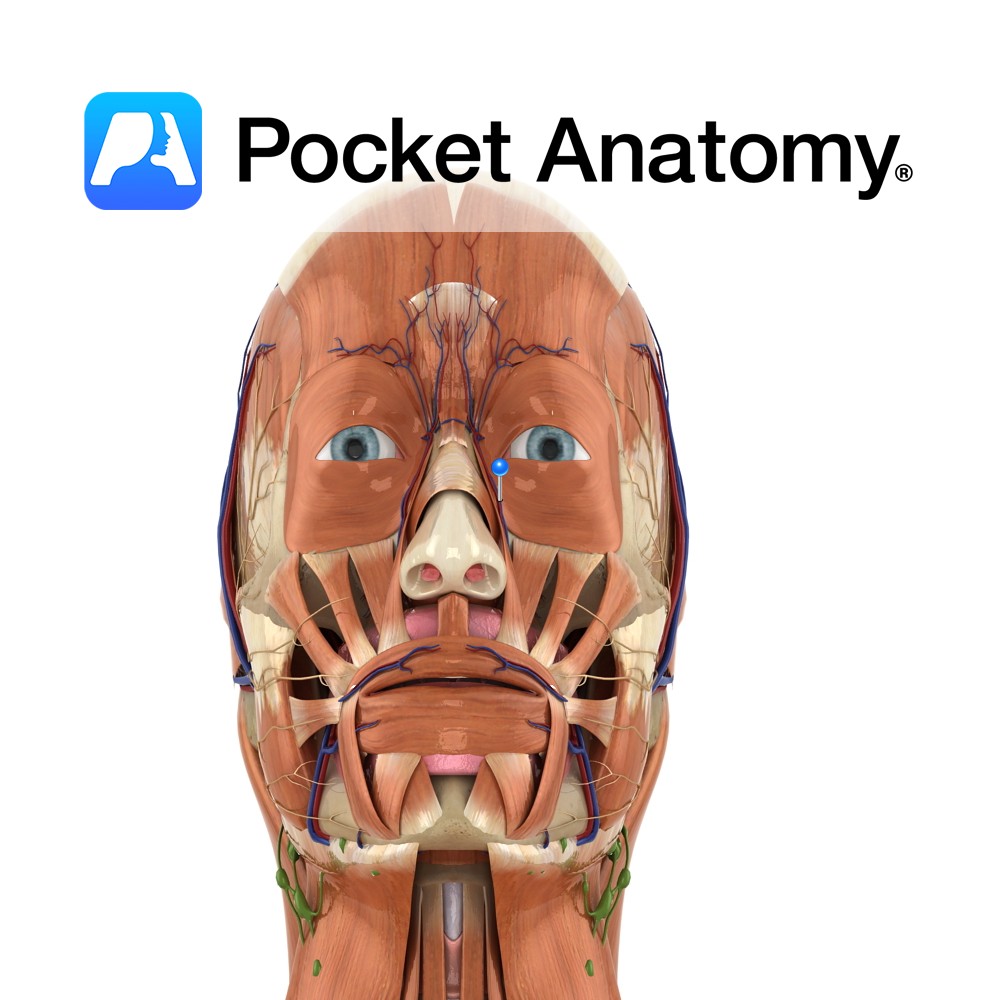
Anatomy Course Arises after the bifurcation of the common carotid artery at the level of the thyroid. As it rises it takes a curved path and rapidly diminishes in size due to the amount of collaterals it gives off. It eventually ends up behind the neck of the mandible where it gives off its terminal
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
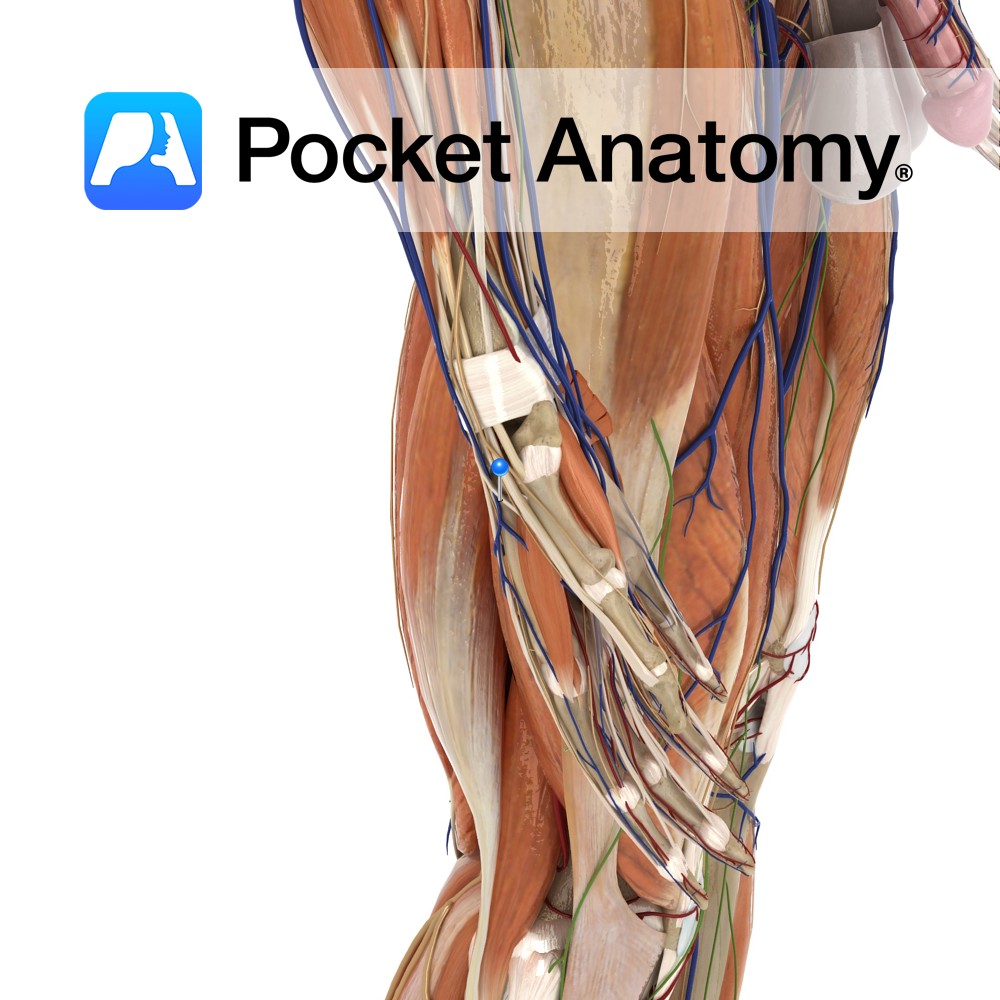
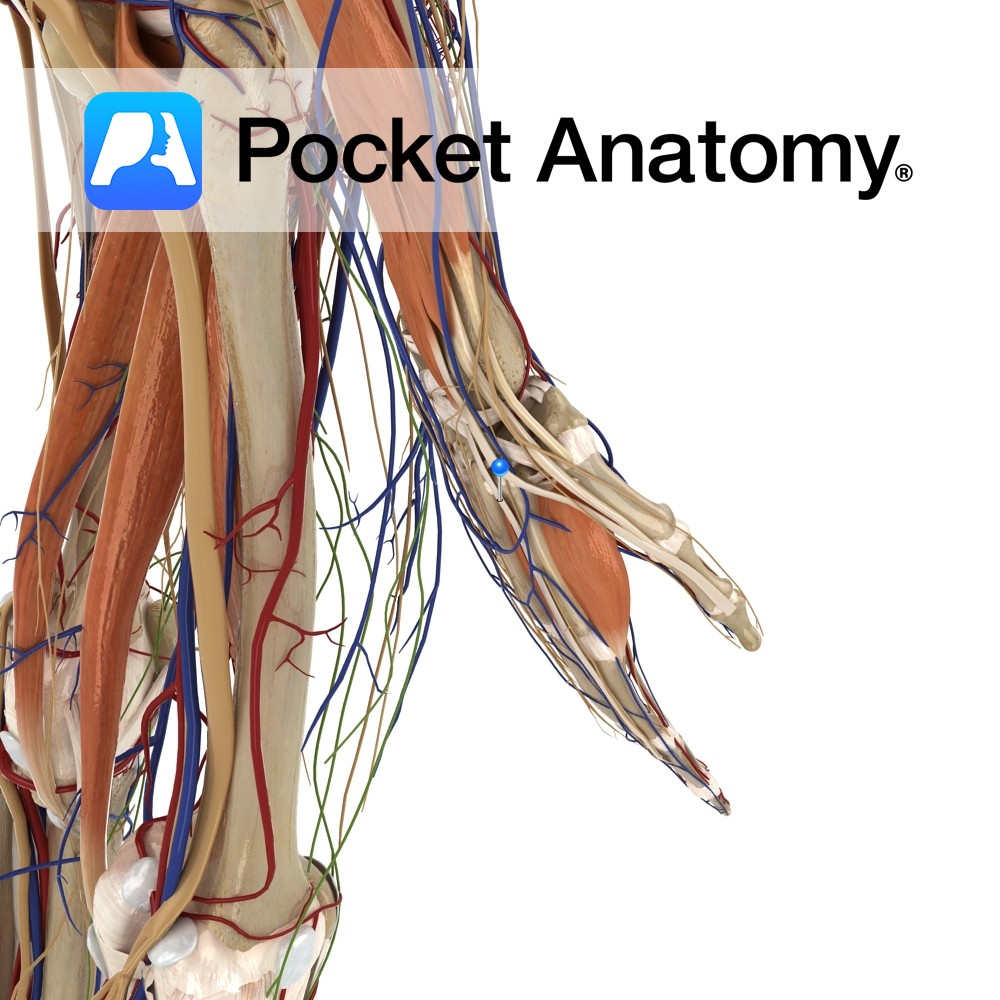
Anatomy Origin: Posterolateral aspect of middle third of ulna and adjacent interosseous membrane. Insertion: Dorsal surface of base of the distal phalanx of thumb. Key Relations: -The tendon of extensor pollicis longus passes underneath the extensor retinaculum in its own compartment. -Its tendon forms the posterior boundary of the anatomical snuffbox. -One of the six
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
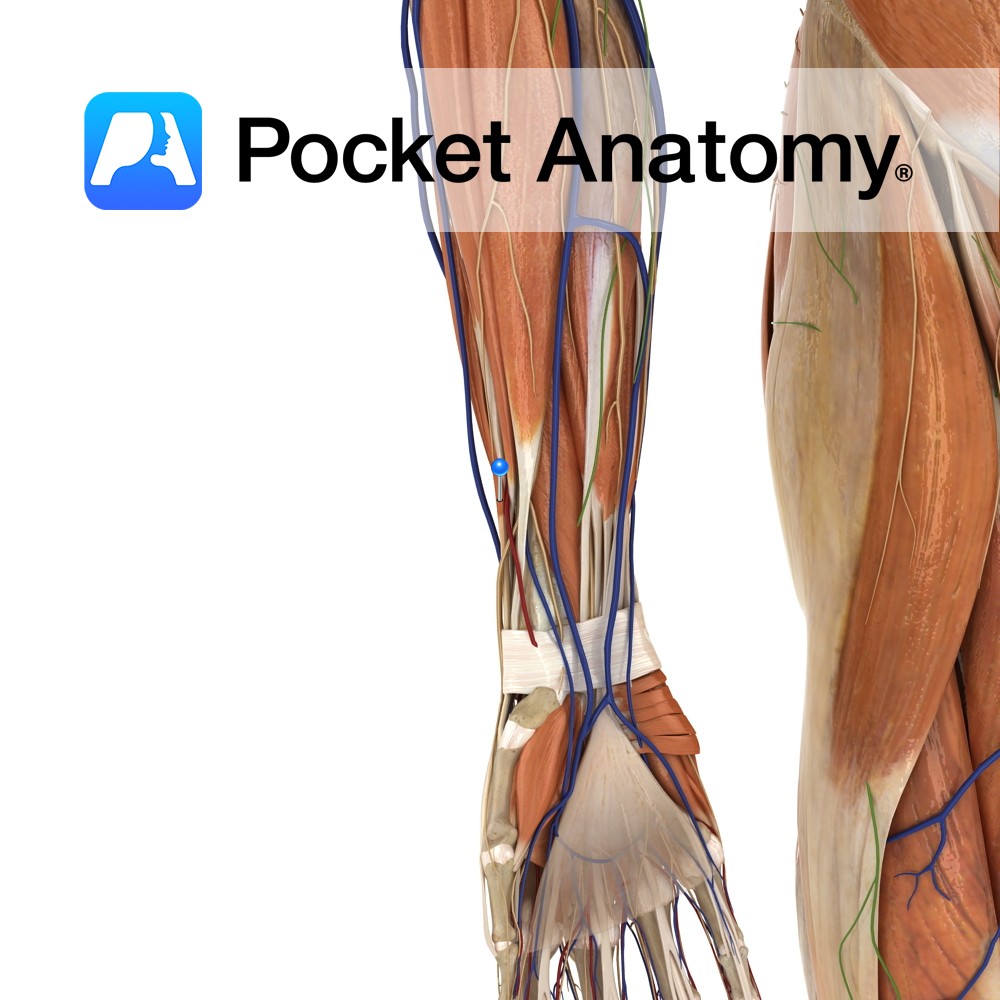
Anatomy Origin: Posterior of distal radius and adjacent Interosseus membrane. Insertion: Dorsal surface of base of proximal phalanx of thumb. Key Relations: -Its tendon together with the tendon of abductor pollicis longus forms the anterior boundary of the anatomical snuff box. -One of the six muscles in the deep posterior compartment of the forearm. Functions
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Junction of middle and distal thirds of ulna and adjacent interosseous membrane. Insertion: Extensor hood of index finger. Key Relations: The tendon of extensor indicis passes under the extensor retinaculum in a compartment with extensor digitorum. One of the six muscles in the deep posterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Extends index finger
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins