PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Oblong eminence at lateral/outer aspect of lower femur, separated in the front from medial condyle by trochlear groove, at back by intercondyloid fossa. Articulates at front with patella, bottom and back with tibia. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Most superior/proximal part femur, the ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint (acetabulum the socket), connected by neck to shaft, globular, points up in and forward, coated with cartilage (other than fovea which gives attachment to ligament of head of femur). Clinical Fracture of femoral head is usually due to significant (high force) trauma, and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
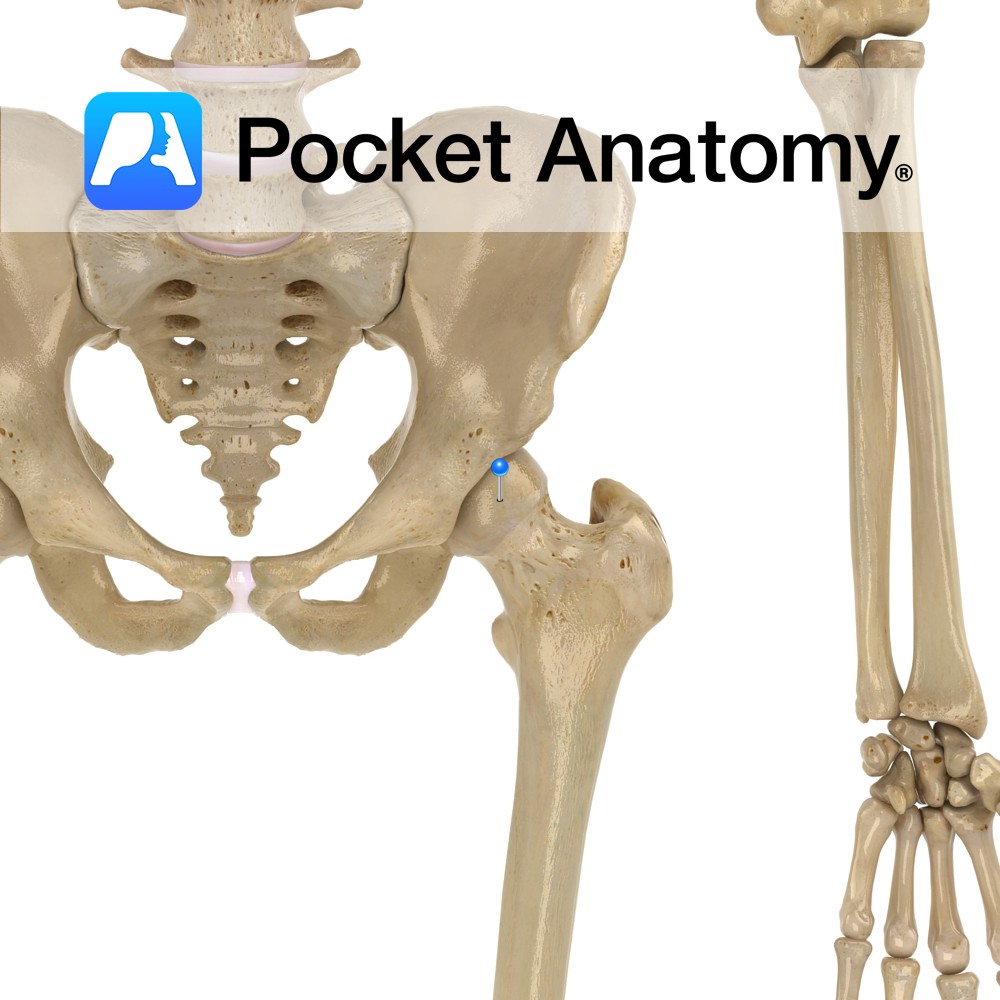
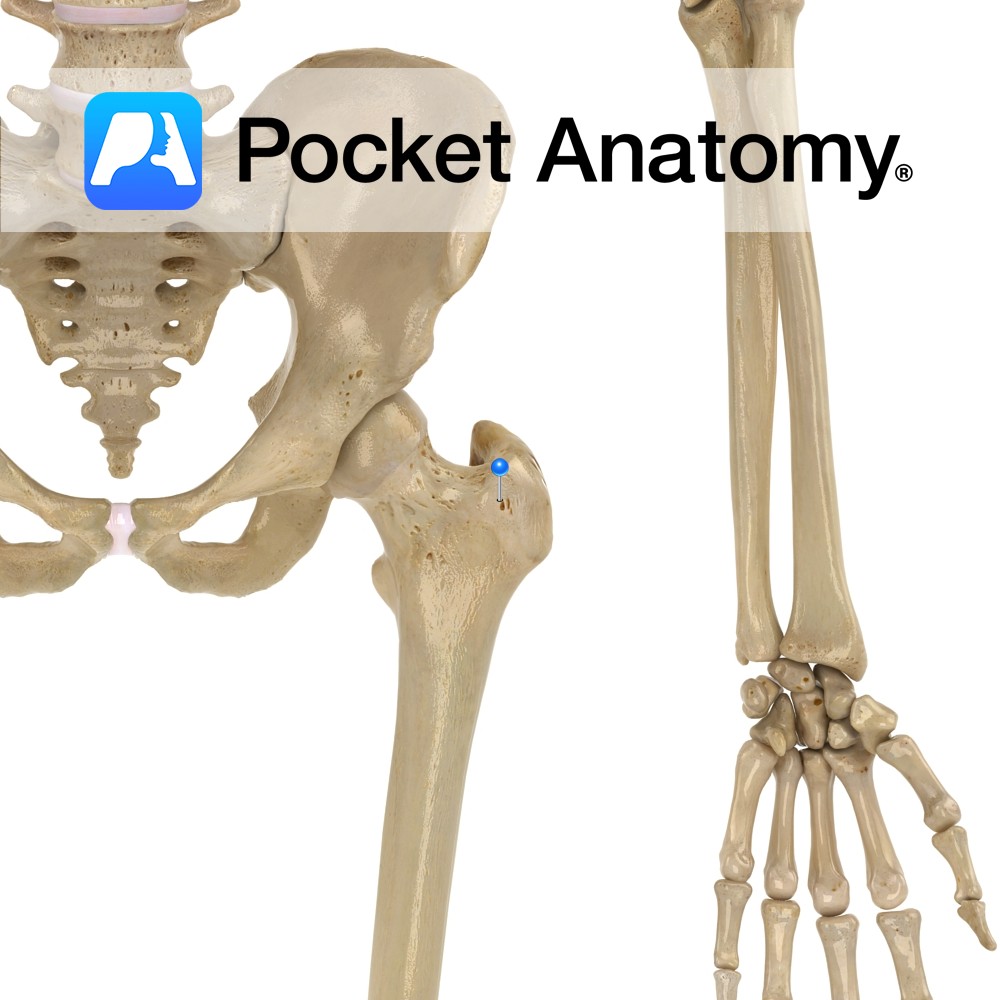
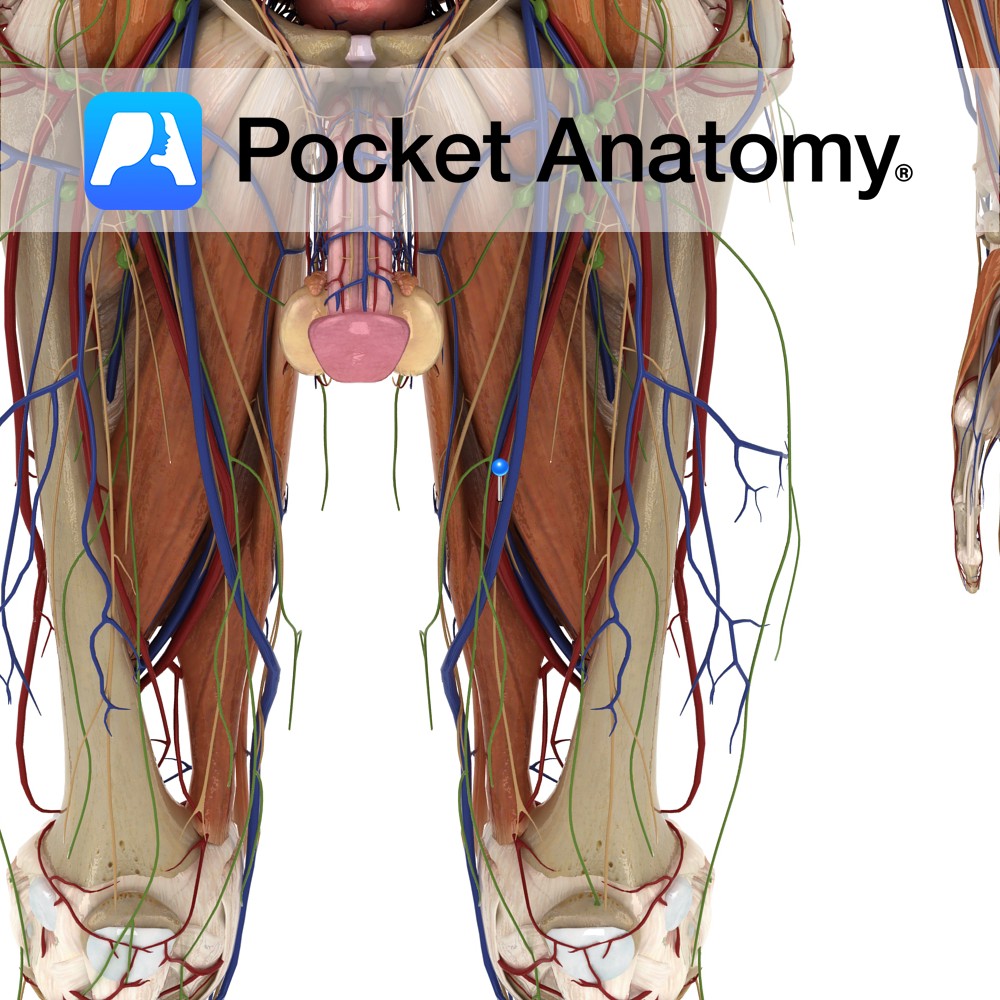
Anatomy Large bulge back and out from junction neck and shaft, main attachment of many muscles involved in complex hip movement (including rotation) manifested eg as postural gait; including vastus lateralis, obturator internus/externus, superior/inferior gemellus, piriformis, gluteus medius/minimus. The greater and lesser trochanters bulge out from top of femur and give leverage to muscles that
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
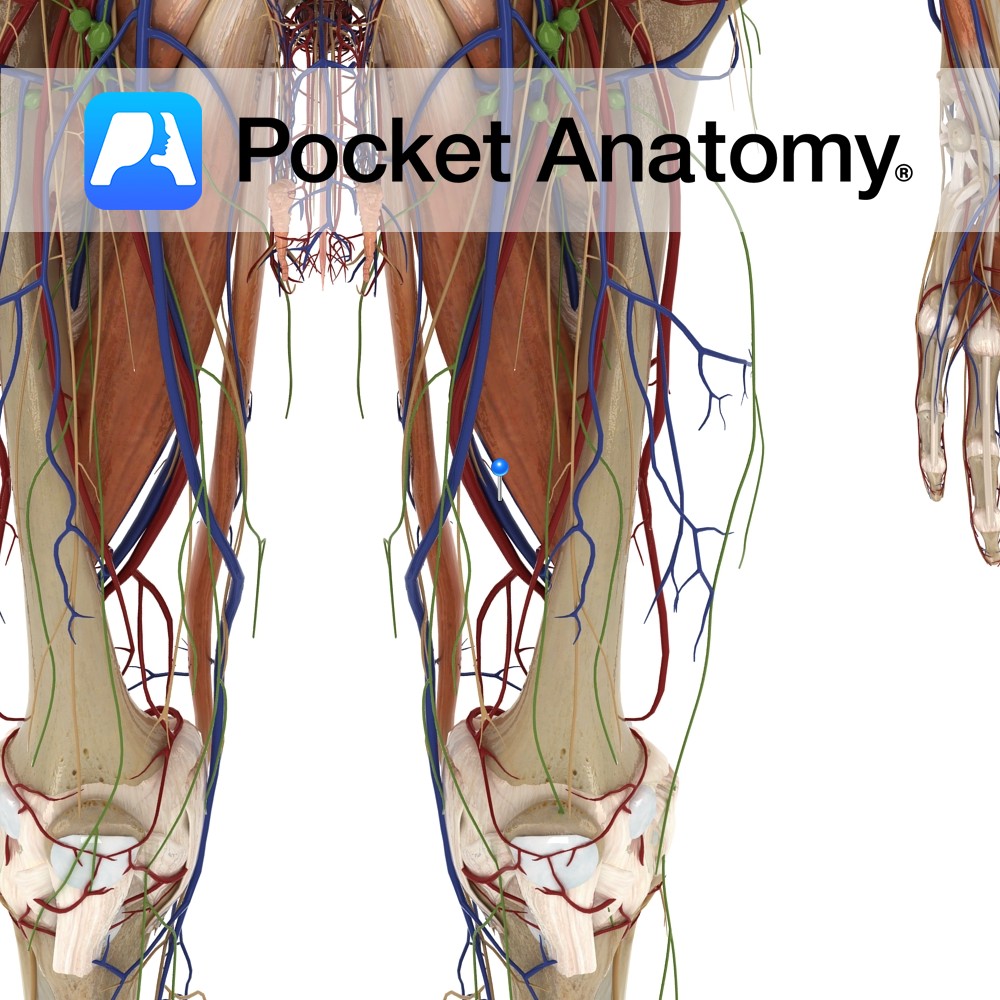
Anatomy Course Continuation of the popliteal artery when it enters the adductor canal. It travels along with its associated artery in the femoral sheath until it passes beneath the inguinal ligament, where it becomes the external iliac vein. Drain Drains the lower limb. Clinical Common site for injection of recreational drugs. Interested in taking our
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
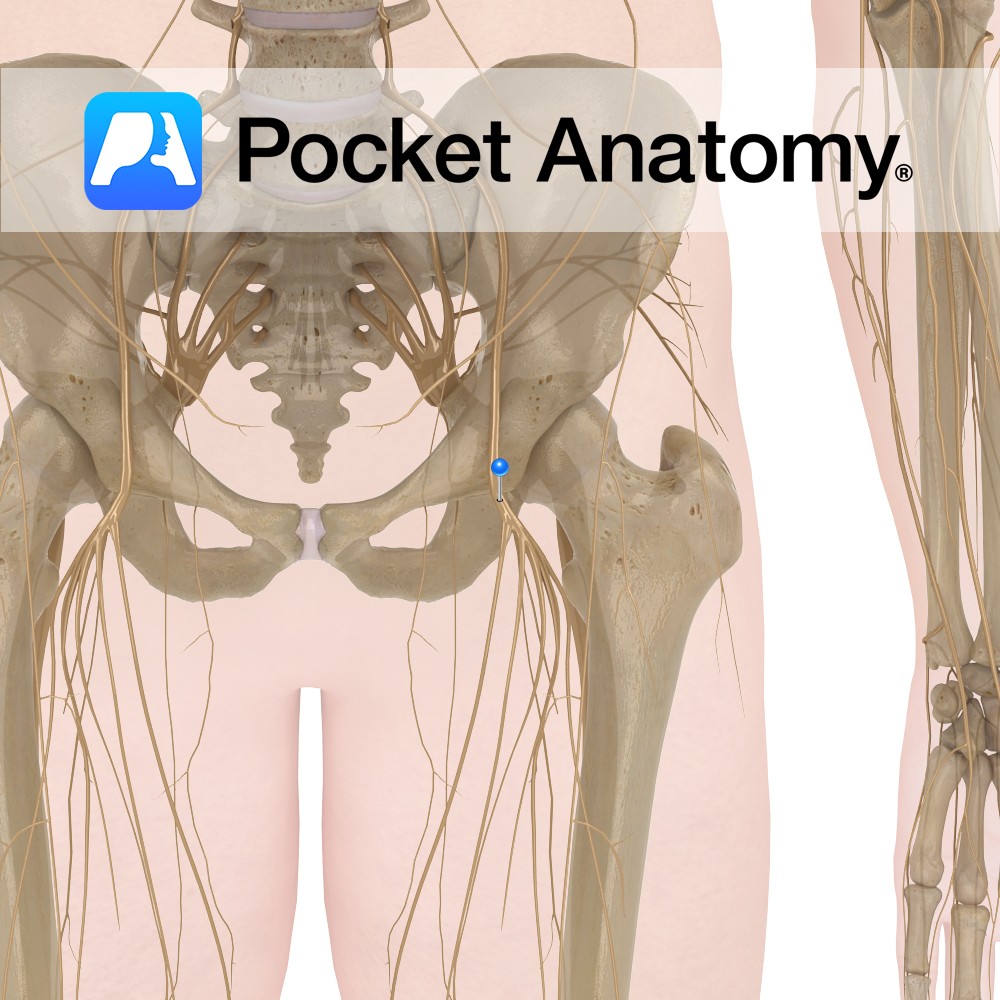
Anatomy Course The largest branch of the lumbar plexus and is composed of the second, third and fourth lumbar nerves. Descends between the iliacus muscle and psoas major muscle and runs below the inguinal ligament where it divides into two branches, anterior and posterior. Supply Motor supply to the quadriceps femoris as well as many
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course The external iliac artery becomes the femoral artery as it passes below the inguinal ligament and enters the femoral triangle, where it then descends in the adductor canal. It eventually exits via the adductor hiatus of the adductor magnus muscle, where it becomes the popliteal artery. Supply Supplies cutaneous regions of the lower
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
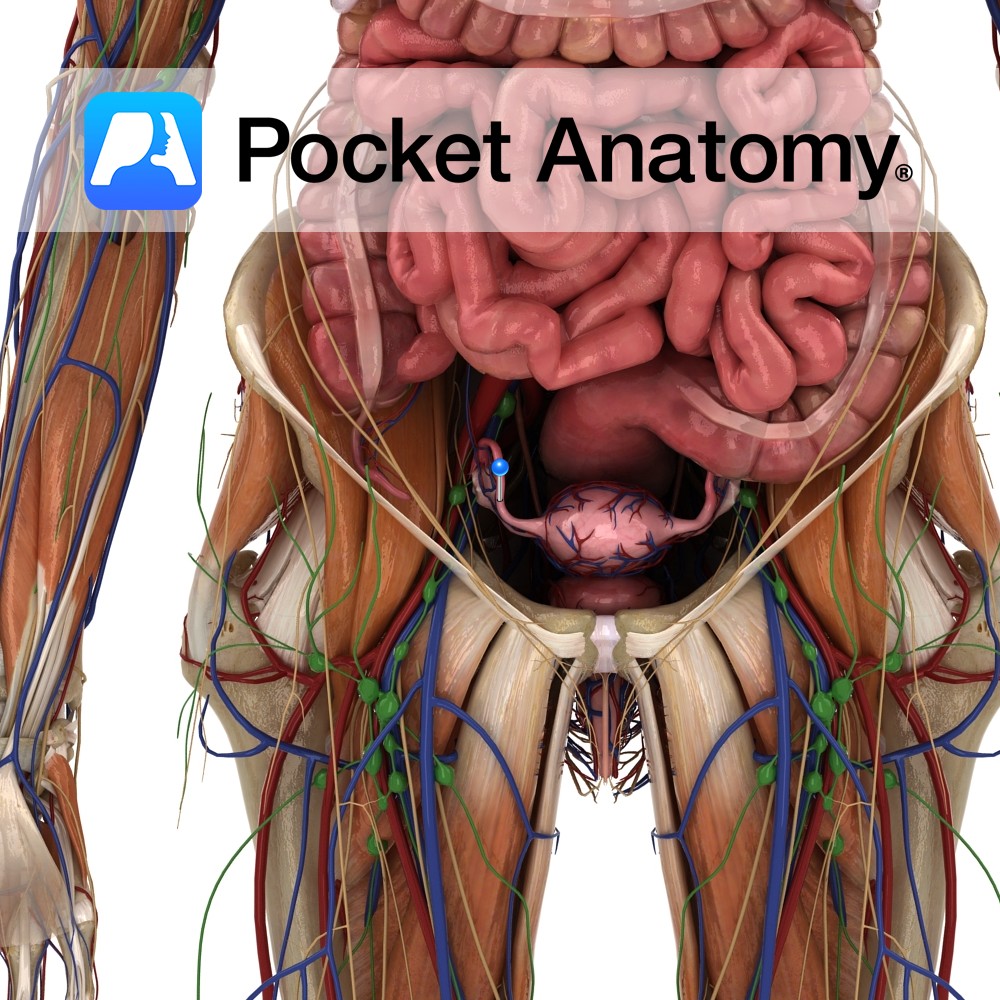
Anatomy Paired narrow muscular tubes (also known as uterine tubes, oviducts, salpinges), continuous with uterus medially, expanded laterally to envelop/overlay much of the ovary. Lateral to medial sections; wide infundibulum with fimbriae and ostium, ampulla, isthmus, intramural/interstitial part, uterotubal junction with ostium. The ends of the fallopian tube are termed ostia. The pinhead-sized proximal/medial/inner ostium
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
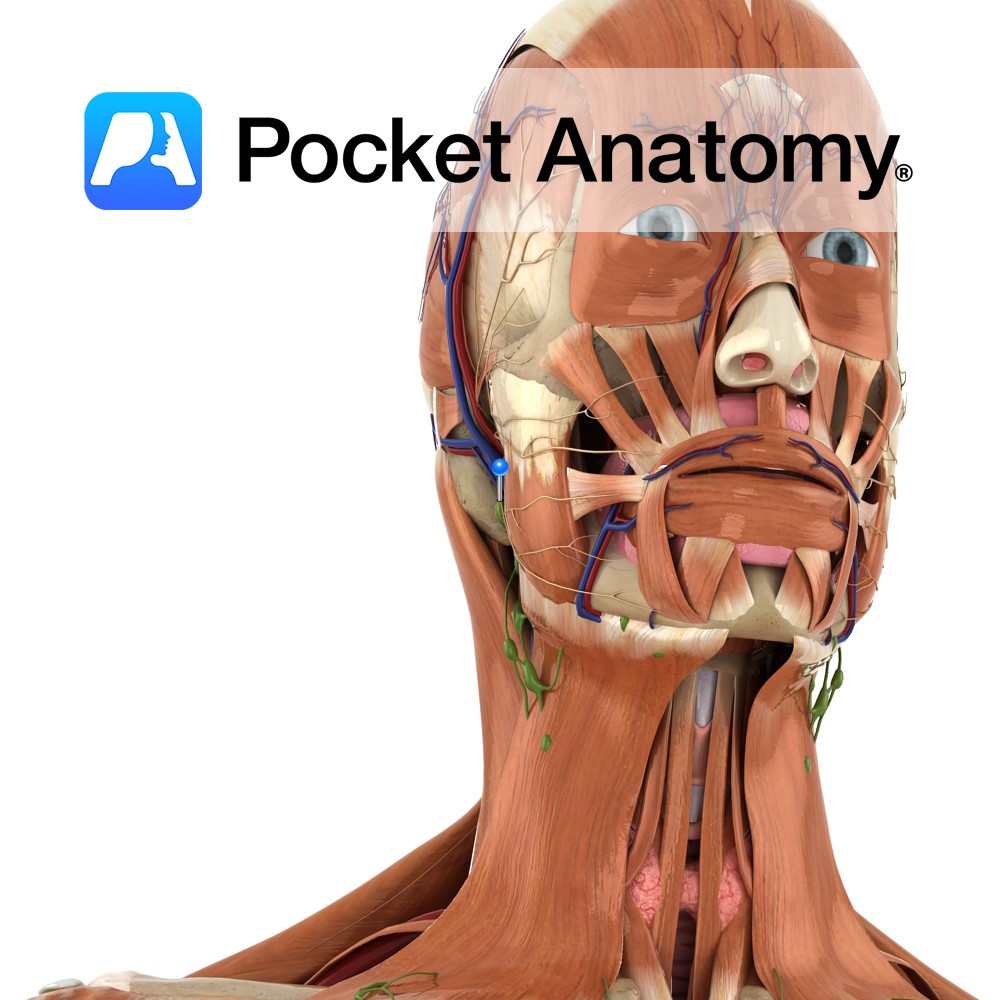
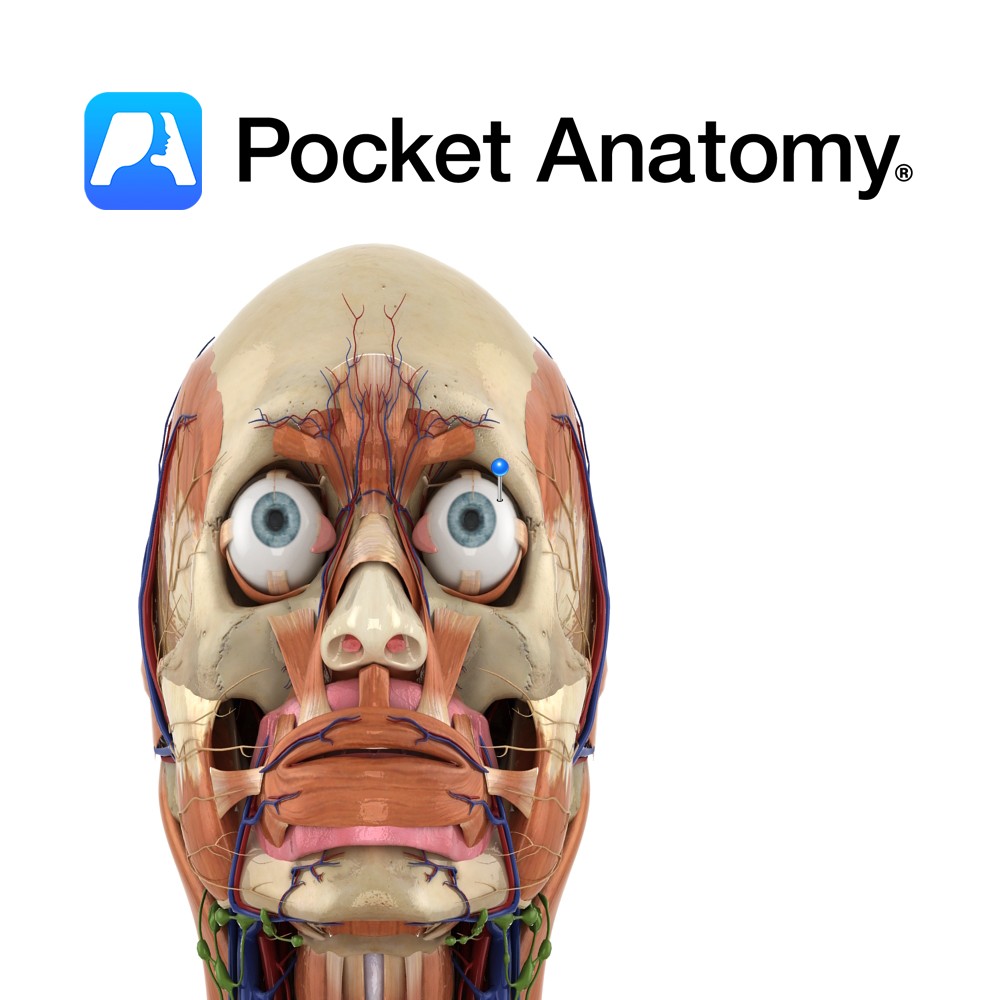
Anatomy Course Continuation of the angular vein at the base of the nose. It travels with the facial artery, but is considerably less tortuous. It can either empty directly into internal jugular vein or it can join with the retromandibular vein to form the common facial vein. Drain Drains the superficial veins of the face.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Also known as the seventh cranial nerve. Has a motor and sensory origin that join together to form the nerve. It passes through the internal auditory meatus through the facial canal and finally exits from the stylomastoid foramen, and into the parotid gland where it divides into its terminal branches (temporal, zygomatic, buccal,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
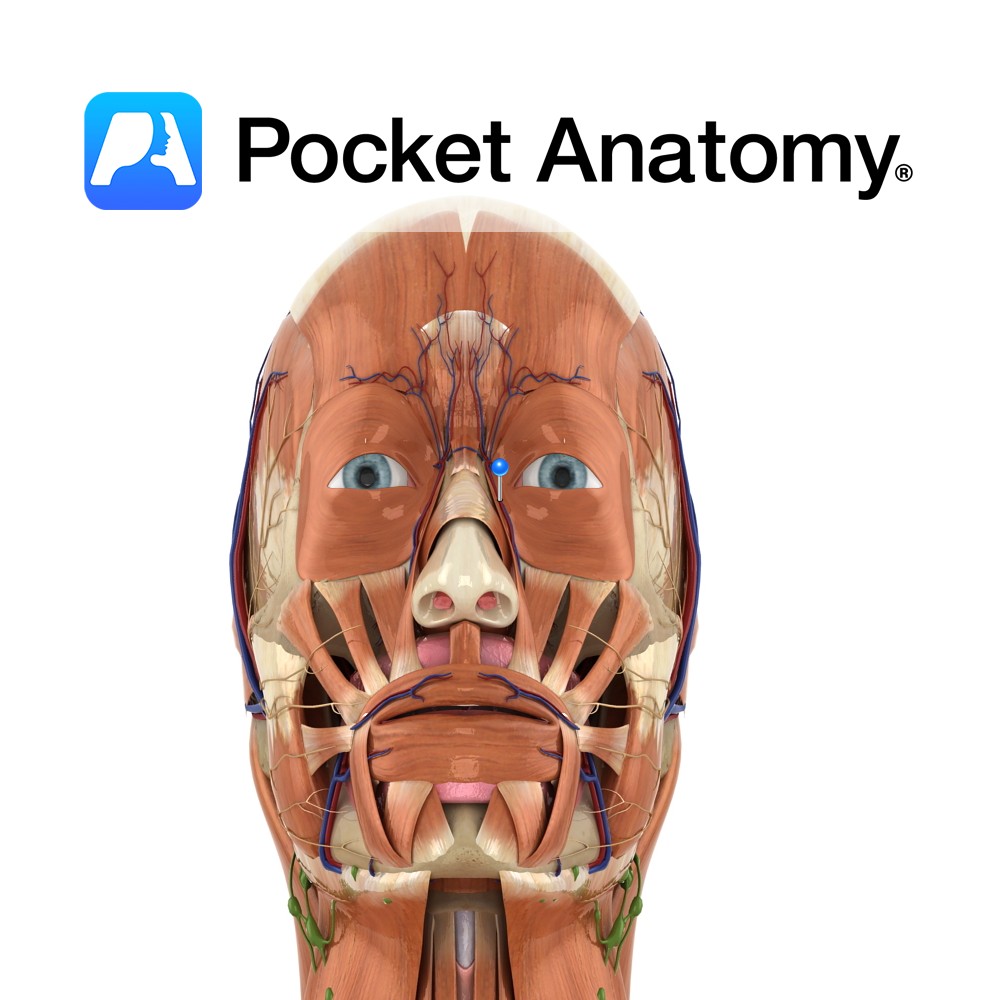
Anatomy The human eyes are the organs of vision, located in the bony orbits in the front of the skull, on either side of the bridge of the nose. Functions The eye detects light and transforms it into impulses that are sent to the brain. Light enters through an opening in the iris called the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins