PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
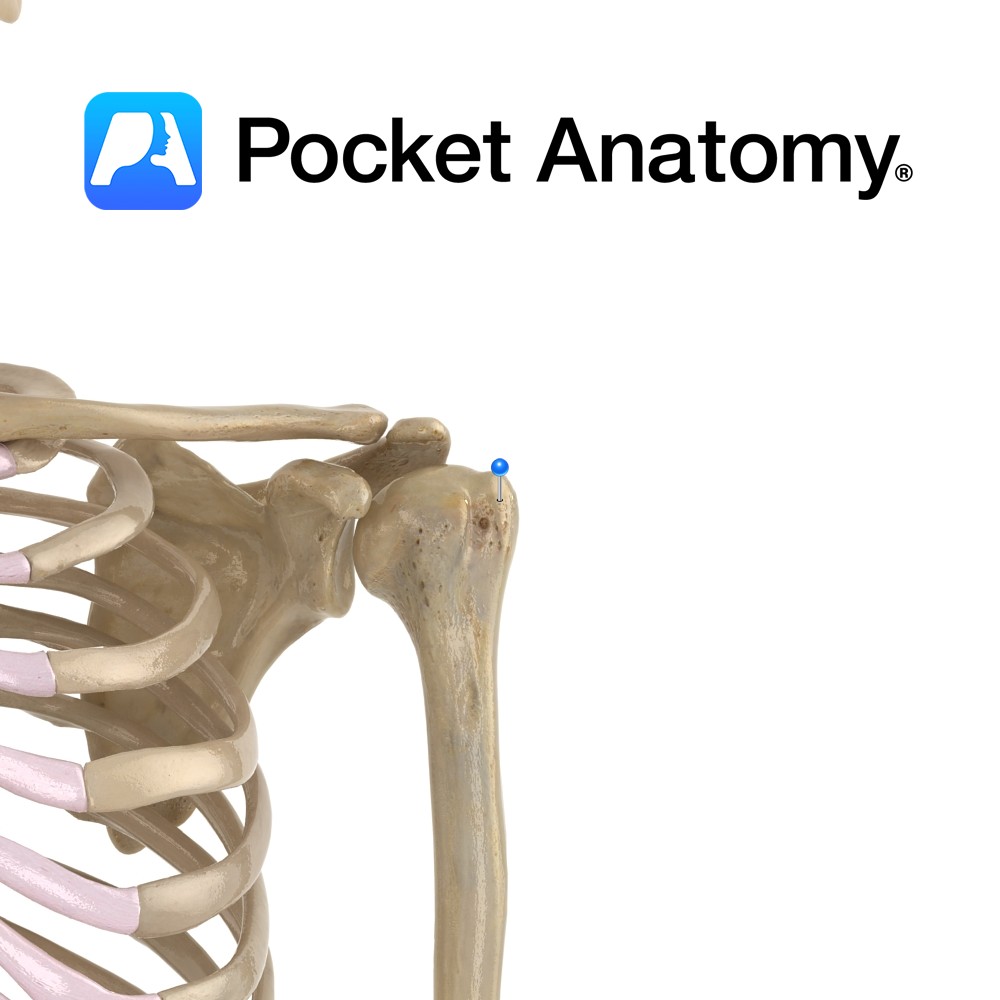
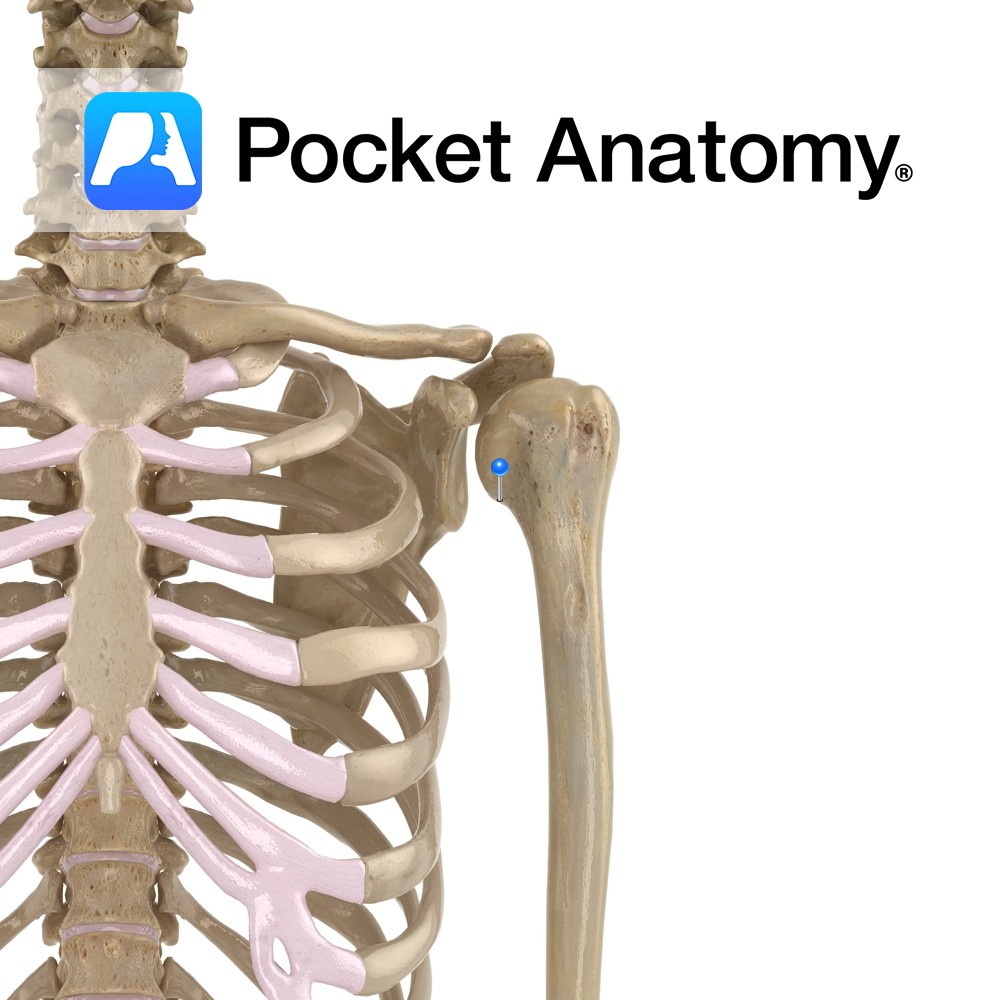
Anatomy Swelling lateral to humeral head, above and behind lesser tubercle. Attachments; supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
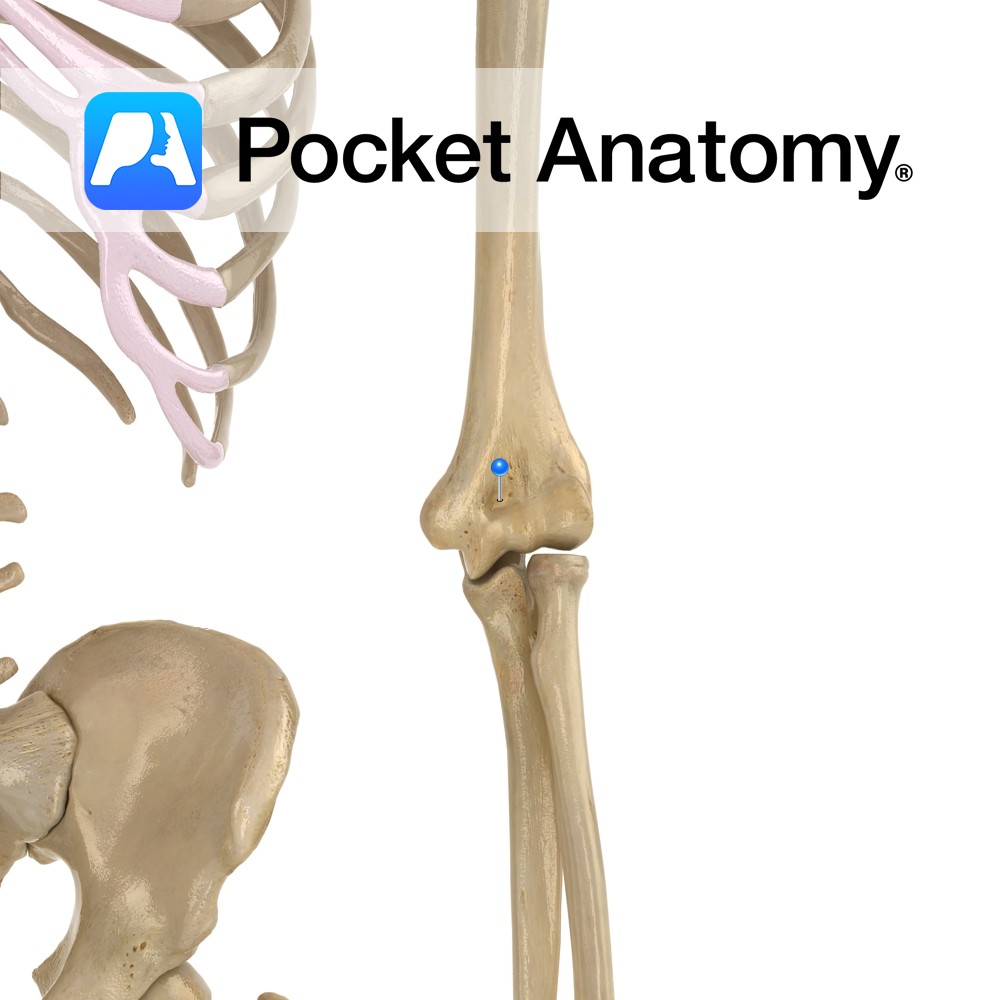
Anatomy Just above the trochlea (which articulates with head of ulna) at bottom of humerus medially. When the arm is bent (ie elbow hinge joint flexed), the coronoid process of ulna sits in the coronoid fossa (limiting further flexion). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
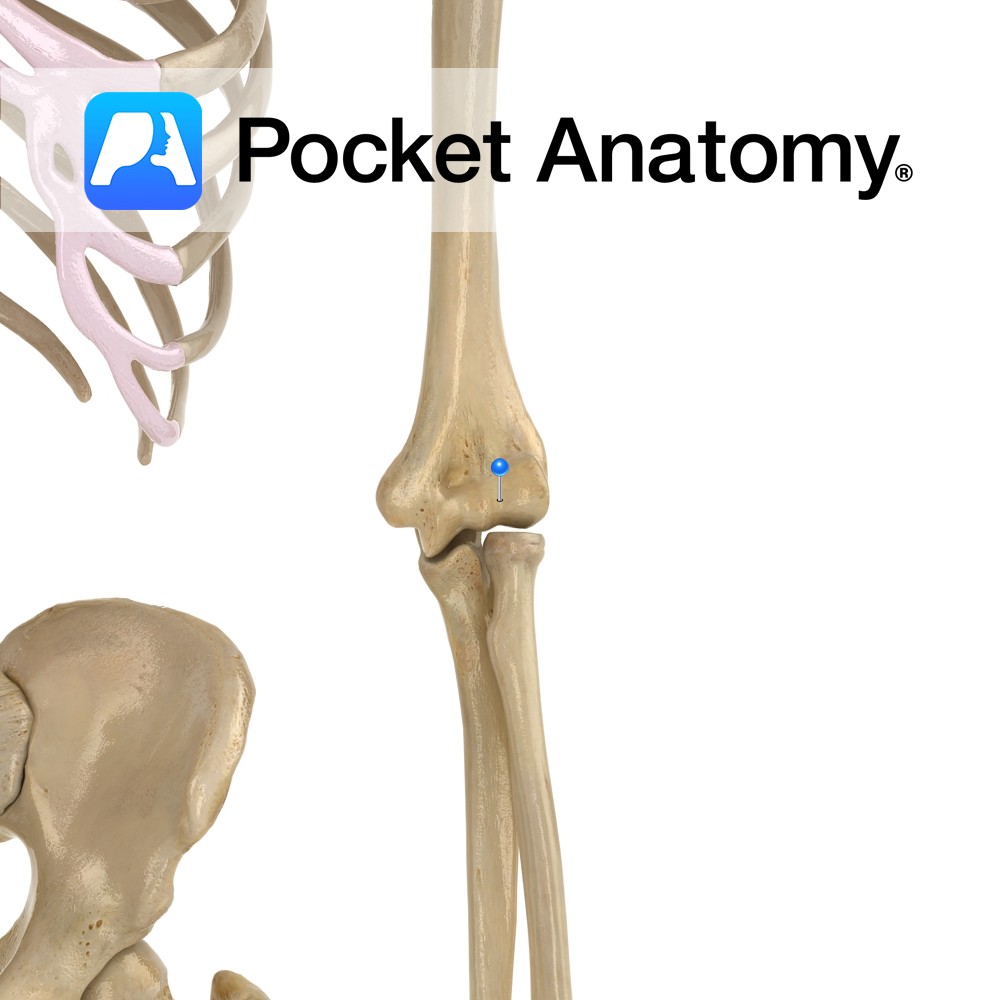
Anatomy The articular surface of the bottom of humerus is divided into trochlea medially (for trochlear notch of ulna, which is between coronoid process and olecranon) and capitulum laterally (for head of radius). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Oblique groove just below humeral head (separating it from greater and lesser tubercles) where shoulder joint capsule attaches. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
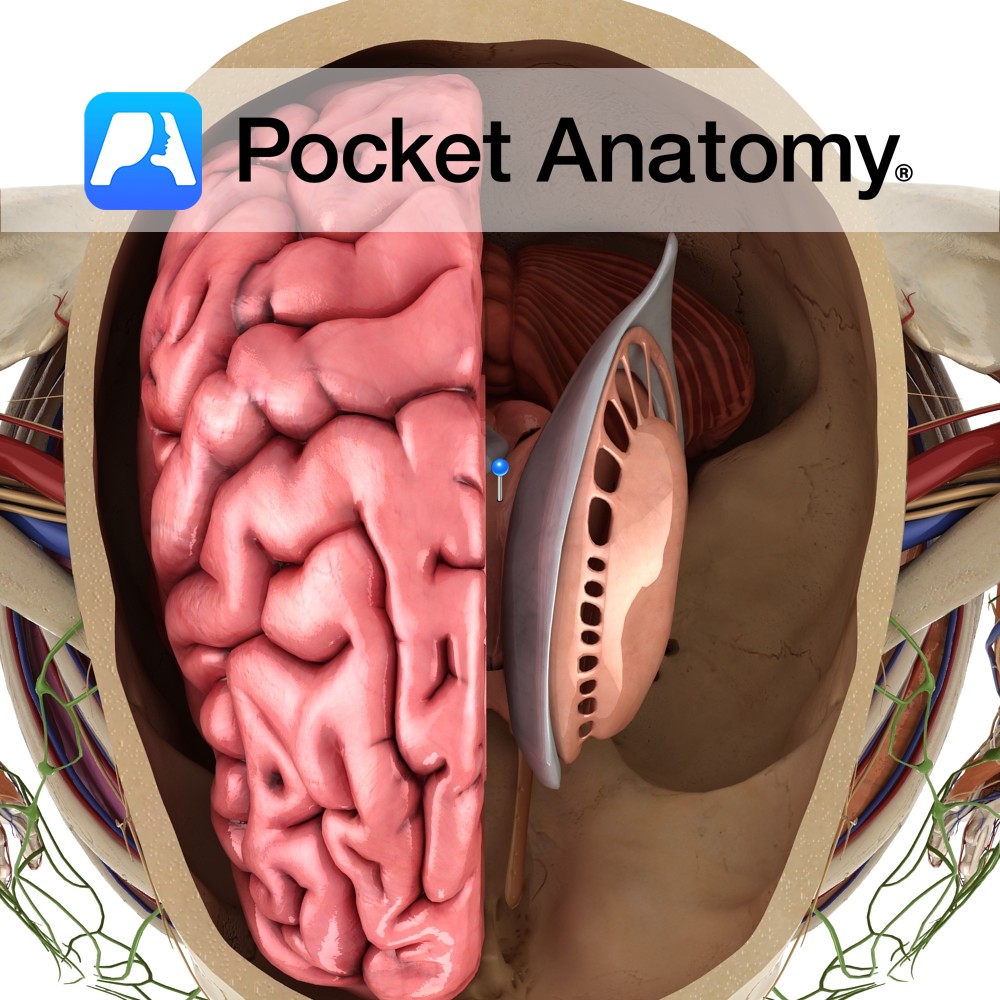
Anatomy A paired structure located in the medial temporal lobe that forms the floor of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle. Blood Supply: Supplied by branches of the internal carotid and posterior cerebral arteries. Functions The hippocampus may act as a neural map of the external environment. It receives information regarding the body’s position
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
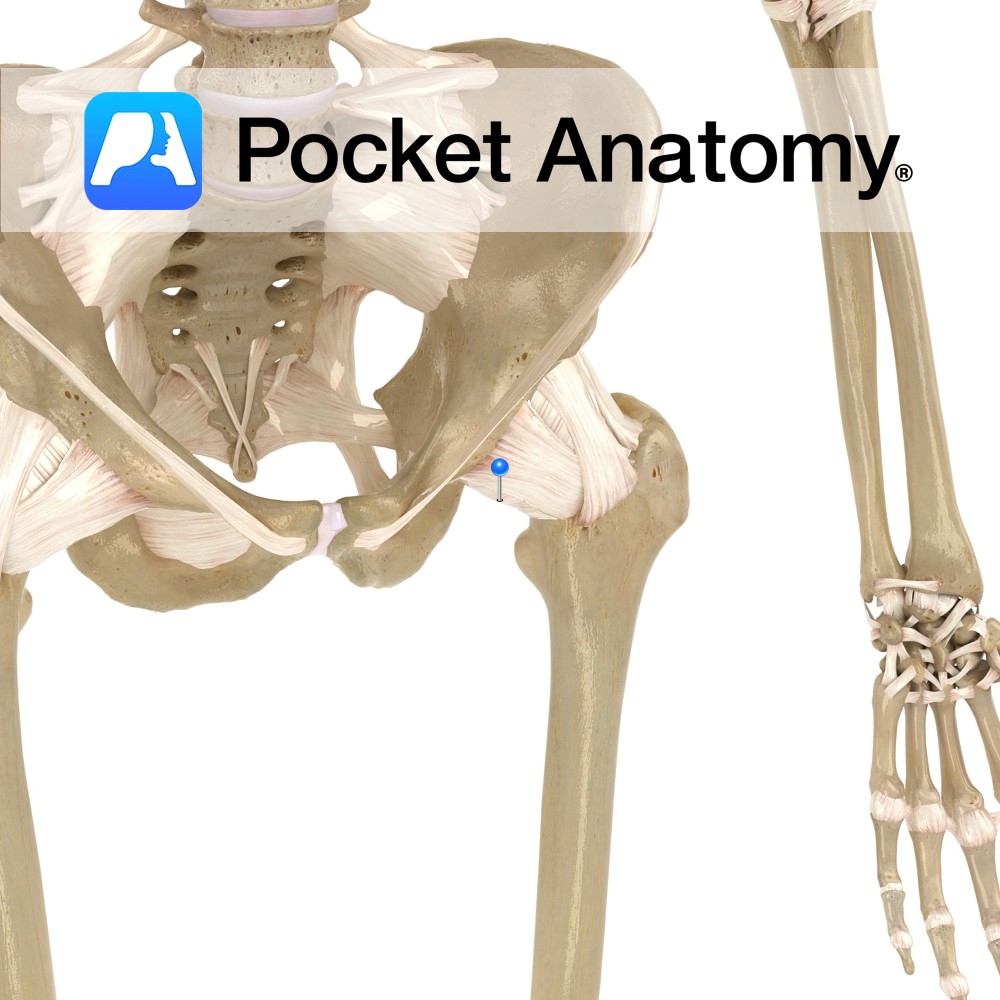
Anatomy Strong and dense capsular ligament, which provides support to the hip joint. Attaches superiorly to margin of the acetabulum, and anteriorly to the outer margin of the labrum. It consists of both circular and longitudinal fibers, which are thicker superiorly and anteriorly, where most support is needed. Functions Gives general support to the hip
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Motion The hip joint is a multiaxial synovial ball and socket joint. It is formed by the articulation between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone. It can be flexed, extended, abducted, adducted, medially rotated, laterally rotated and circumducted. Circumduction is the complex circular movement of the joint combining flexion,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
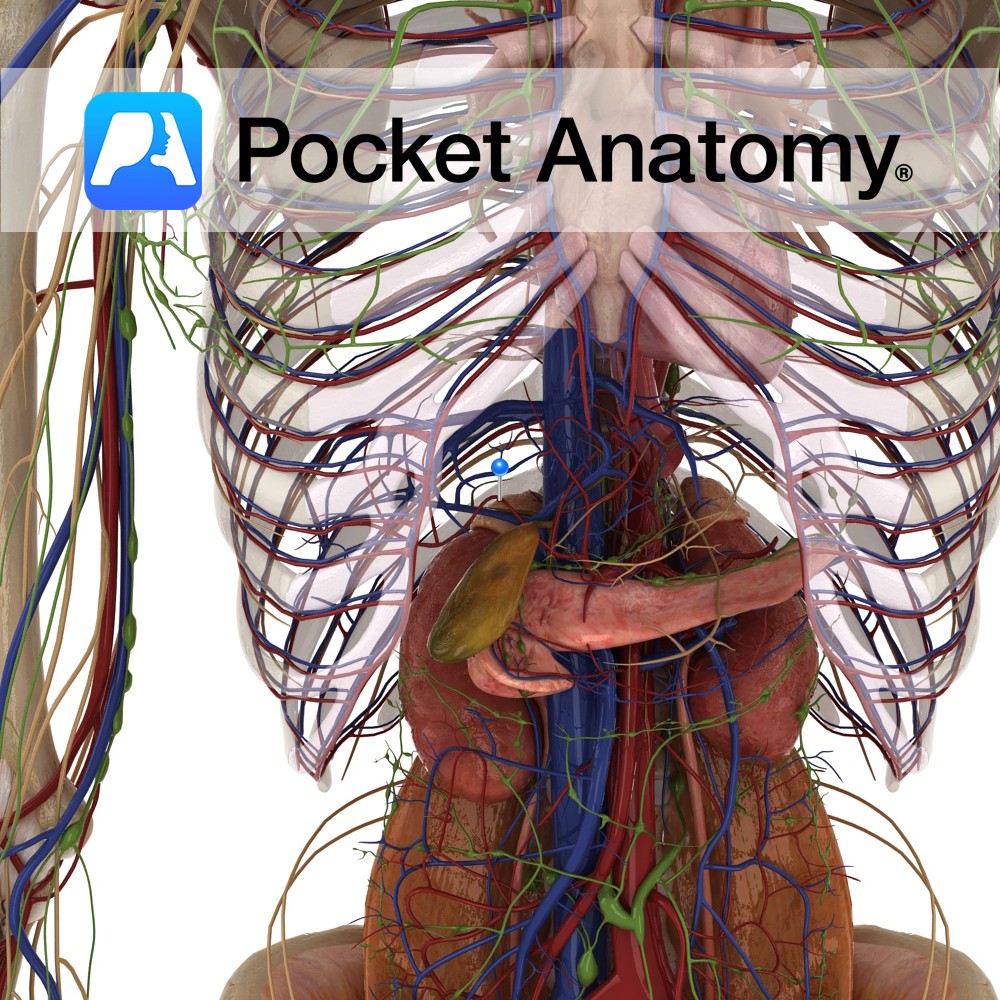
Anatomy Course Originates from the vessels inside the liver like the central vein. They drain deoxygenated and filtered blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava. Drain Liver and other abdominal viscera. Clinical Occlusion can cause Budd-Chiari Syndrome. Patients often present with ascites, hepatomegaly and complain of abdominal pain. Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
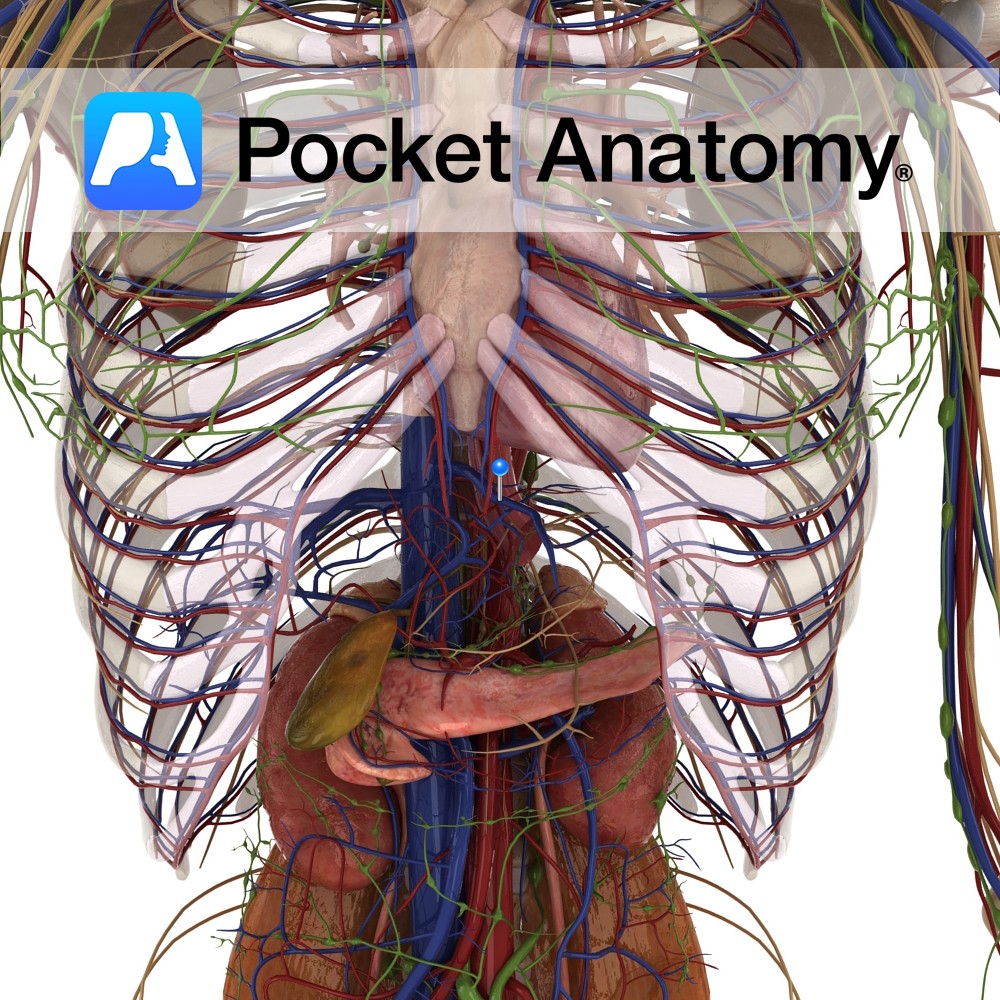
Anatomy Course Branches off the celiac trunk and travels to the right for a short period of time before it divides into its terminal branches. Supply Via its branches it supplies the liver, pylorus and duodenum with oxygenated blood. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
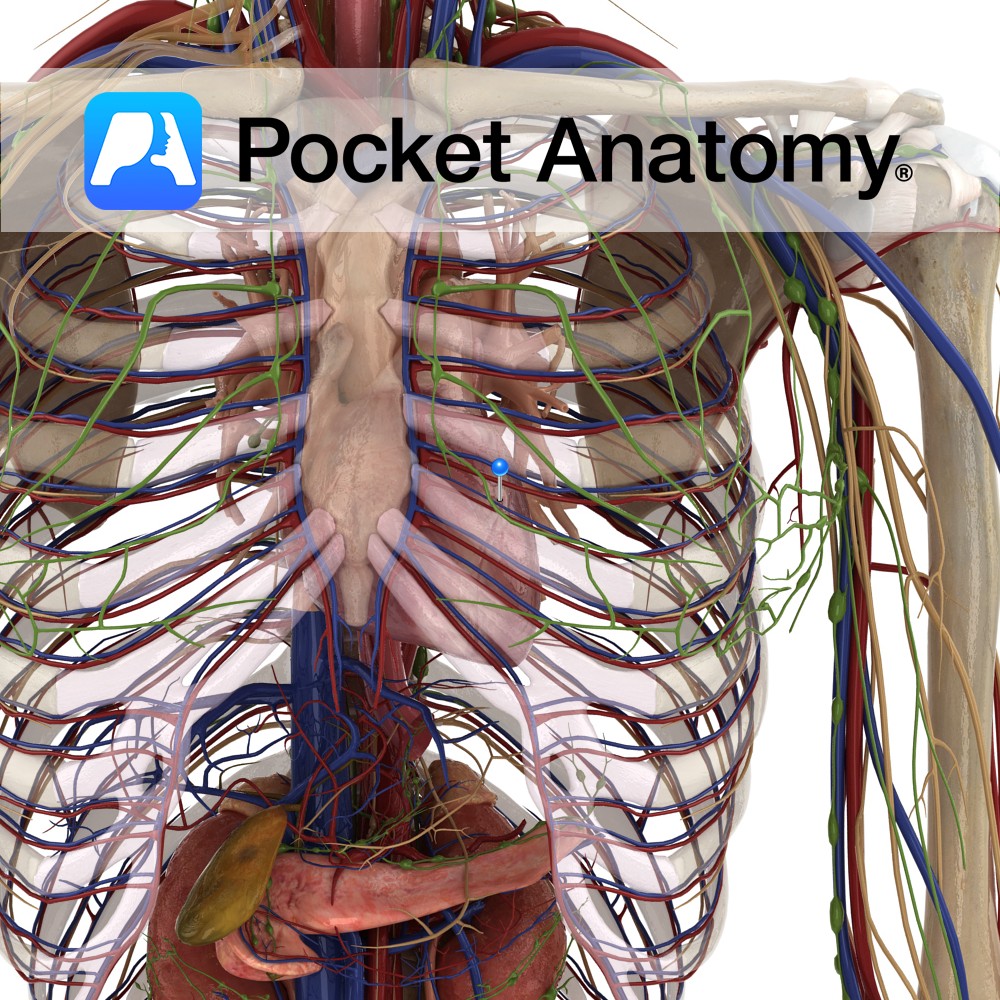
Anatomy Fist-sized blood- pumping muscular (involuntary striated) organ, left of centre in thorax. A double pump with separating septum, each part/side (right and left) comprising 2 chambers – an atrium (into which a vein delivers blood) and a ventricle (from which blood is pumped to an artery) and 2 valves (cuspid between atrium and ventricle,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)