PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
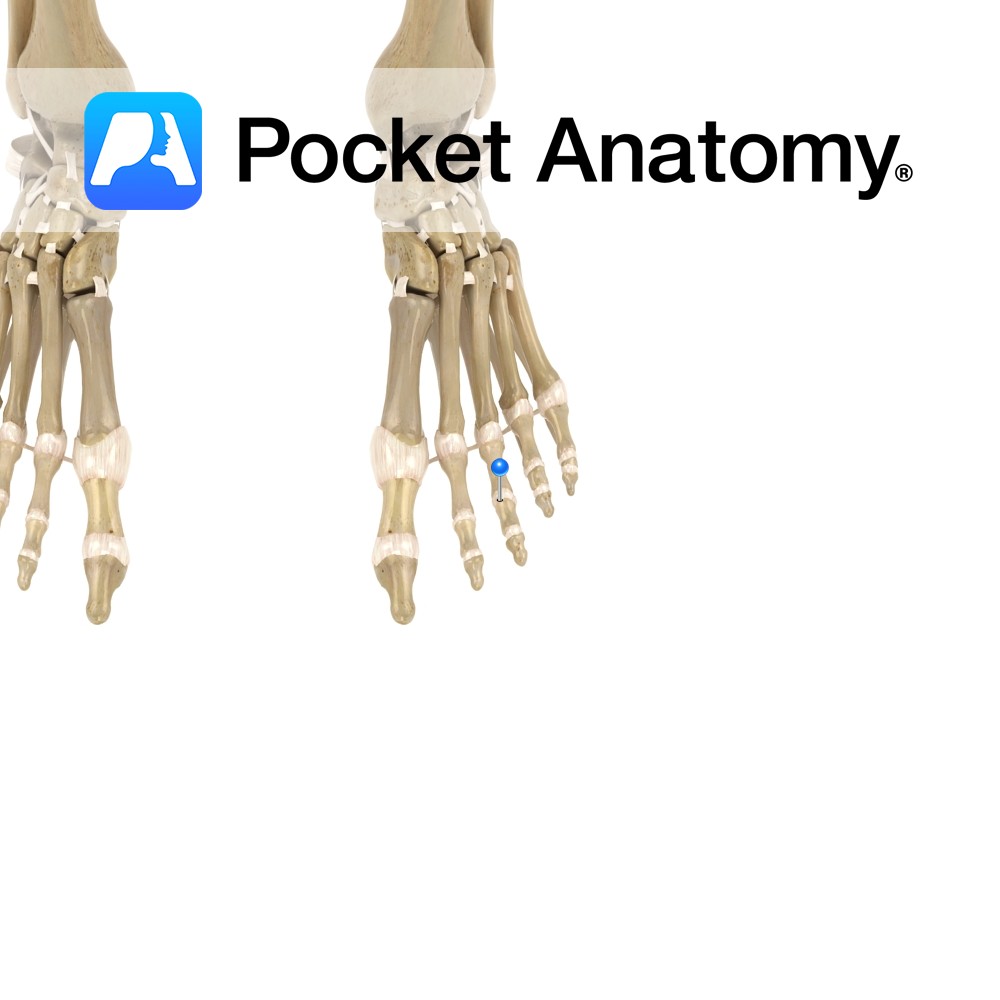
Motion The interphalangeal joints are synovial hinge joints. They involve the articulations between the proximal, middle and distal phalanges of the toes. They allow mainly flexion and extension. Stability The fibrous capsules surrounding the joints plays a role in their stability. The joints are reinforced by the following ligaments: -Medial collateral ligament -Lateral collateral ligament
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
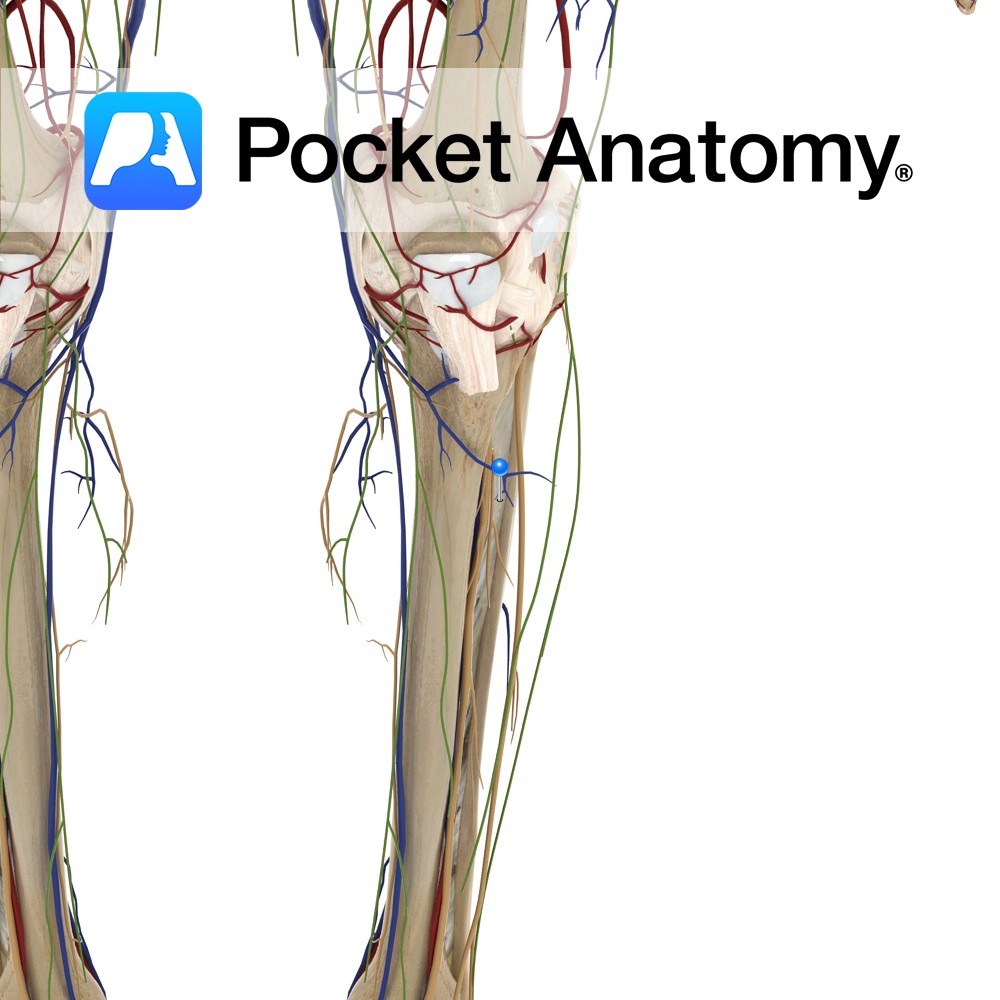
Anatomy A thin, fibrous sheet attaching between the interosseous crests of the tibia and fibula. The fibres pass downwards in criss-cross directions. Its upper margin does not quite reach the proximal tibiofibular joint, and there is a hole in its distal end. These holes are for passage of vessels in the lower limbs. Functions Connects
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
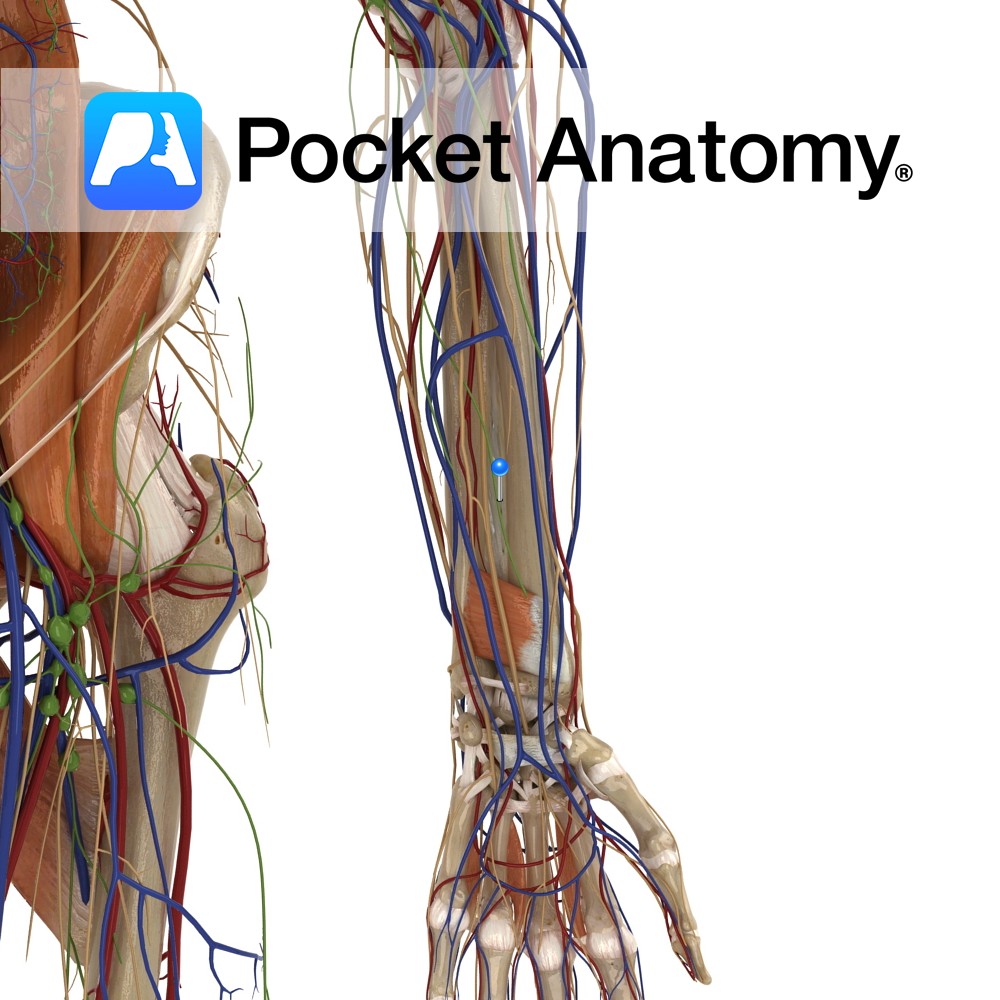
Anatomy A thin, fibrous sheet connecting between the medial border of the radius to the lateral border of the ulna. The collagen fibres pass obliquely downwards from the radius to the ulna. It has a free upper margin inferior to the radial tuberosity and a small hole in its distal third. These holes allow passageway
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course The main veins draining the perineum. They travel superiorly to join the internal iliac veins. Drain Drain the perineum. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
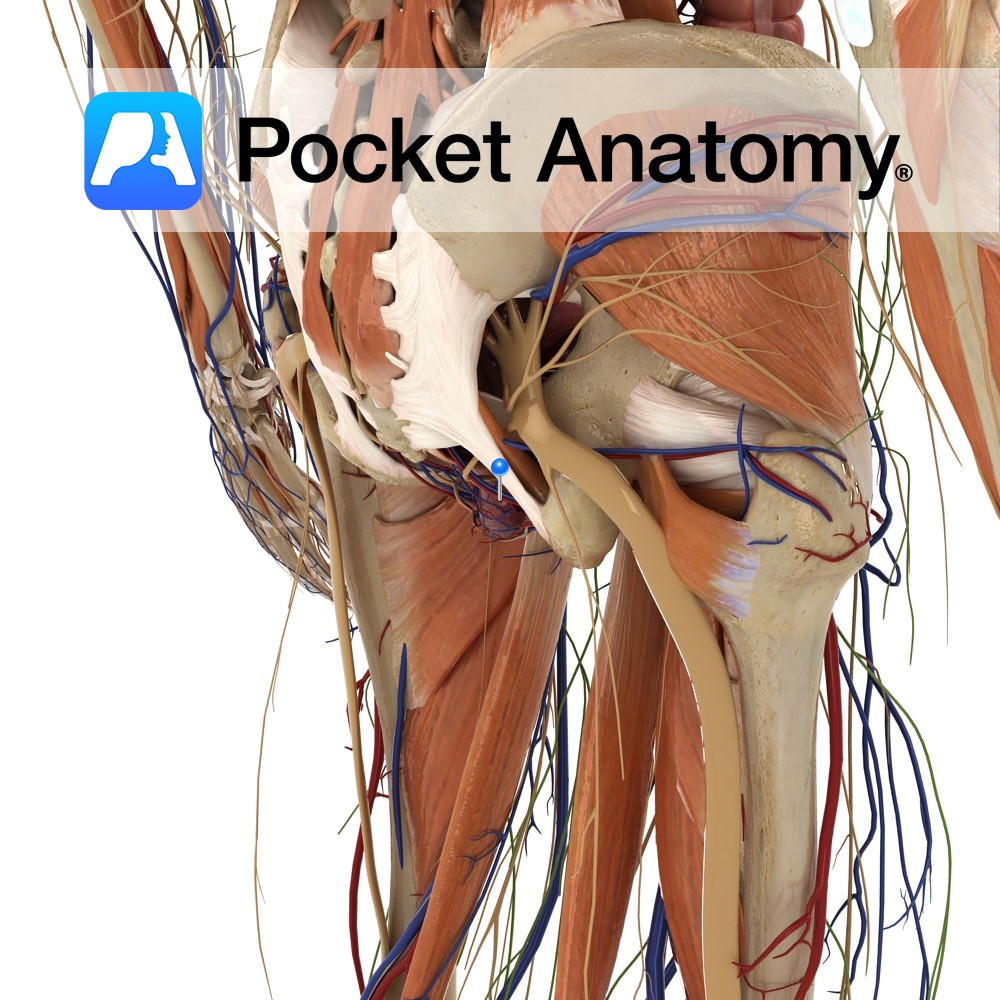
Anatomy Course Branches off the anterior trunk of internal iliac artery where it then leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen below the piriformis muscle. It then enters the perineum via the lesser sciatic foramen. Supply Main supplier of the perineum, specifically the erectile tissues such as the penis and clitoris. Interested in taking
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
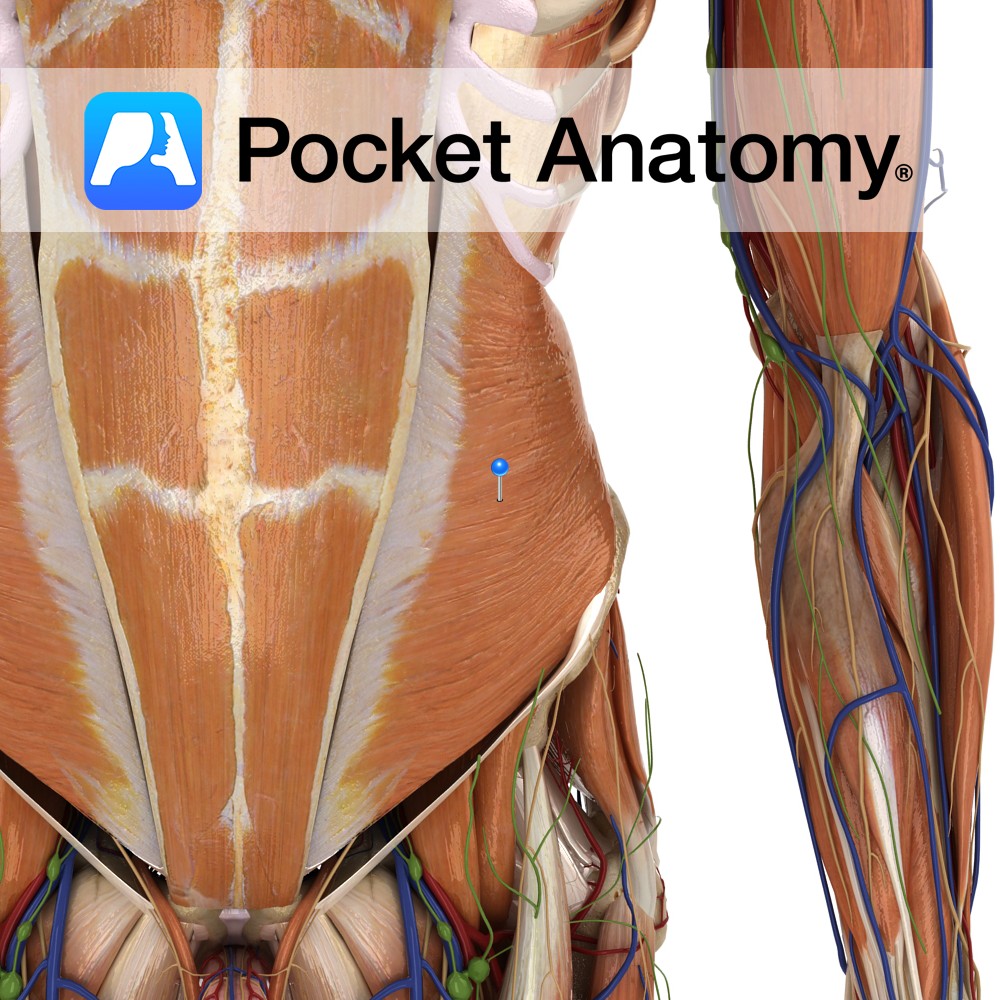
Anatomy Origin: Thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest and the lateral two thirds of inguinal ligament. Insertion: Inferior border of 9th /10th to 12th ribs, aponeurosis to linea alba, pubic crest and pectineal line. Key relations: -Deep to the external obliques. -Muscle fibres run superomedially. Functions -Compresses abdominal cavity and raises intrabdominal pressure e.g raking leaves. -Flexes
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
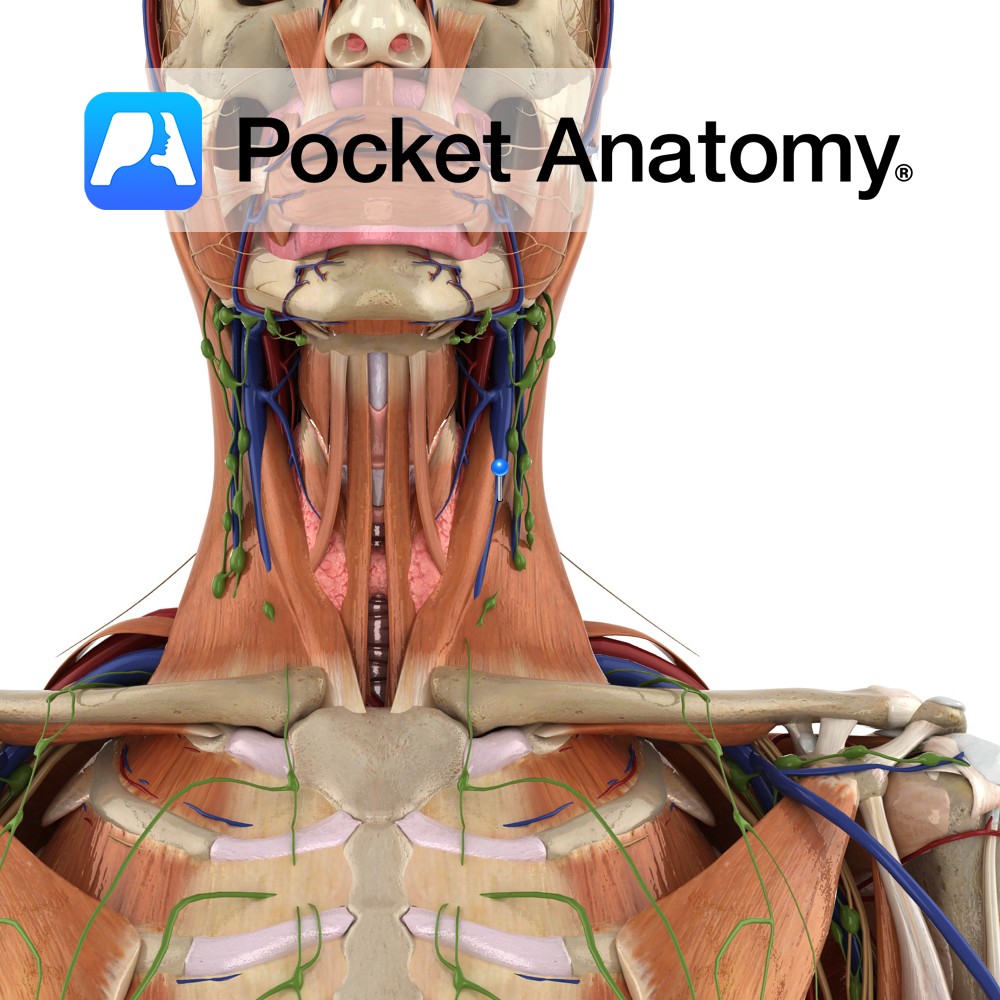
Anatomy Course Starts when the inferior petrosal sinus and sigmoid sinus come together. It leaves the cranium via the jugular foramen and descends lateral to the internal and common carotid arteries. On both sides, it joins the subclavian veins to form the brachiocephalic veins. Drain Drains blood from the brain, neck and superficial face. Clinical
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
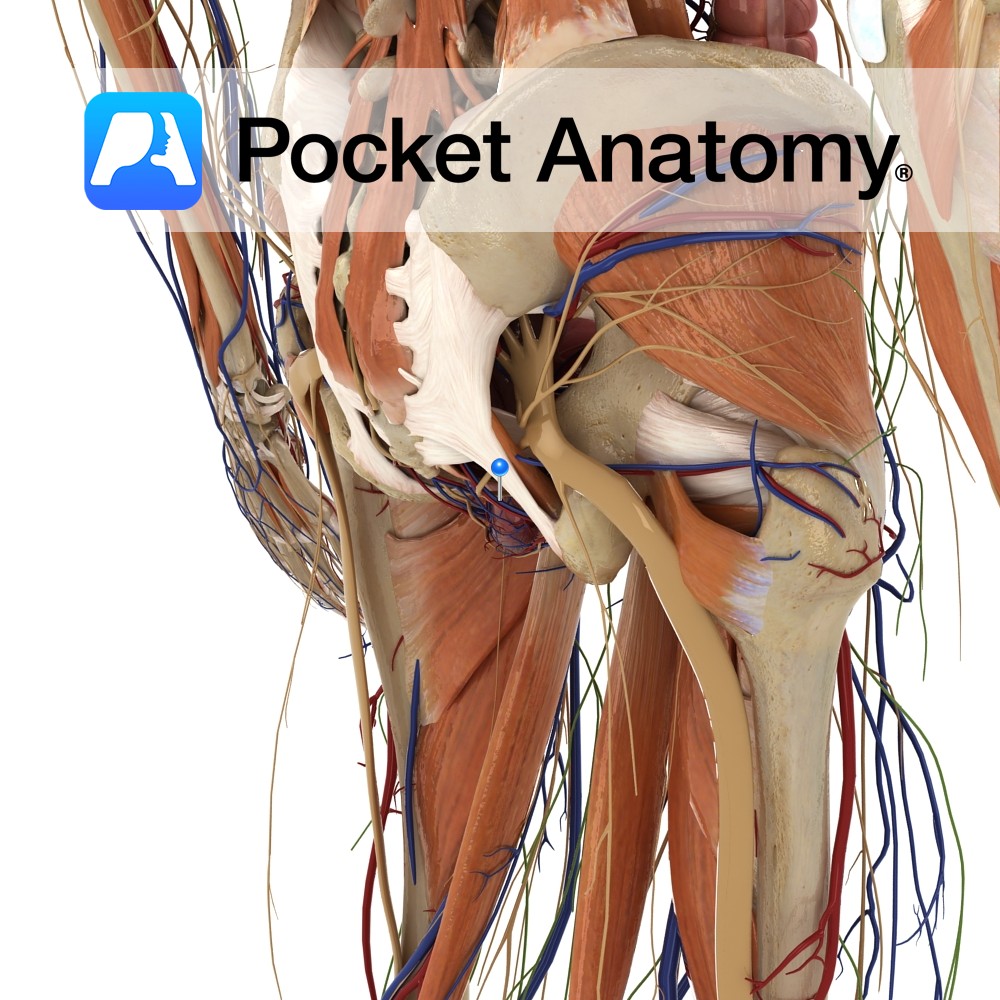
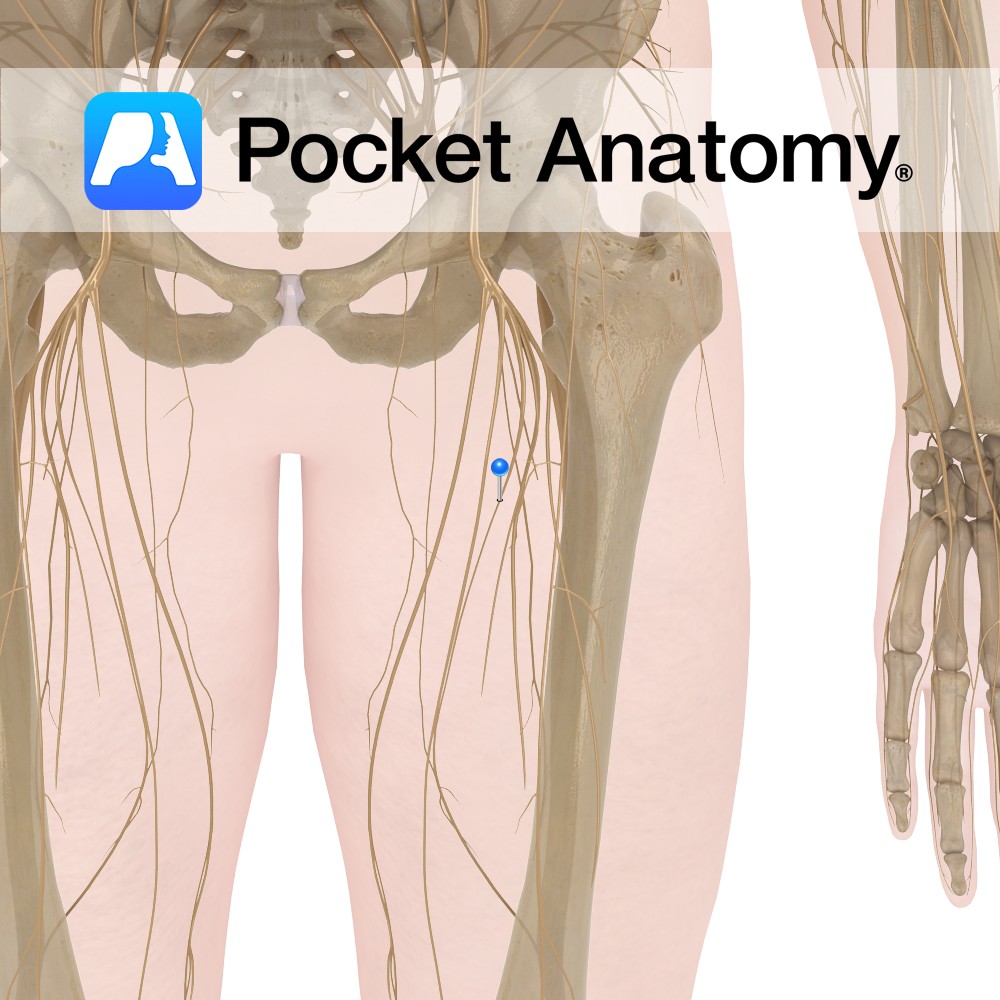
Anatomy There are two anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve: Intermediate femoral cutaneous nerve and Medial femoral cutaneous nerve. Course The femoral nerve is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus and is composed of the second, third and fourth lumbar nerves. Descends between the iliacus muscle and psoas major muscle and runs below
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
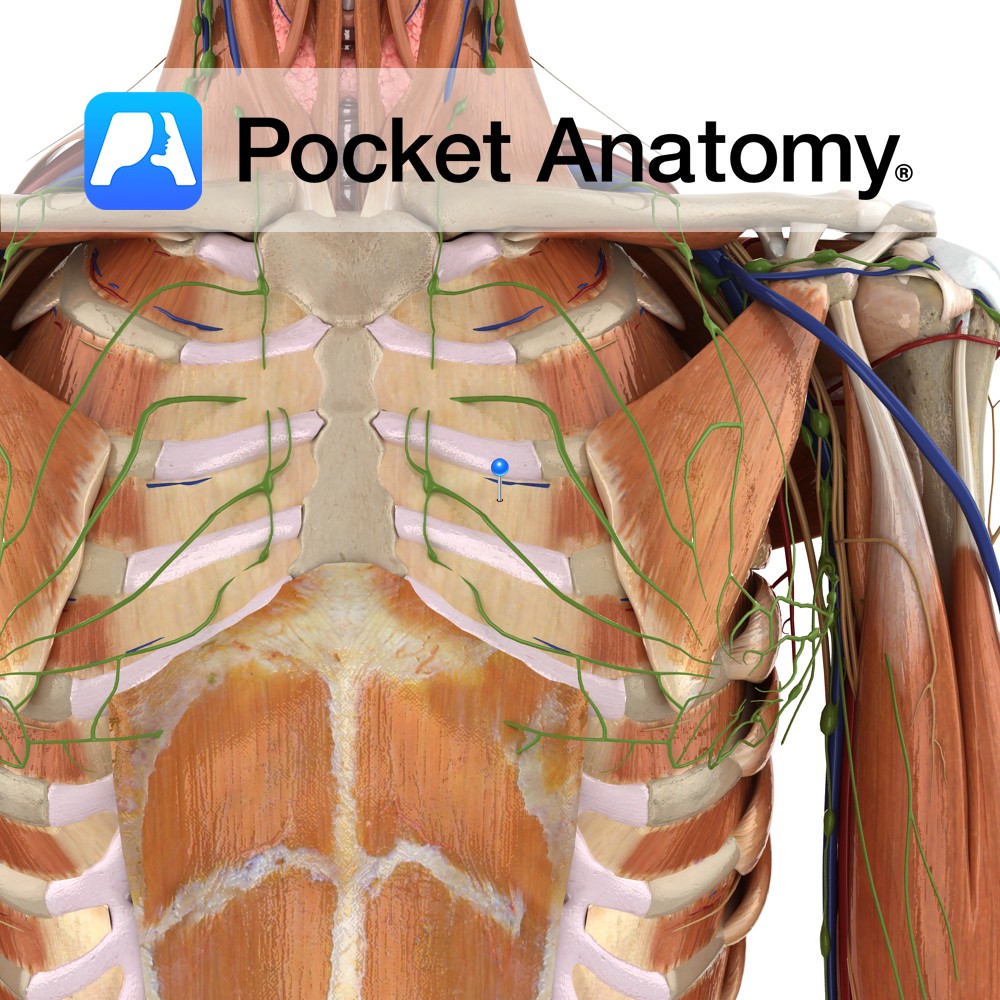
Anatomy Origin: Lateral edge of costal groove of the rib above. Insertion: Superior surface of the rib below. Key relations: -Muscle fibres run in the opposite direction to the external intercostals i.e. run obliquely posteroinferiorly. -Insert deep to the insertion of the external intercostals. Functions -Moves ribs inferiorly during expiration, thereby contracting the thoracic cavity.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
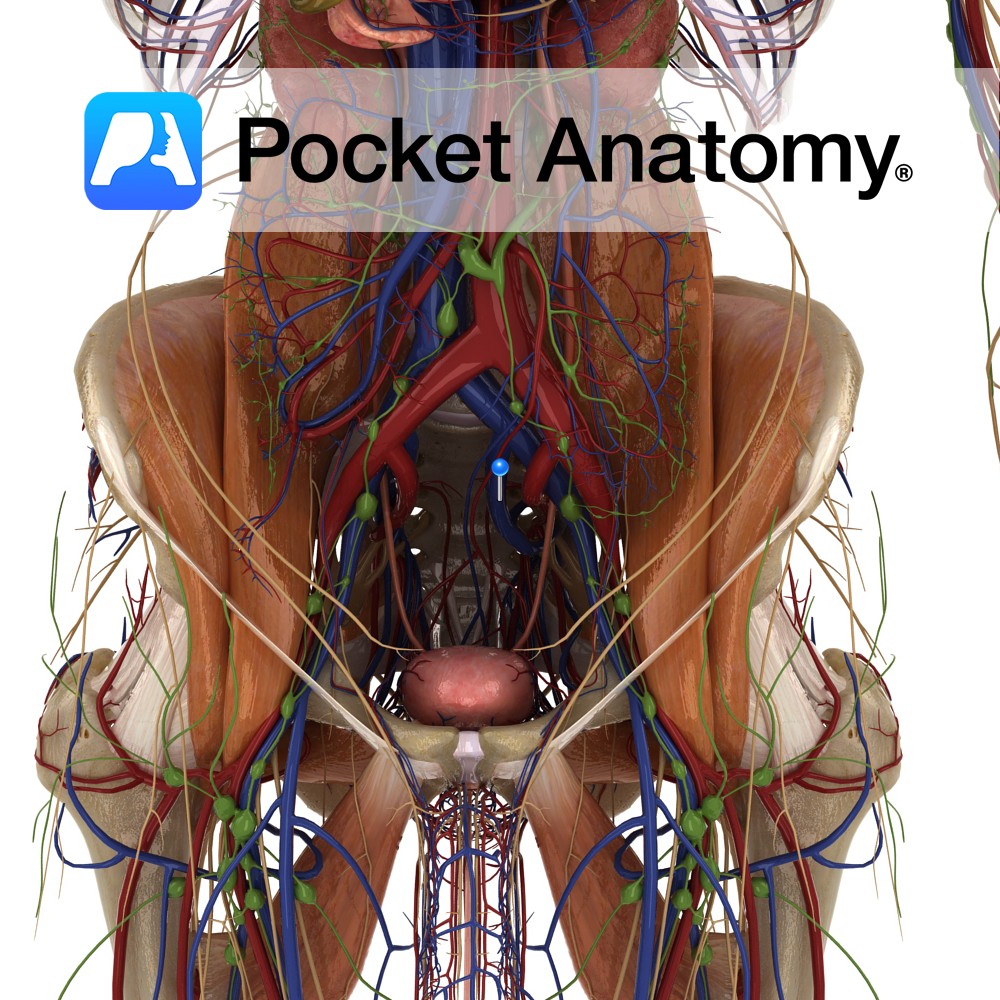
Anatomy Course Starts at the greater sciatic foramen where it ascends behind and medial to the internal iliac artery until it reaches the prim of the pelvis. At this stage it joins with the external iliac vein, where it becomes the common iliac vein. Drain Drains the peritoneal area as well as the part of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins