PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Paired organ upper abdomen, in paravertebral gutter behind peritoneum (both just below diaphragm, right one behind liver, a little smaller and lower than left, behind spleen; adrenal gland on top of each). Bean-shaped, convex lateral and concave medial surfaces. 11th, 12th ribs afford some protection behind. Hilum at medial surface; artery from aorta, vein
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
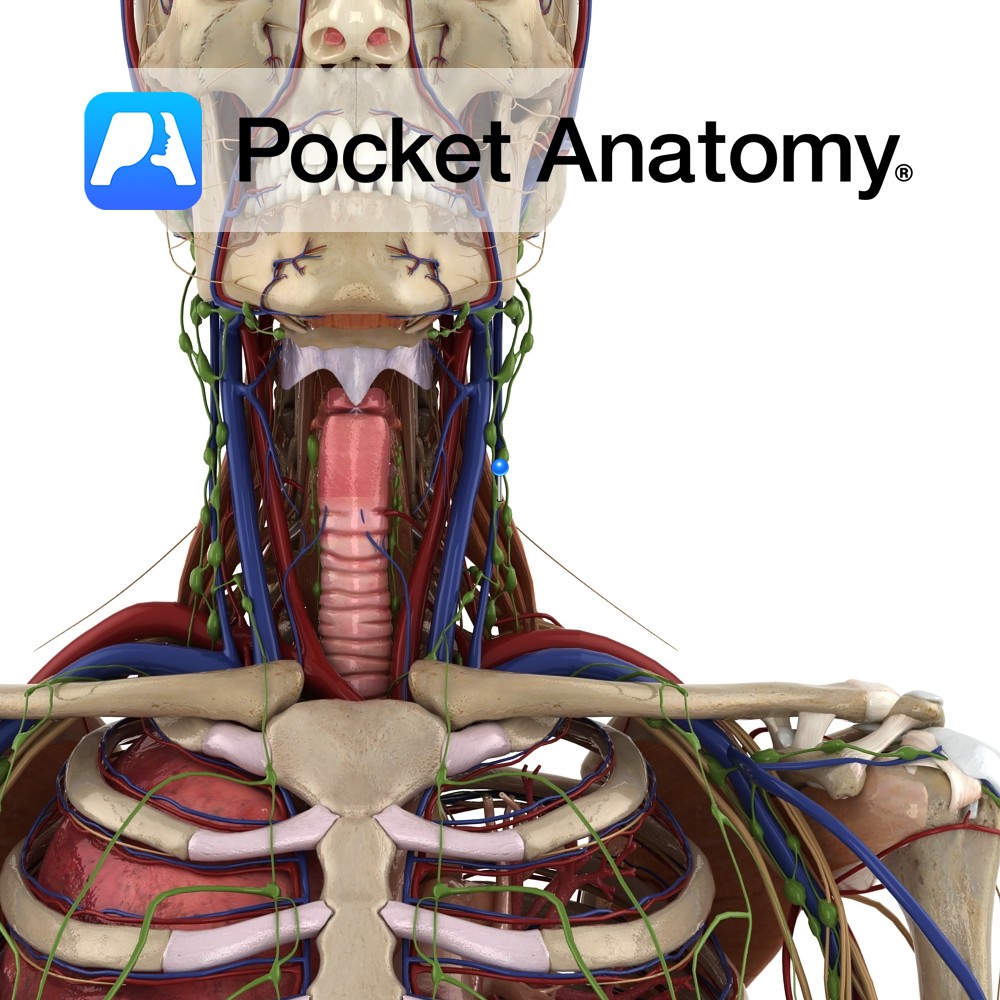
Anatomy One of 4 (Jugular, Subclavian, Bronchomediastinal, Lumbar) paired lymphatic trunks. Drains head and parts of the neck. On R, empties into venous system at junction R Subclavian and R Internal Jugular Veins. On L, empties into Thoracic Duct. Clinical There is an overlap of Lymphatic System (recycling Plasma) and Lymphoid System (identifying and responding
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
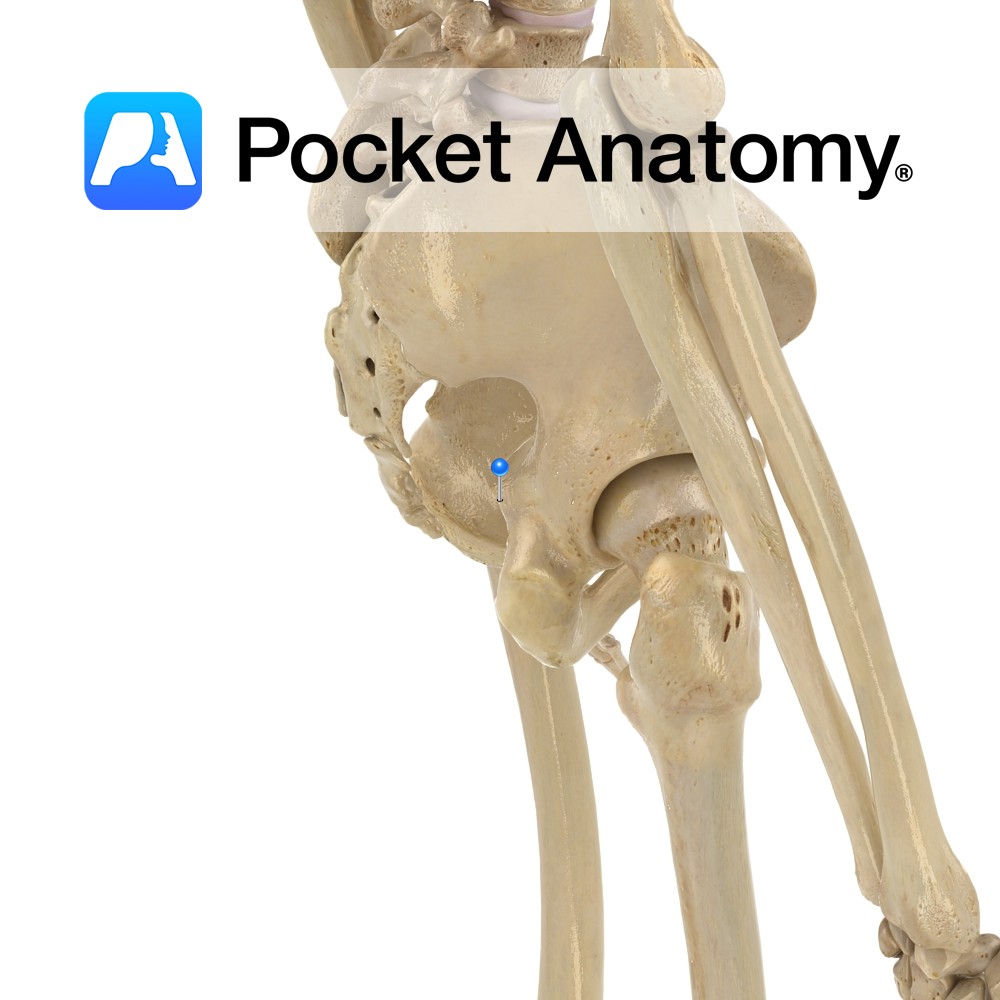
Anatomy Small notch between ischial spine and ischial tuberosity, converted to a foramen by sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
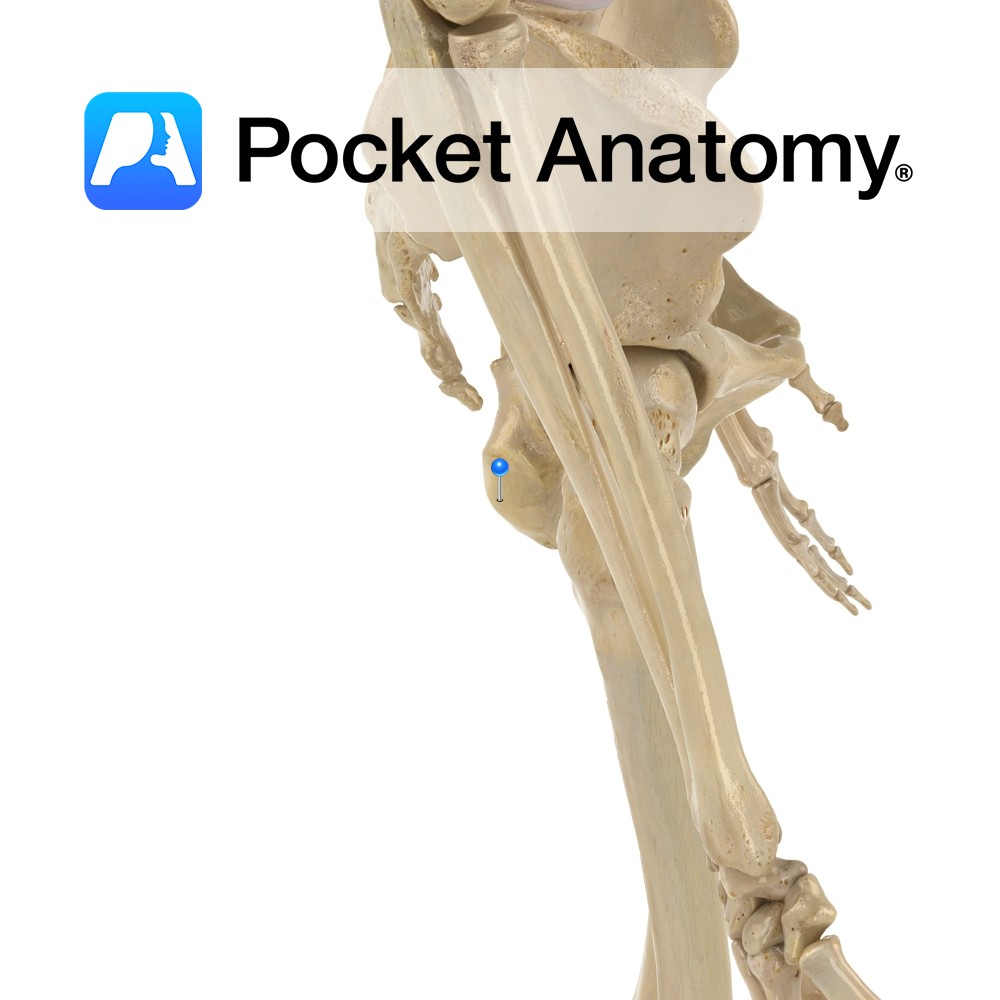
Anatomy Large swelling of posterior part of superior ramus of ischium, forming lowermost part of pelvis, giving attachment to biceps femoris, semimembranosus and semitendinosus (hamstrings) and adductor muscles and sacrotuberous ligaments. Clinical Sitting bone; one sits on and with one’s ischial tuberosity. Common site of pain in athletes, due to avulsion injuries cause by pull
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
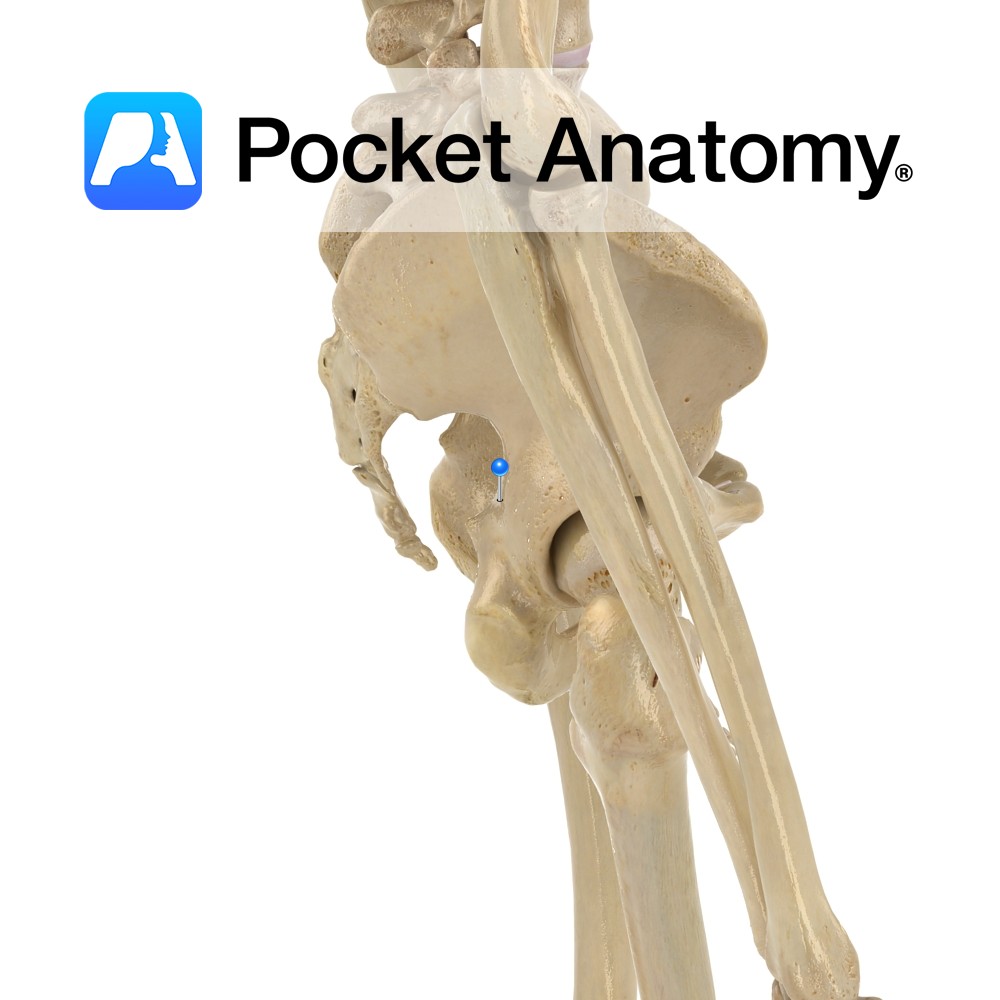
Anatomy Triangular posterior projection from back of body of ischium, between greater (above) and lesser (below) sciatic notches. Clinical Pudendal block (obstetrical procedure); injection of local anaesthetic near ischial spine, to relieve pain during 2nd stage of labour. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
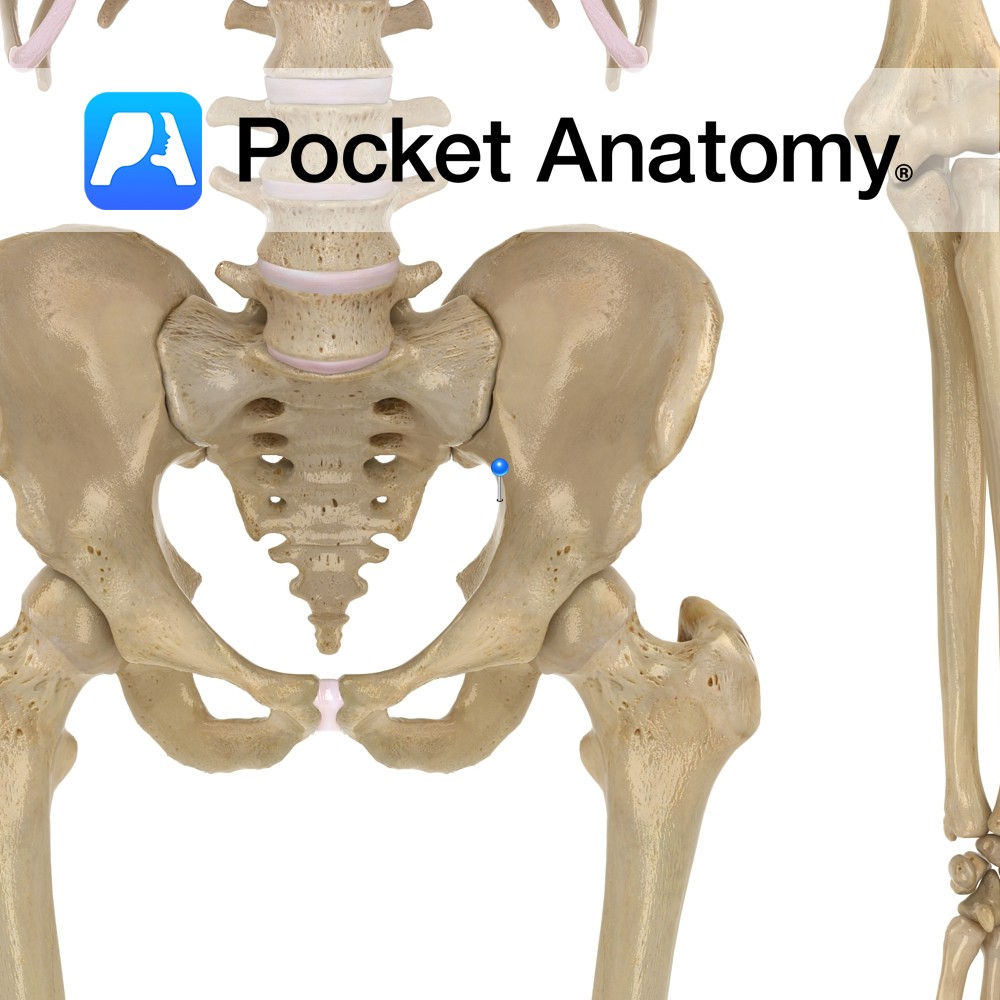
Anatomy Large notch, between posterior inferior iliac spine and ischial spine, which the sacrospinous ligament (triangular, ischial spine to lateral margins sacrum and coccyx) converts to a foramen. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
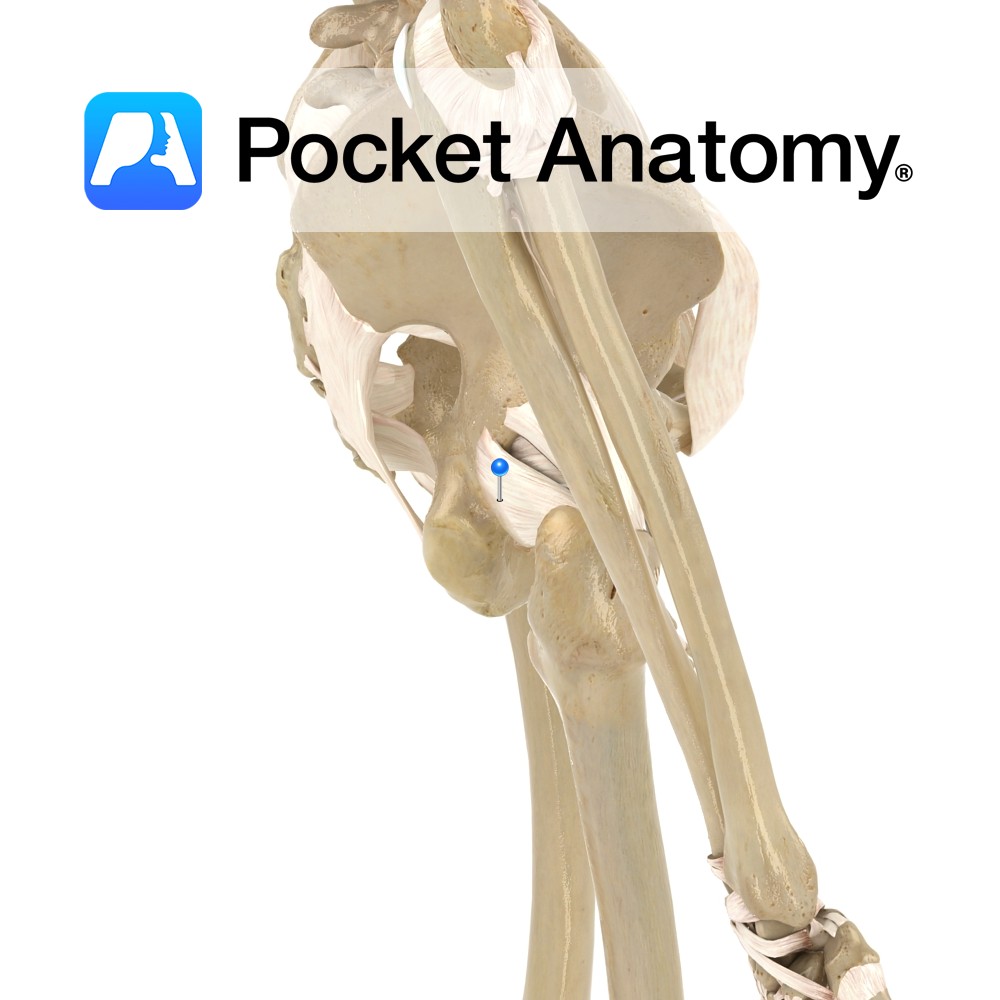
Anatomy Attaches medially to the ischium, just posterior inferior to the acetabulum and laterally to the greater trochanter deep to the iliofemoral ligament. Functions Provides static stability to the hip joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
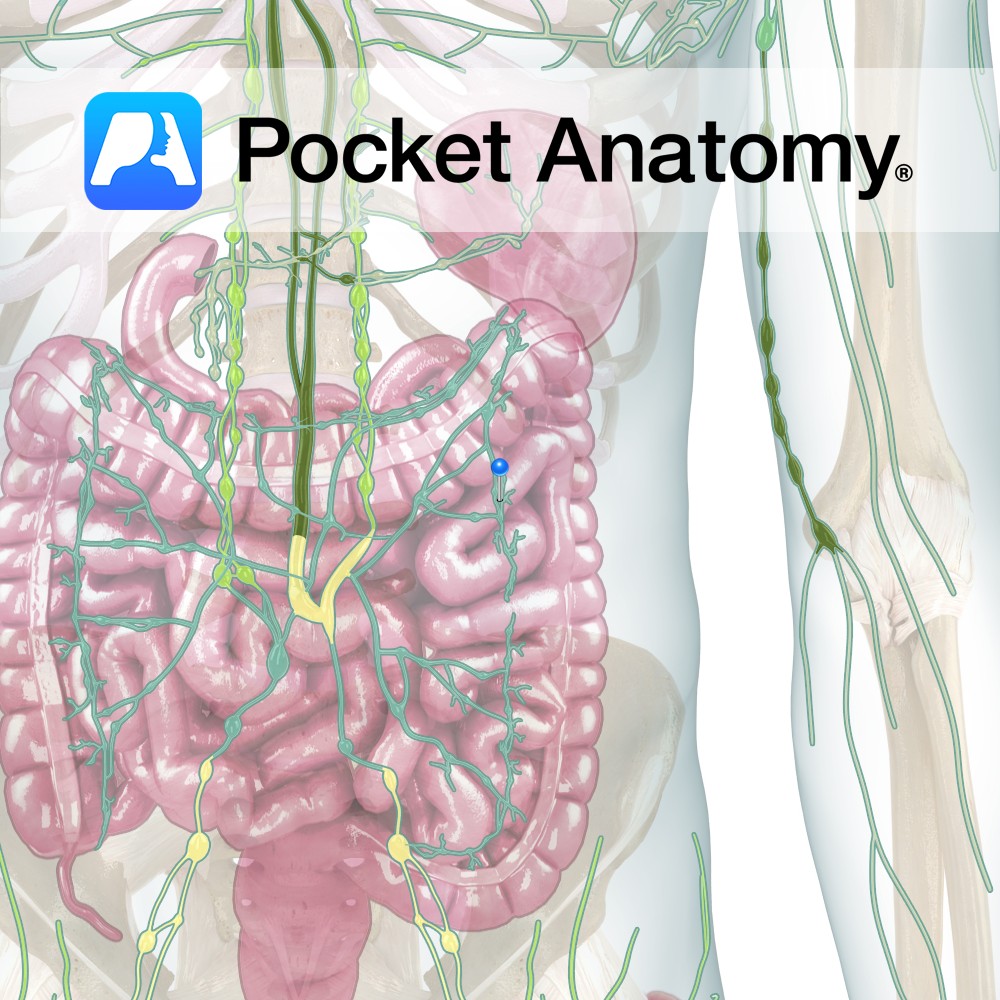
Anatomy The only unpaired lymphatic trunk. Formed by union of efferents draining gut, liver, pancreas, spleen. Empties into Thoracic Duct. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
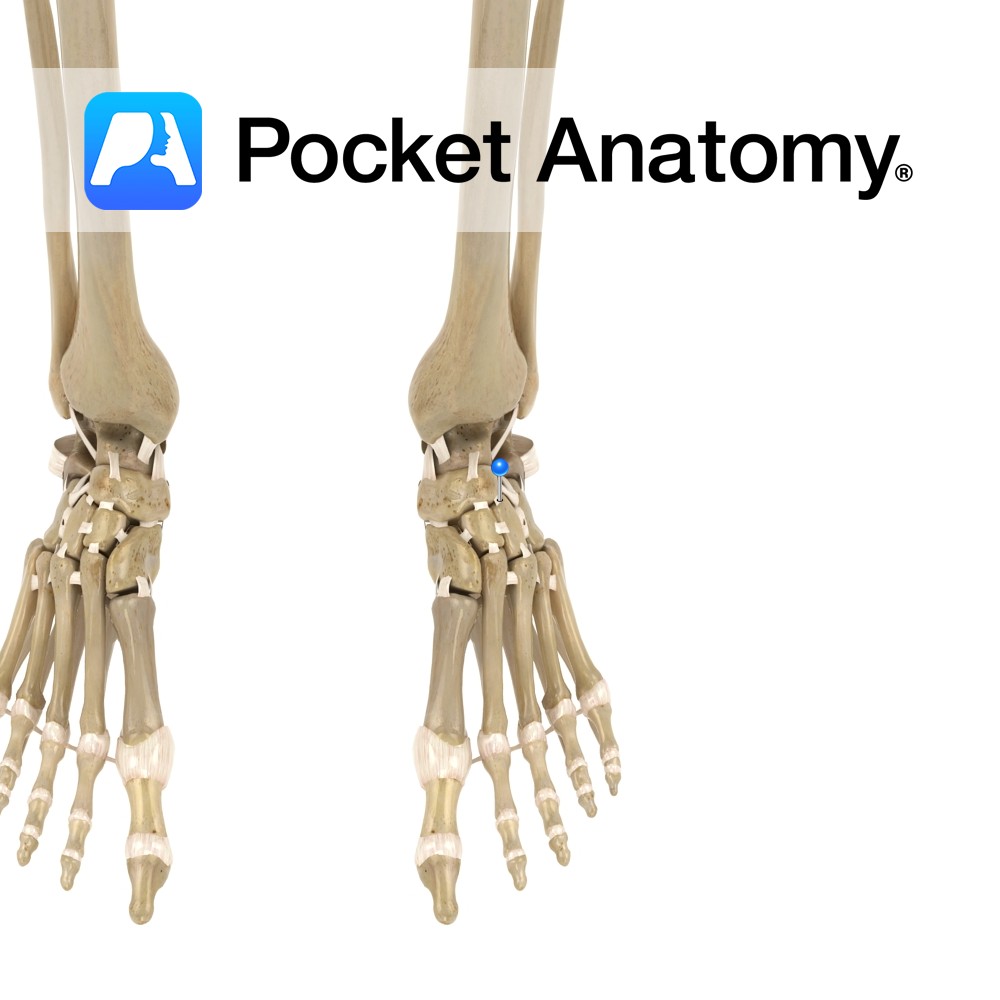
Motion The various synovial joints between the individual tarsal bones invert, evert, supinate and pronate the foot. They allow the foot to adapt and maintain contact with the ground on irregular surfaces. The intertarsal joints are made up of the following individual articulations: Talocalcaneal, Talocalcanealnavicular, Calcaneocuboid, Cuneonavicular, Cubonavicular (normally fibrous), Intercuneiform, and Cuneocuboid. The talocalcaneonavicular
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Motion These are uniaxial synovial hinge joints. They involve the articulations between the proximal and middle phalanges, and the articulations between the middle and distal phalanges. The movements possible at these joints are flexion and extension, greater at the proximal joints than at the distal. Stability Each joint has its own fibrous capsule. Stabilizing ligaments
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins