PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
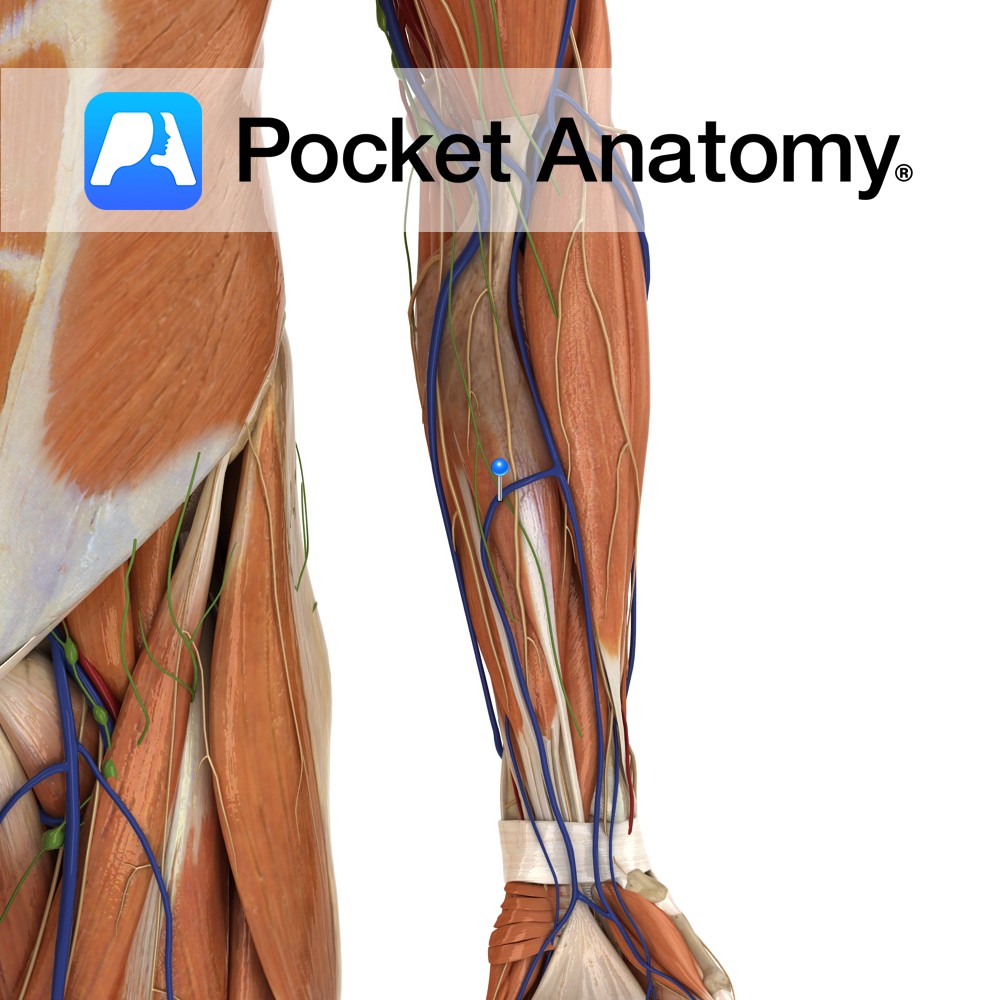
Anatomy Course A superficial vein that drains the palmar network of the hand. It ascends on the ulnar side of the forearm to drain into the median cubital vein. Drain Drains the palmar surface of the hand. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
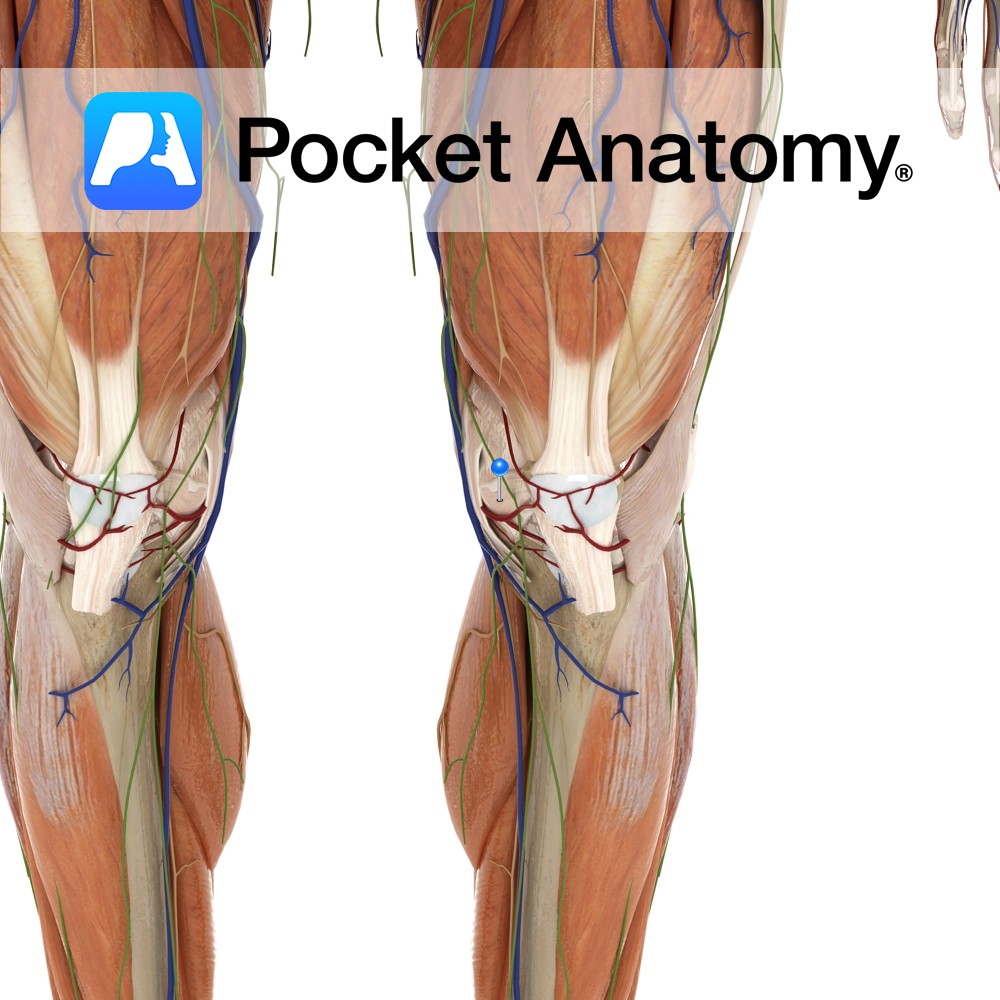
Anatomy Attaches from the inferior medial margins of the patella to the inferior margin of the medial tibial condyle. It also blends with the patella ligament. Functions Provides static stability to the patella. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
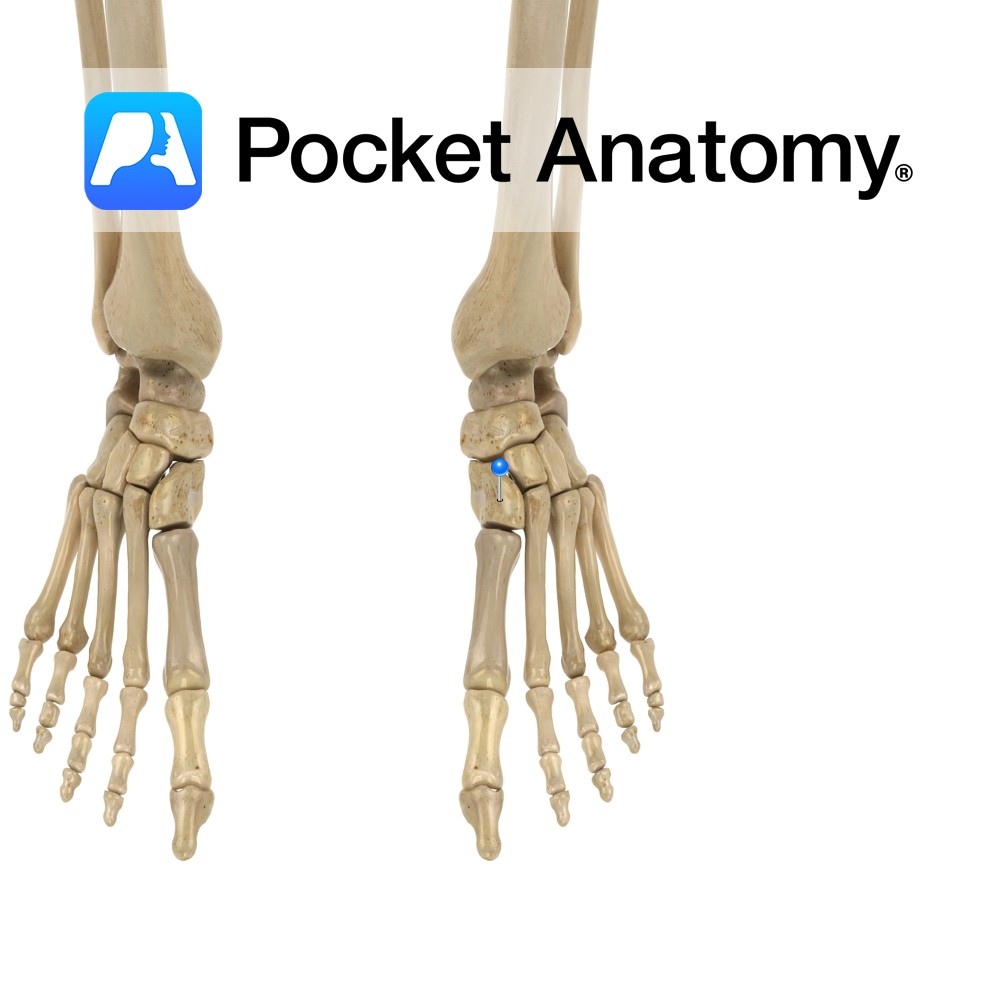
Anatomy Tarsal bone, wedge-shaped, largest of the cuneiforms, articulates forward with 1st (big toe) and 2nd metatarsals, laterally/out with middle/intermediate cuneiform, proximally with navicular. Vignette Hindfoot; talus, calcaneus. Midfoot; cuboid, navicular, cuneiforms (medial, intermediate, lateral). Forefoot; metatarsals, phalanges. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
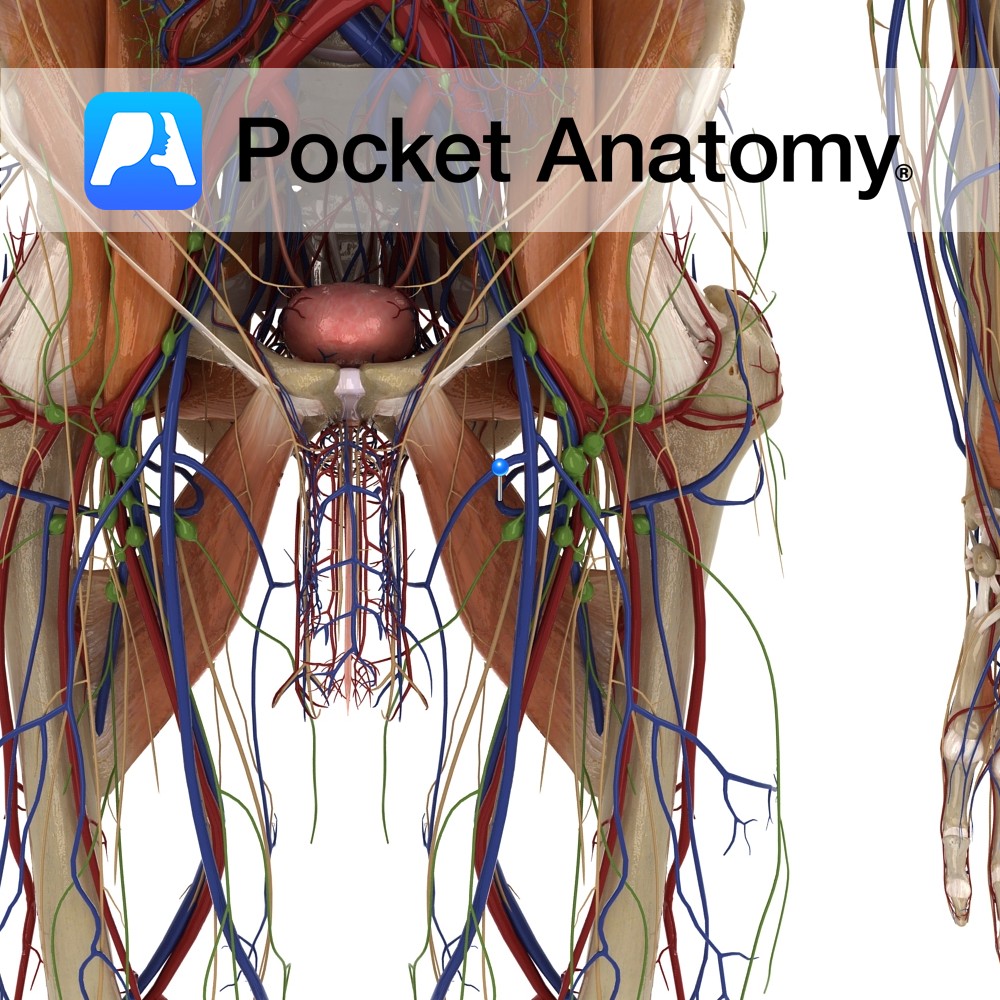
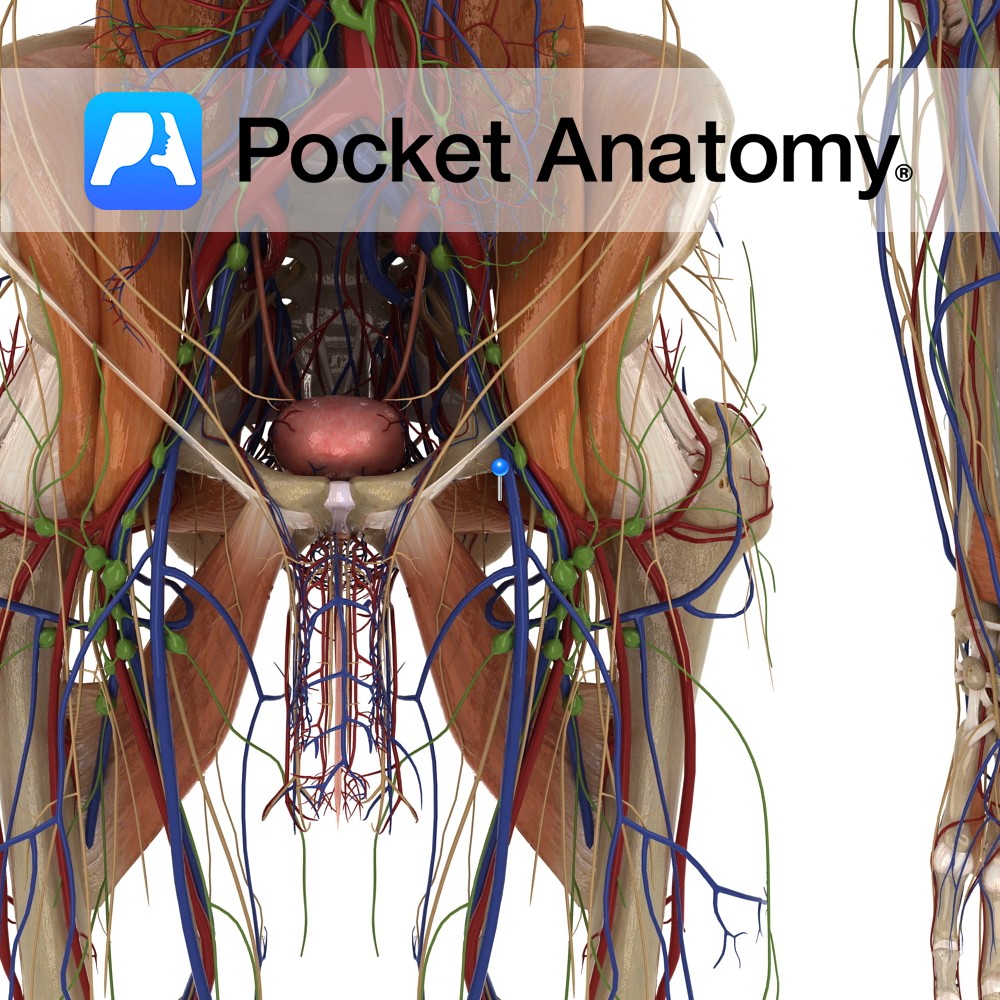
Anatomy Course Begins at the neck of the femur and medially travels above the margin of the adductor magnus. It passes between the obturator externus and adductor brevis muscles, and then between the iliopsoas and pectineus muscle. It drains into the deep femoral vein. Drain Drains the head and neck of the femur. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Originates from the deep femoral artery. It first passes between the iliopsoas and pectineus muscles, and then passes between the obturator externus and adductor brevis muscles. Finally, it passes above the margin of the adductor magnus to travel medially around the neck of the femur. It then divides into two major branches deep
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy A strong band, four centimetres wide by twelve centimetres long. It attaches from the medial epicondyle, below the abductor tubercle, to the subcutaneous surface of the tibia, a hand’s breadth below the joint line. It has deep and superficial fibres with the deep fibres binding with the joint capsule. Functions Provides static stability to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
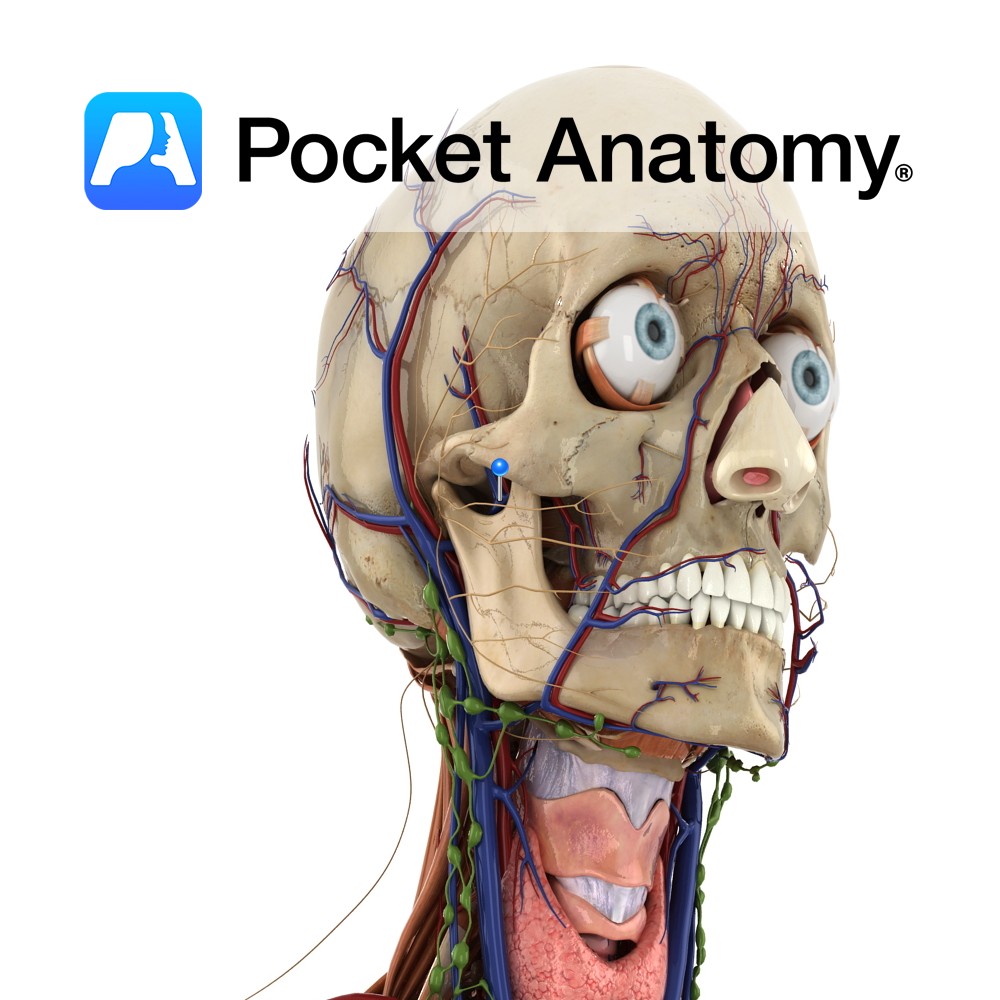
Anatomy Course The final vein of the pterygoid plexus. It is a short vein and it flows into the retromandibular vein. Eventually it flows into the external carotid vein. Drain Drains the deep structures of the face. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the external carotid artery. It begins just behind the neck of the mandible, and passes forward just beneath the bone and then through the infratemporal fossa. The artery then enters the pterygopalatine fossa by passing through the pterygomaxillary fissure. Once in the pterygopalatine fossa it splits into several terminal branches.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
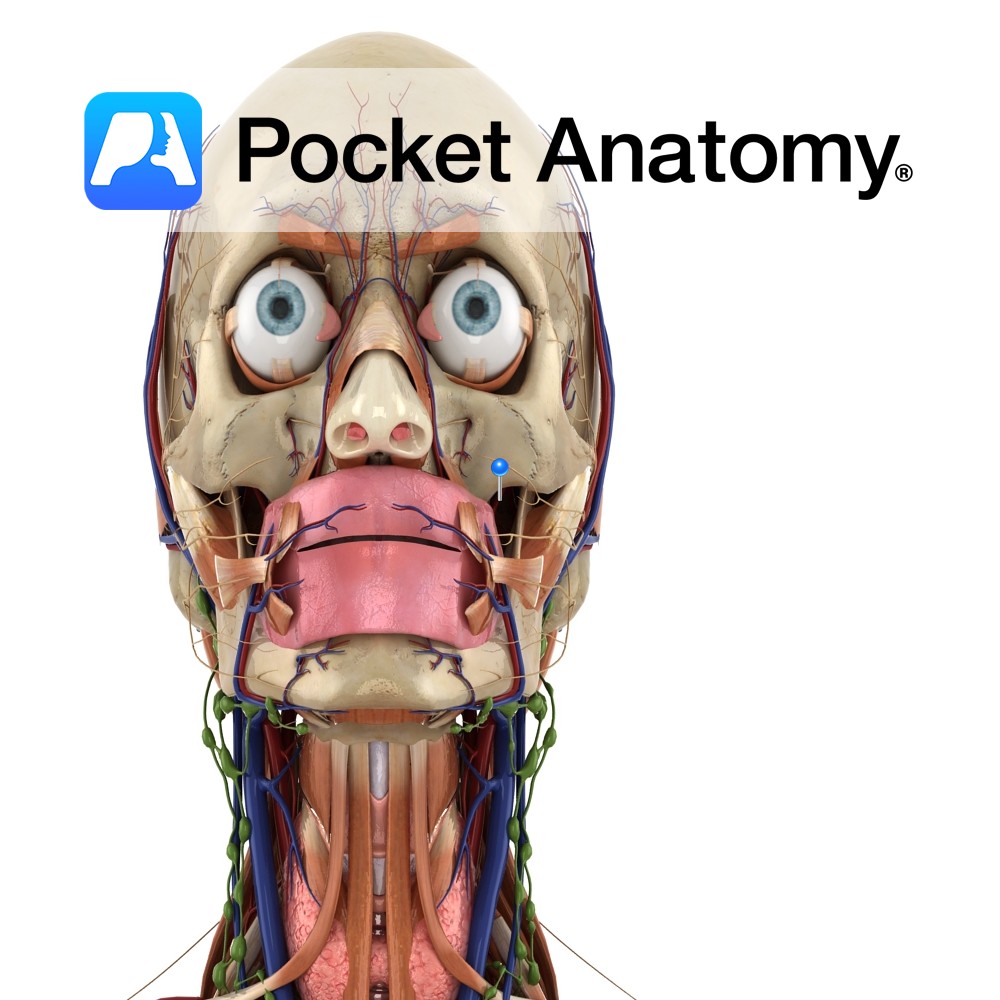
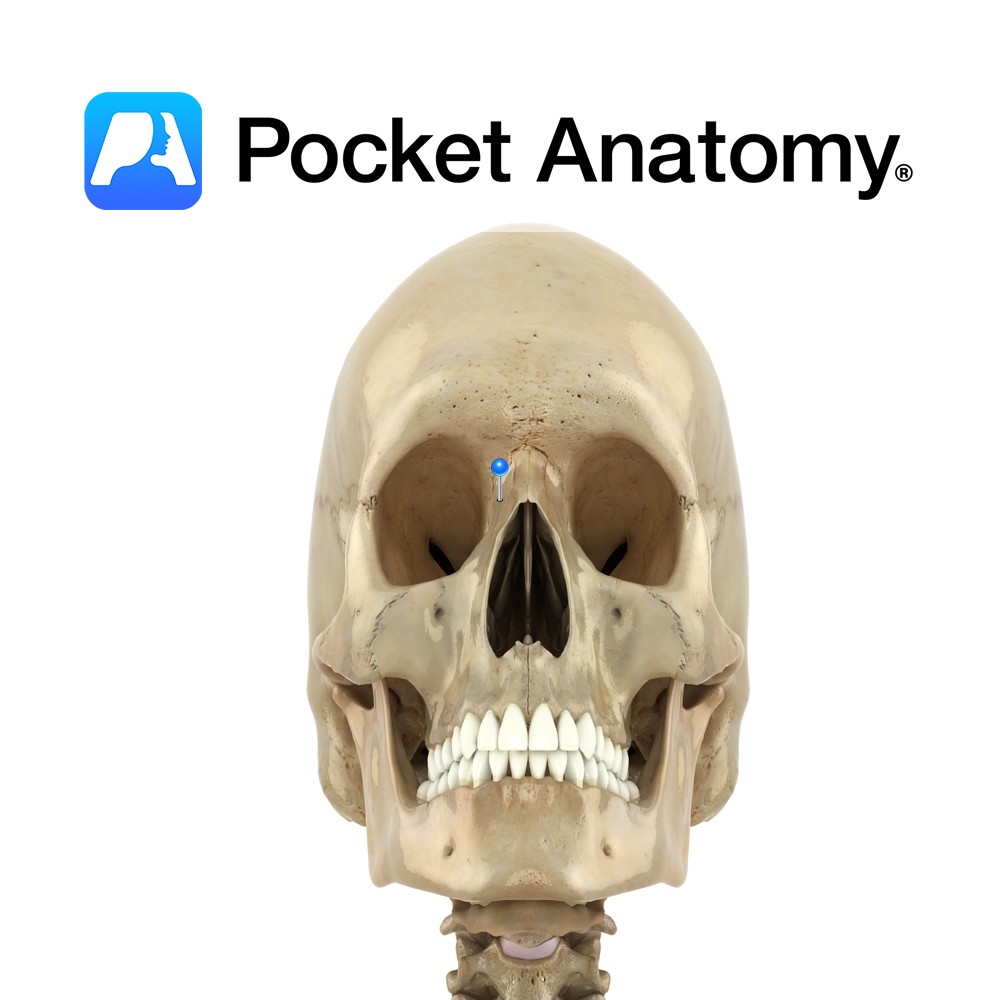
Anatomy Frontal bulge that articulates with frontal process zygoma (cheekbone). Vignette Can felt as bony prominences lateral to edges of mouth, down from the eyes. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Paired. One of the four processes of maxilla bone. Also called nasal process. Strong plate pointing up, in and back from body of maxilla; forms part of lateral wall of nasal cavity. Articulates above with frontal bone, and in front with nasal bone. Upper inner surface articulates with ethmoid bone. Interested in taking our
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

-collateral-ligament.jpg)