PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
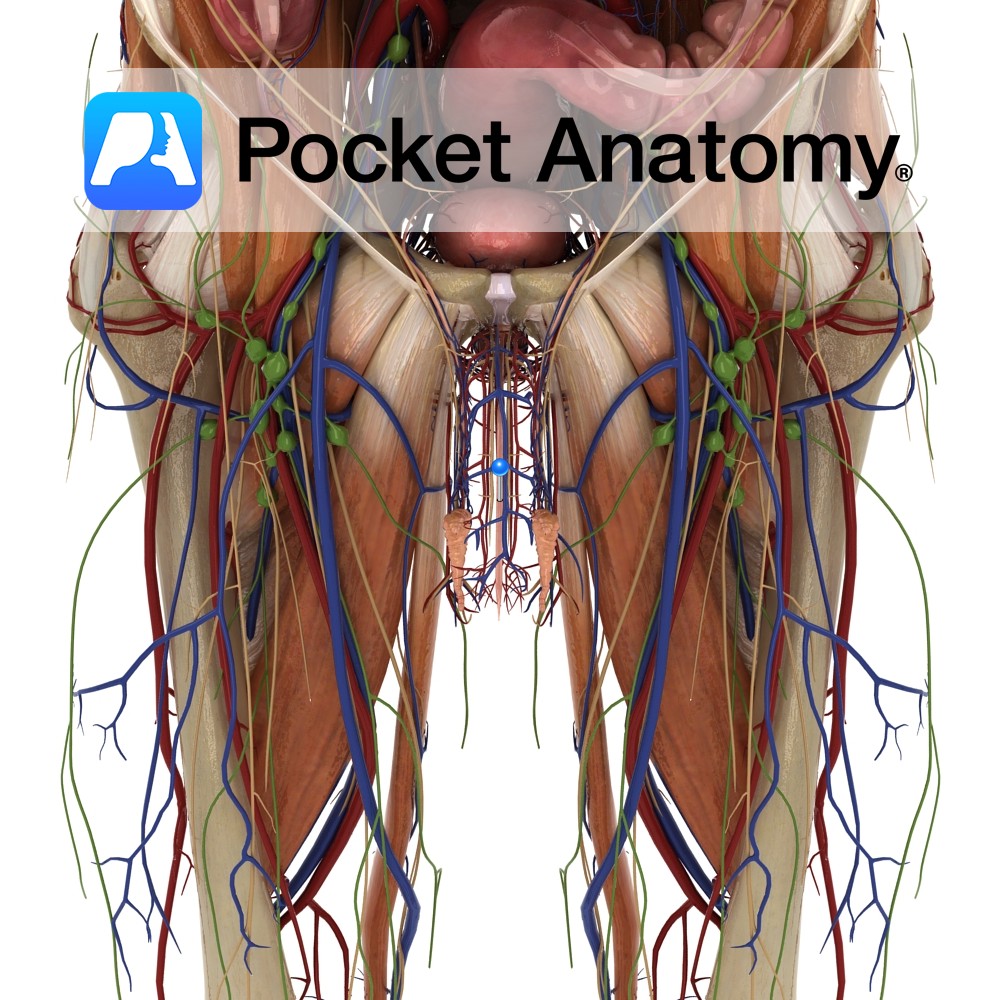
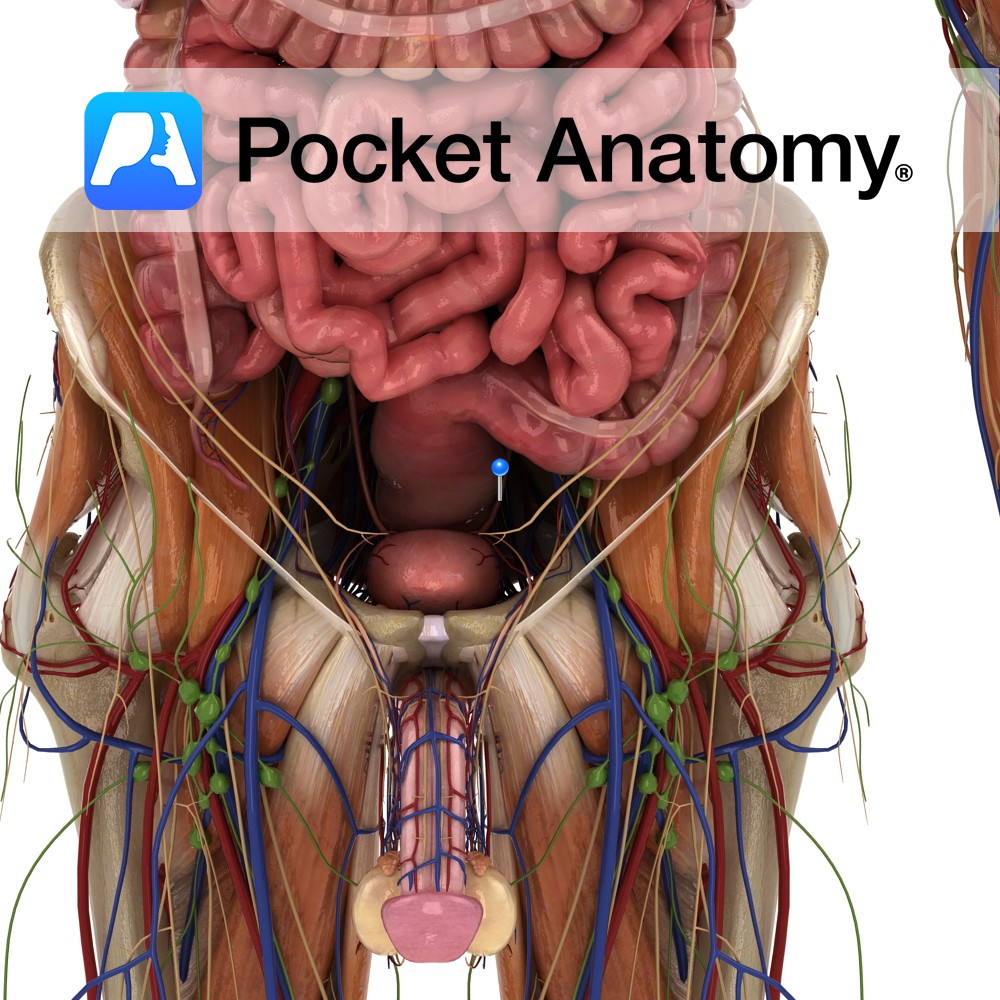
Anatomy 20cm muscular tube/conduit (female 4cm), extending down from the internal urethral orifice (apex of trigone in floor/neck of bladder, behind pubic symphysis) to external urethral orifice (meatus, at tip of glans) at end of penis. There are two functional parts: 1. posterior/sphincter-active (made up of 3 sections – pre-prostatic/intramural in bladder, prostatic, membranous in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
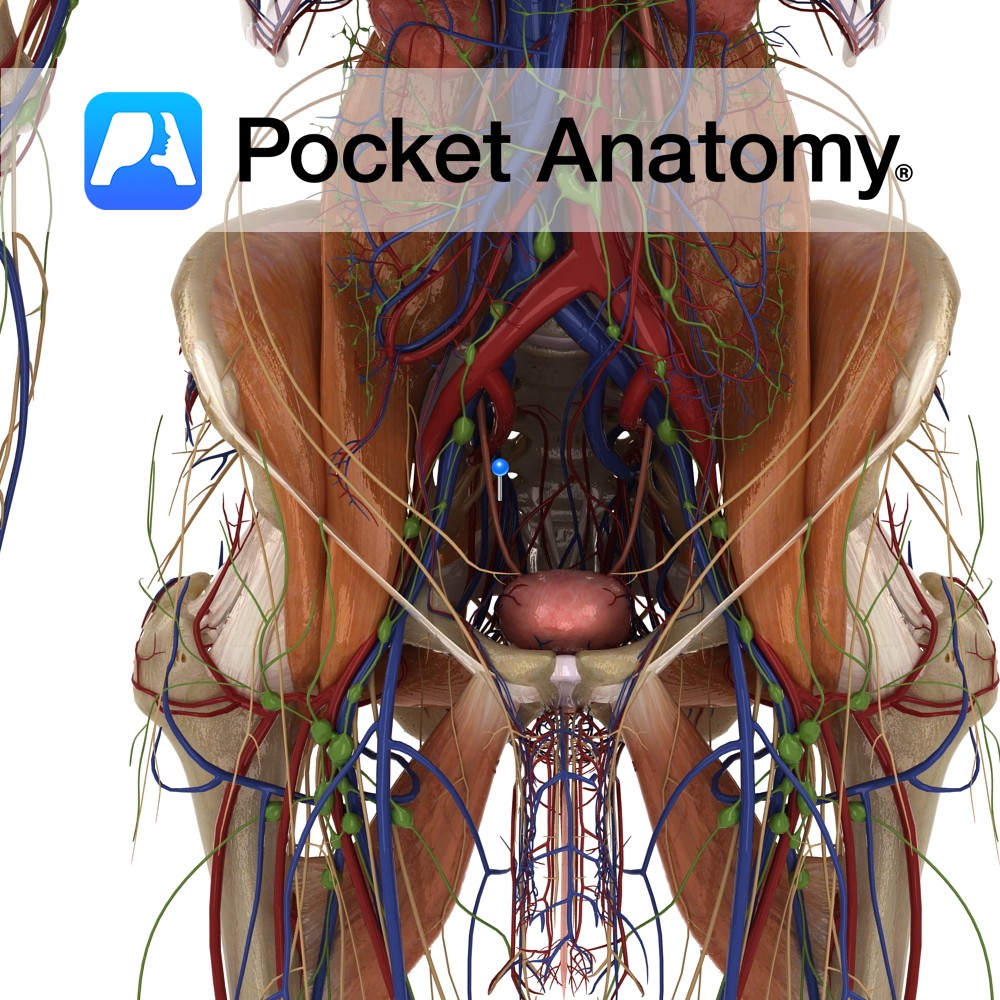
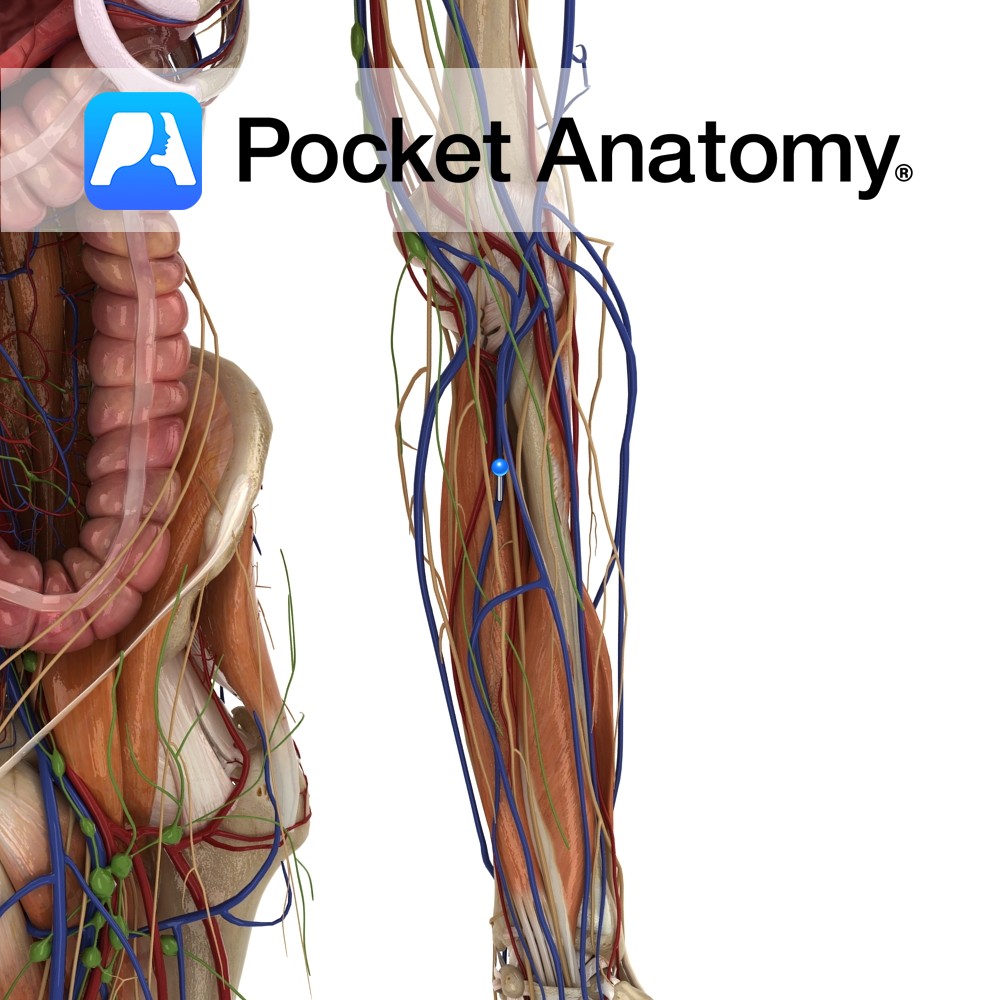
Anatomy Paired autonomically innervated muscular tubes (25cms long, 0.5cm diameter) connecting kidney (medial aspect, at and continuous with renal pelvis, at level 2nd Lumbar vertebra) to bladder (upper aspect posterior/base, at level of pelvic tubercle), through which urine is propelled. Ureter courses down and medially, behind the peritoneum, in front of psoas, crossing pelvic brim
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
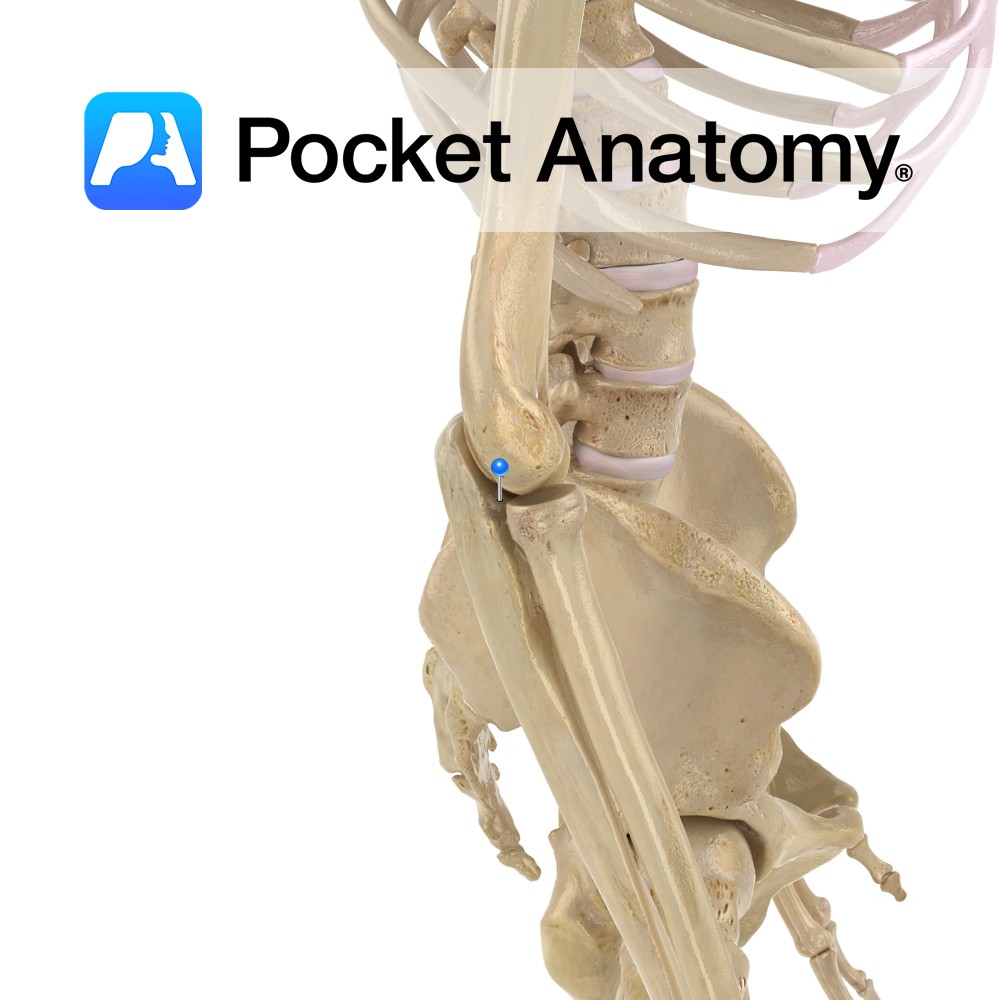
Anatomy Course A branch of the anterior trunk of the anterior iliac artery. It travels anteriorly along the margin of the pelvic inlet and travels superiorly to the anterior abdominal wall. It then travels to the umbilicus. Supply In adults, its relevance is via its branches; the superior vesical arteries, which supply some of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
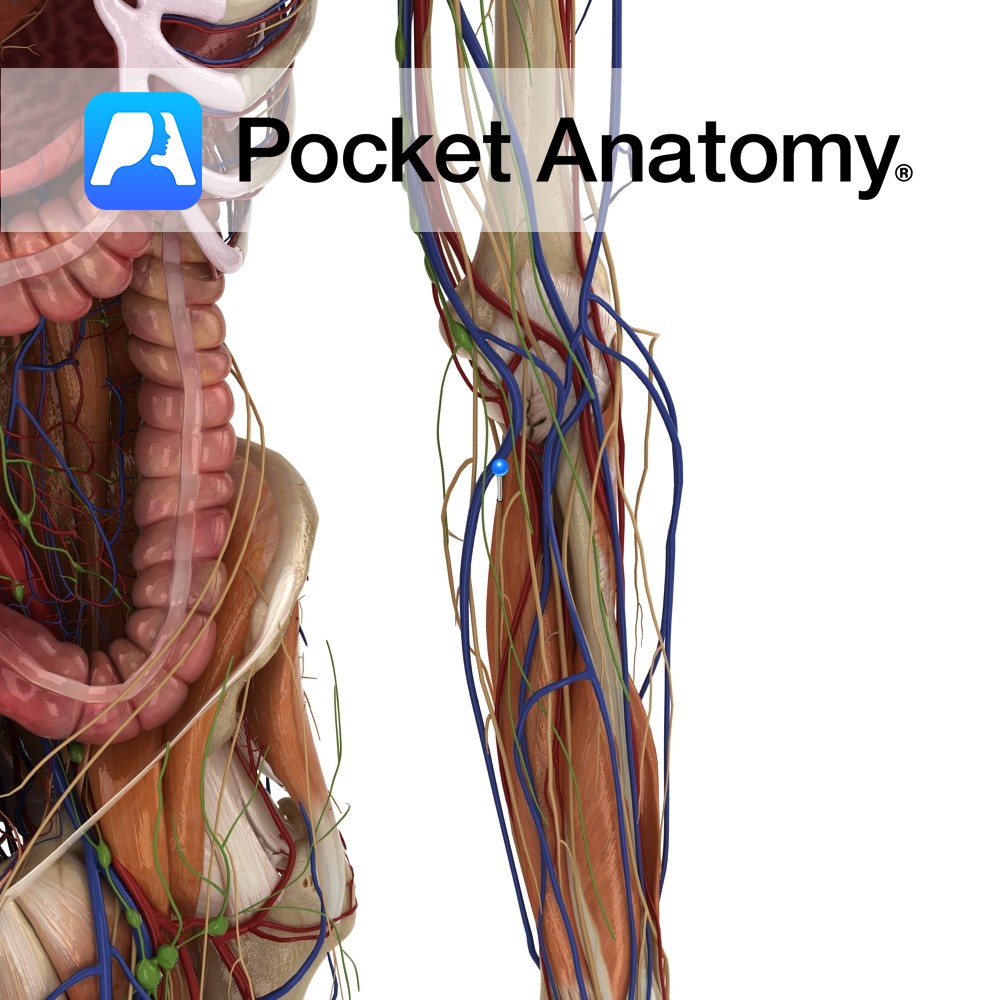
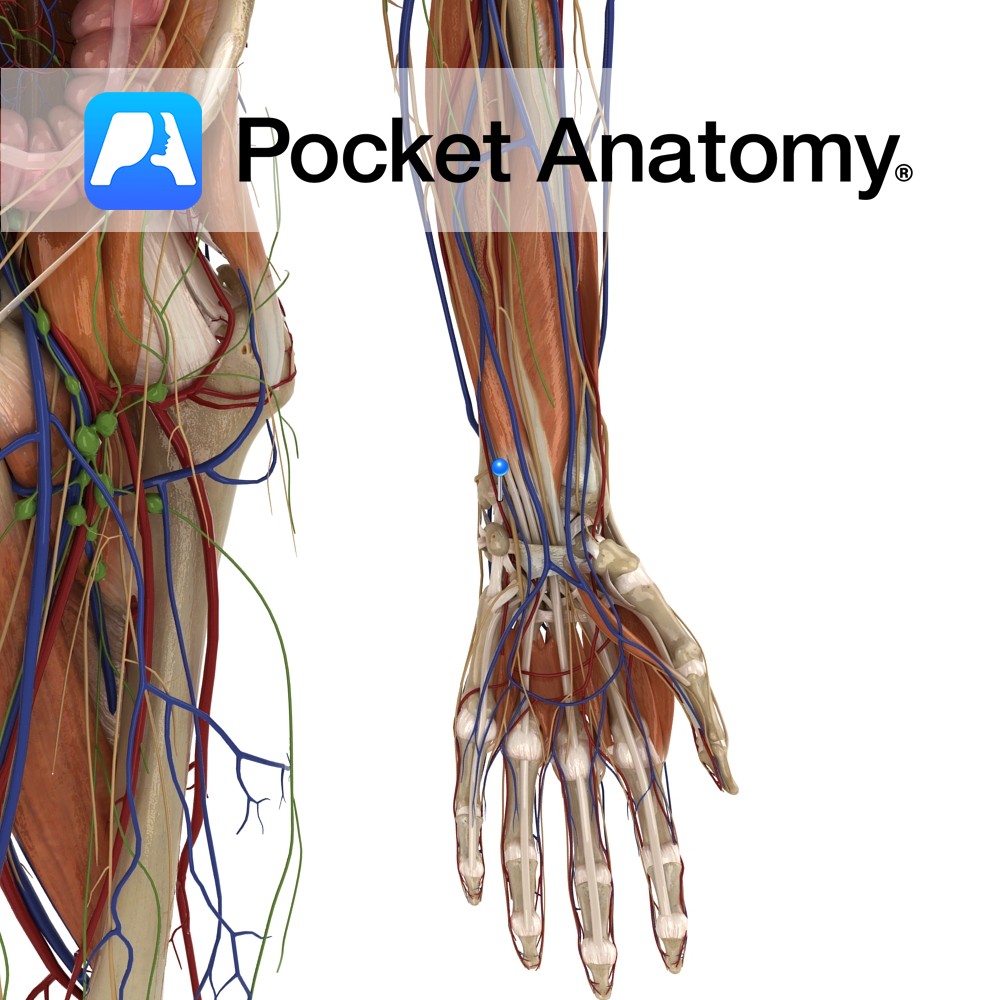
Anatomy Course Begins from the superficial palmar venous arch. It leaves the hand just lateral to the pisiform bone passing over the flexor retinaculum and travels up the arm on the medial side. It runs deep in the arm, travelling along the flexor digitorum profundus muscle for the most of its course. It joins with
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A terminal branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. It enters the arm with the median nerve and then travels on the medial side, until about halfway down the arm, when it pierces the intermuscular septum. Once it pierces the septum it is in the posterior compartment of the arm, and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
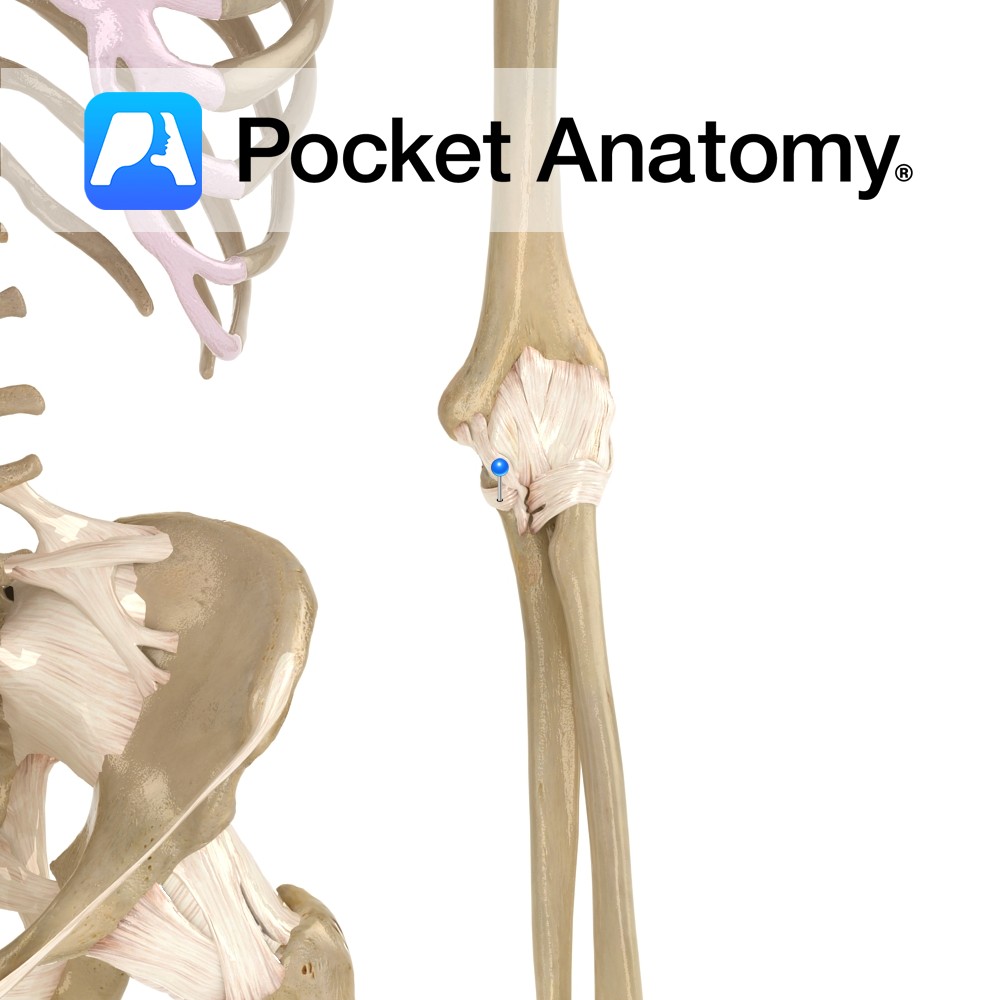
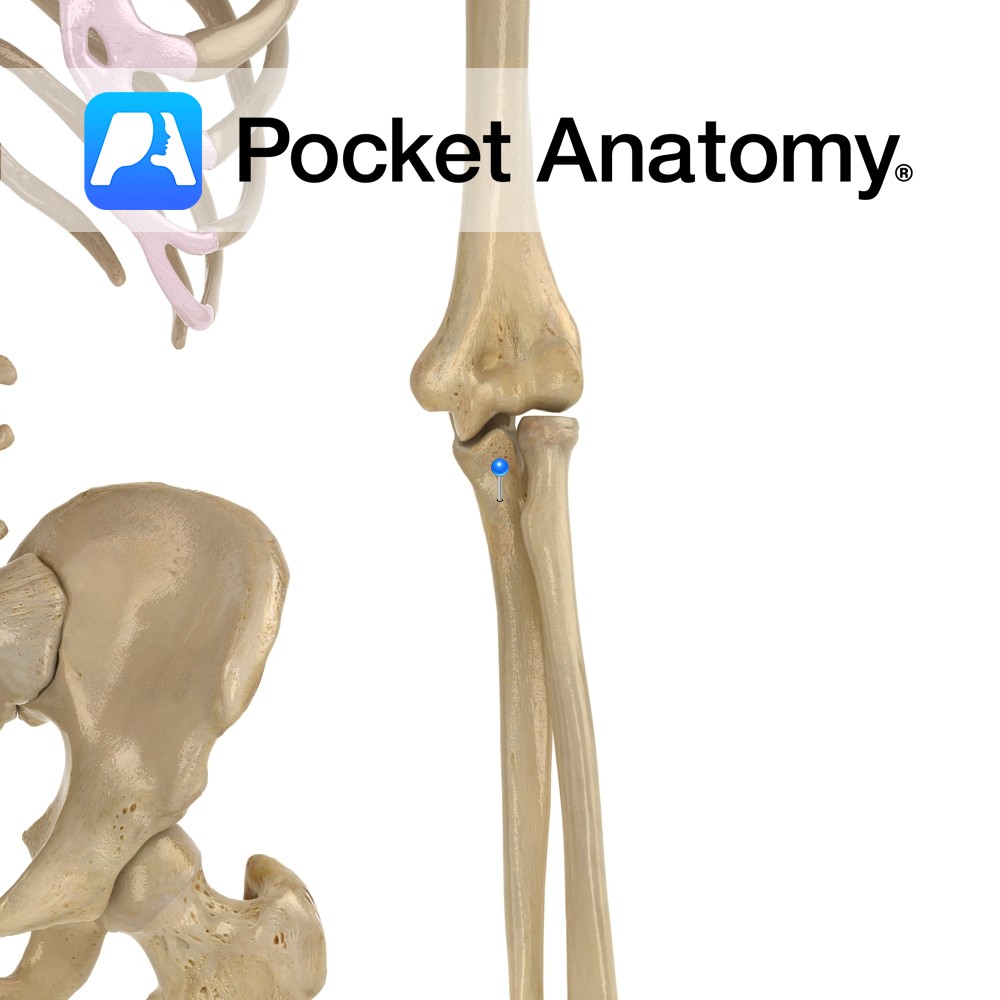
Anatomy Triangular in shape. Its apex being the medial epicondyle of the humerus, passing to the coronoid process of the ulna, and the medial side of the olecranon. The base attaches from the medial surface of the olecranon to the sublime tubercle. Functions Provides medial static stability to the elbow joint. Clinical Ulnar collateral ligament
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
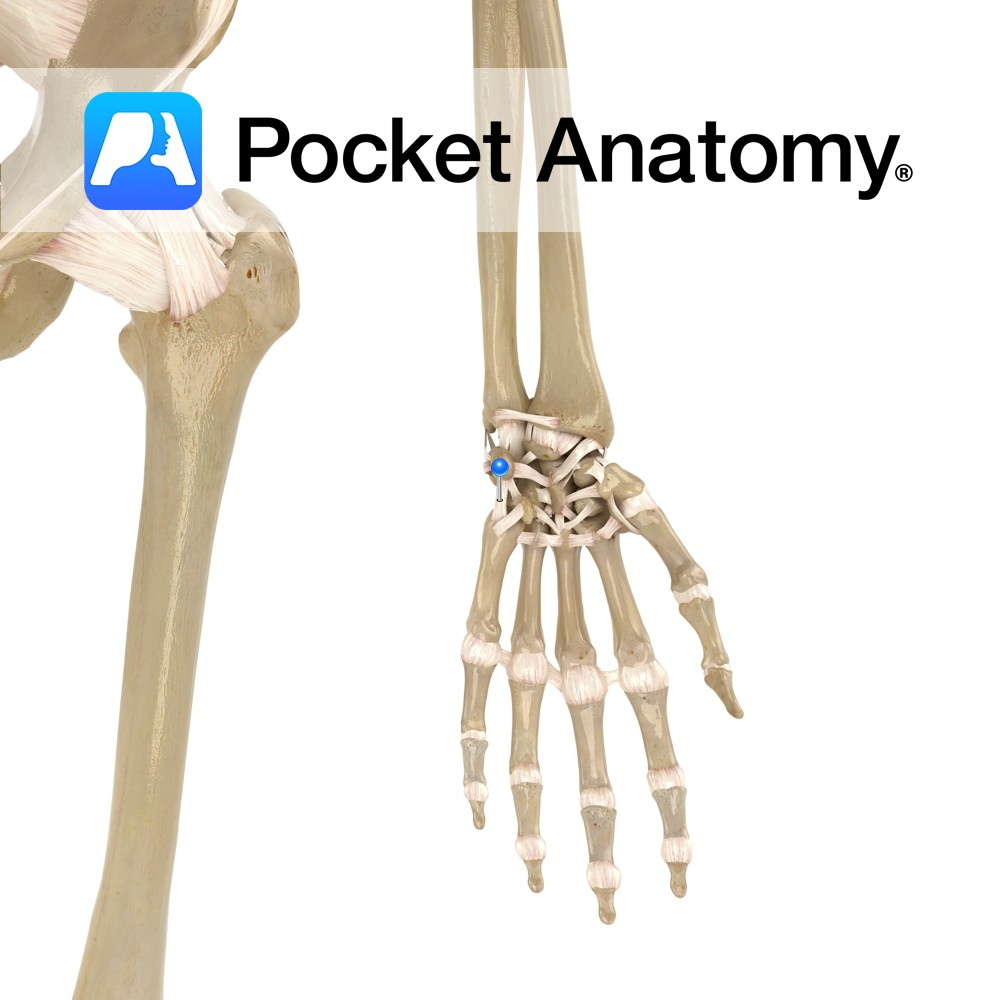
Anatomy Attaches from the palmar surface of the ulna, passing to the medial surfaces of the triquetrum with slips to hamate bone. Functions Provides static stability to the wrist and carpal joints. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the brachial artery. It travels along the medial side of the arm. It runs deep in the arm, running along the flexor digitorum profundus muscle for the most of its course. It becomes most medial about halfway down the ulna. It enters the hand just lateral to the pisiform bone,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Area on medial side of ulna. Attachments: part of brachoradialis, oblique cord (ligament, other end attaches just below radial tuberosity). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Surface which articulates with trochlea of humerus (as radial head does with capitulum, just lateral to trochlea). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins