PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
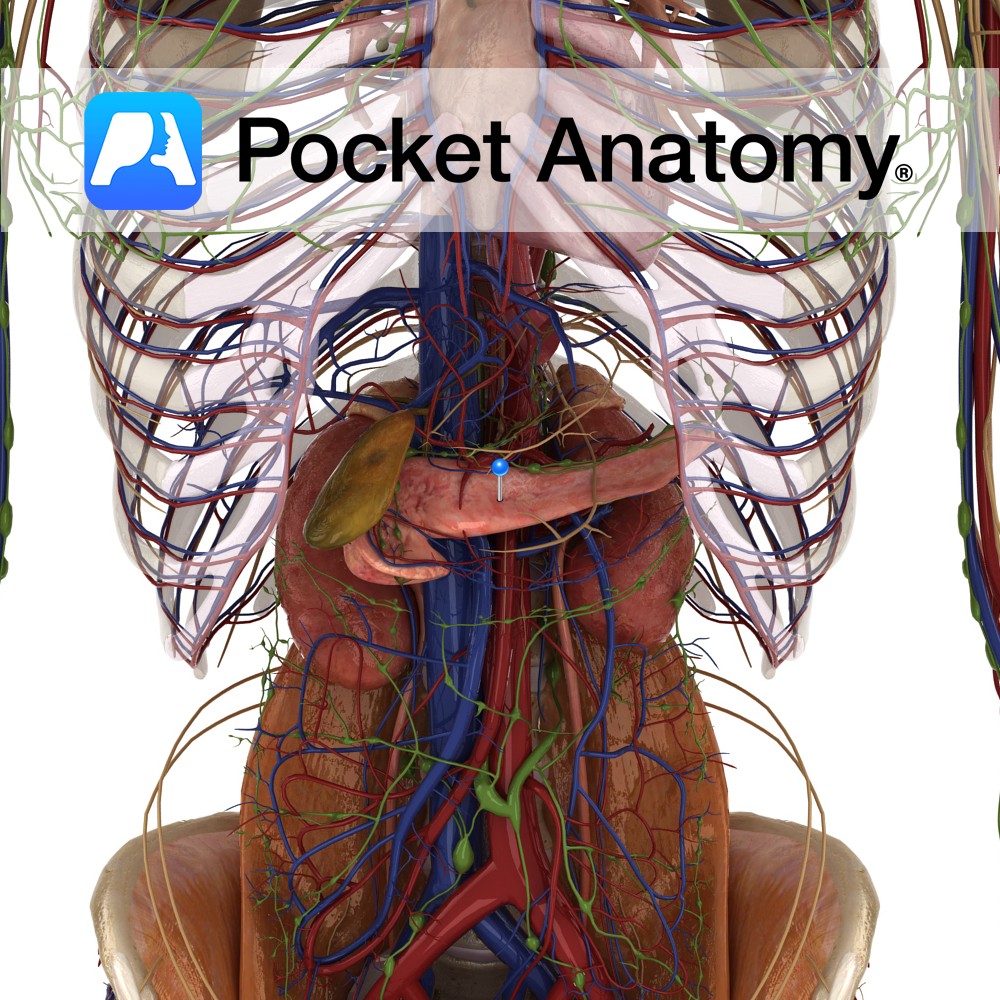
Anatomy 6″ long pennant-shaped gland/organ, transverse on back wall left hypochondriac and epigastric regions of abdomen, retroperitoneal except for tail. Head nestles in curve of duodenum, tail sits front of spleen, neck (slight narrowing) and body behind stomach. Two types of parenchymal (characteristic) tissue; clusters (about a million) of Islets of Langerhans associated with rich
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
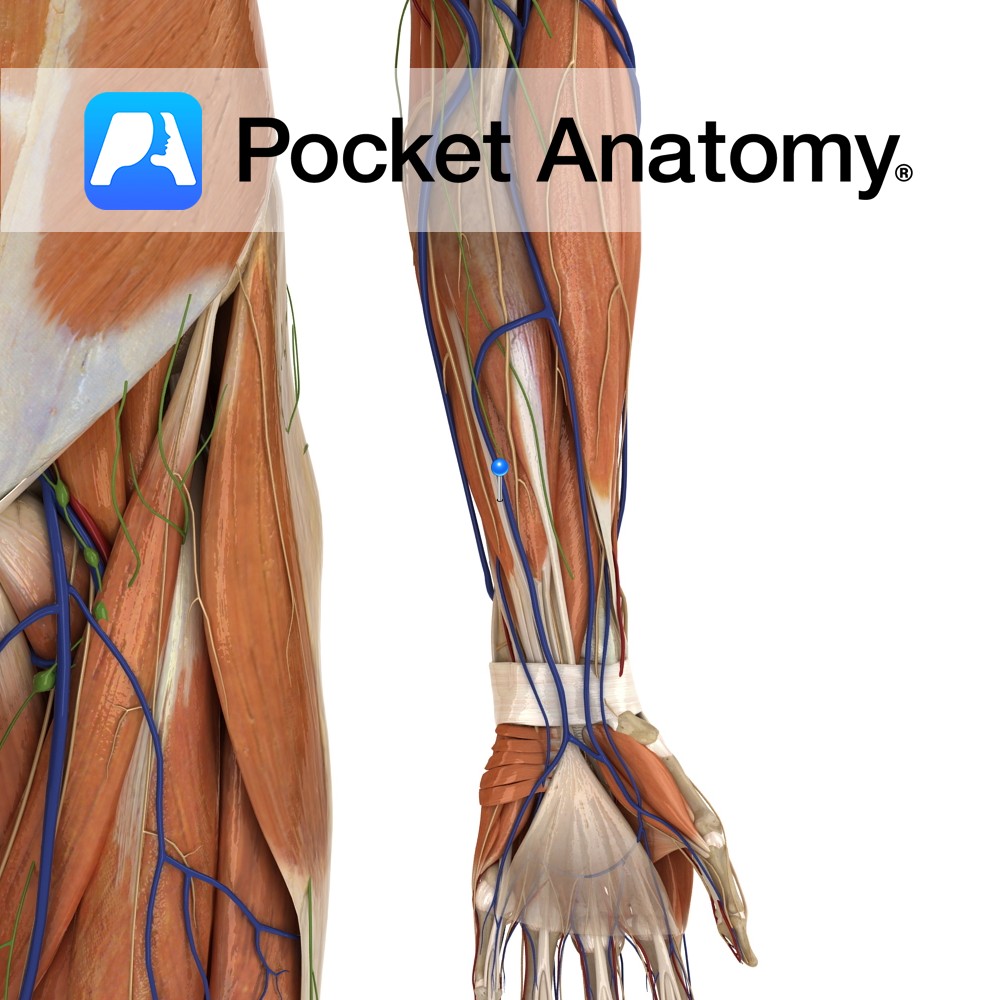
Anatomy Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus via the common flexor tendon. Insertion: Palmar aponeurosis of hand. Key Relations: One of the four muscles in the superficial anterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Tenses the palmar aponeurosis, thereby anchoring the skin of the hand and resisting the shear forces in gripping. Its absence however has been
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Flexor retinaculum and palmar aponeurosis. Insertion: Dermis of the ulnar border of the hand. Functions Wrinkles skin of ulnar palm to support grip. Supply Nerve Supply: Superficial branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1). Blood Supply: Superficial palmar arch. Clinical Bunching of the skin over ulnar area of the palm may be an early
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
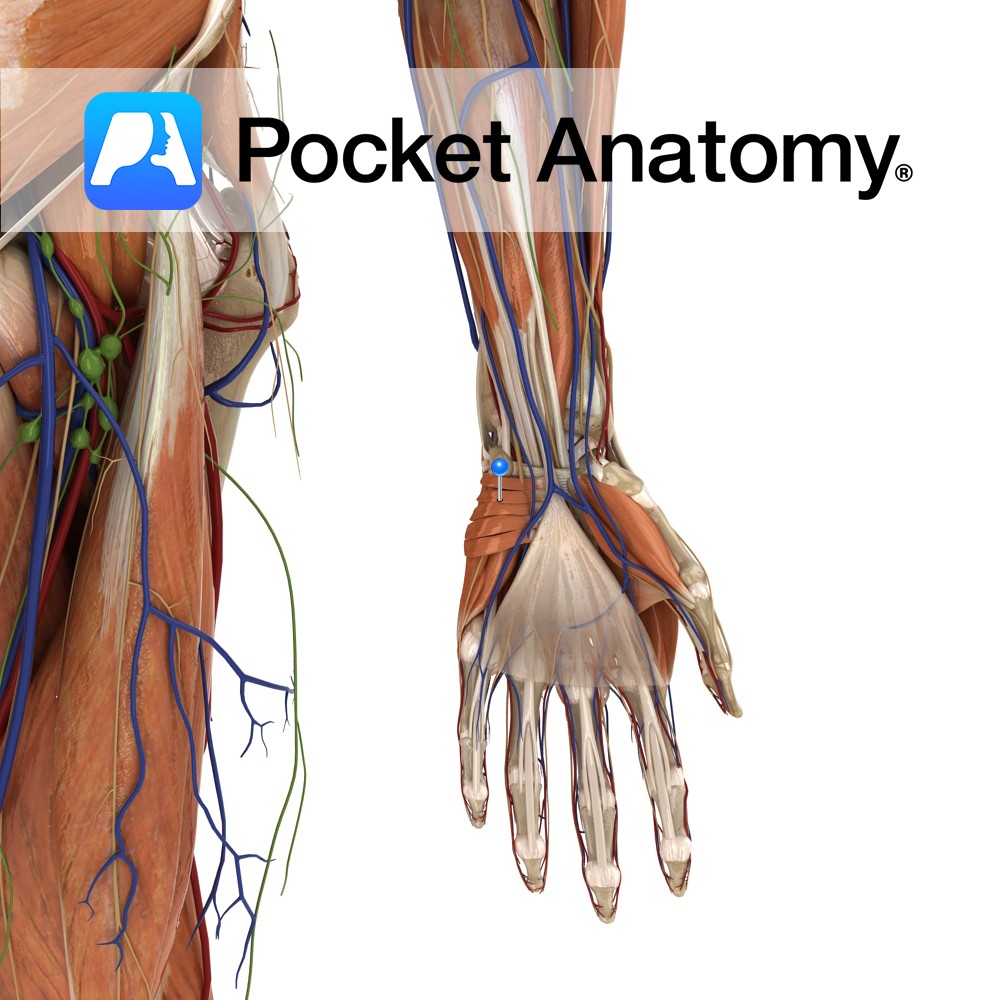
Anatomy Attaches from the ulnar styloid process to the lunate bone. Functions Provides static stability to the wrist joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Attaches from the styloid process of the radius to the lunate bone. Functions Provides static stability to the wrist joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
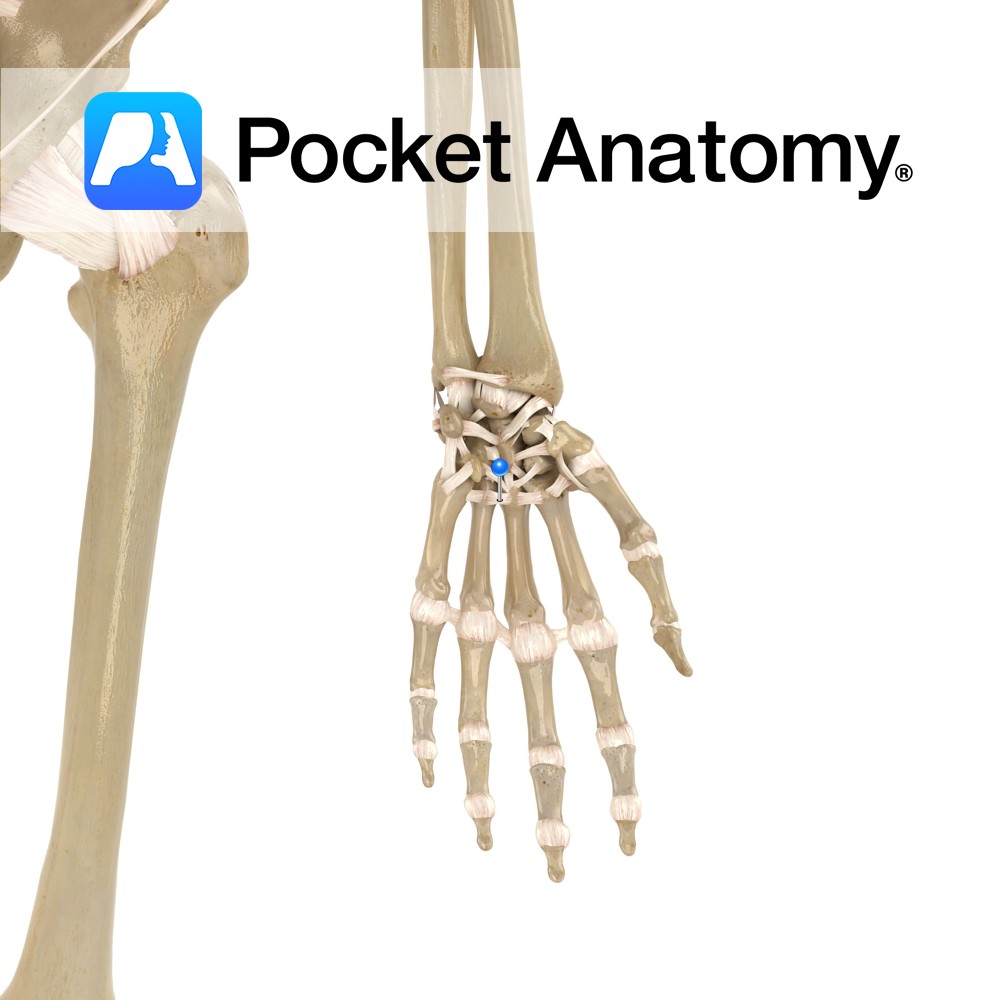
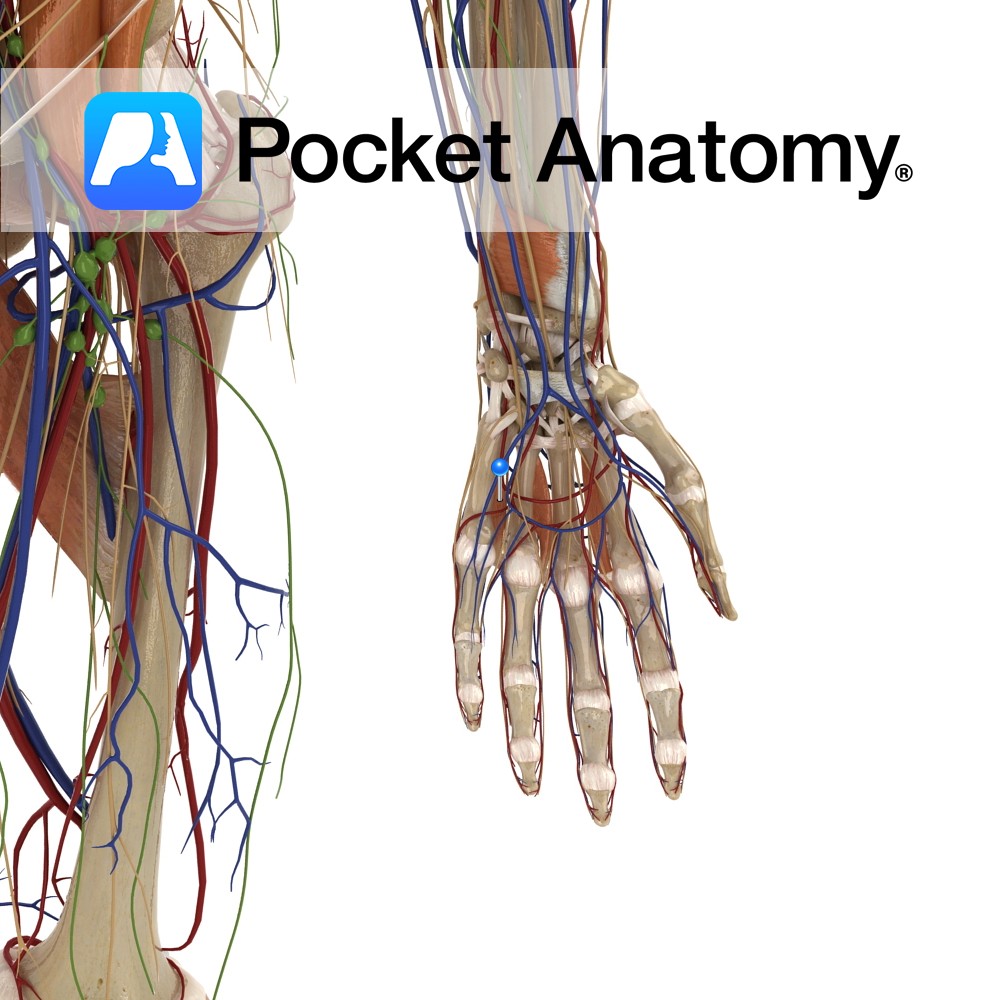
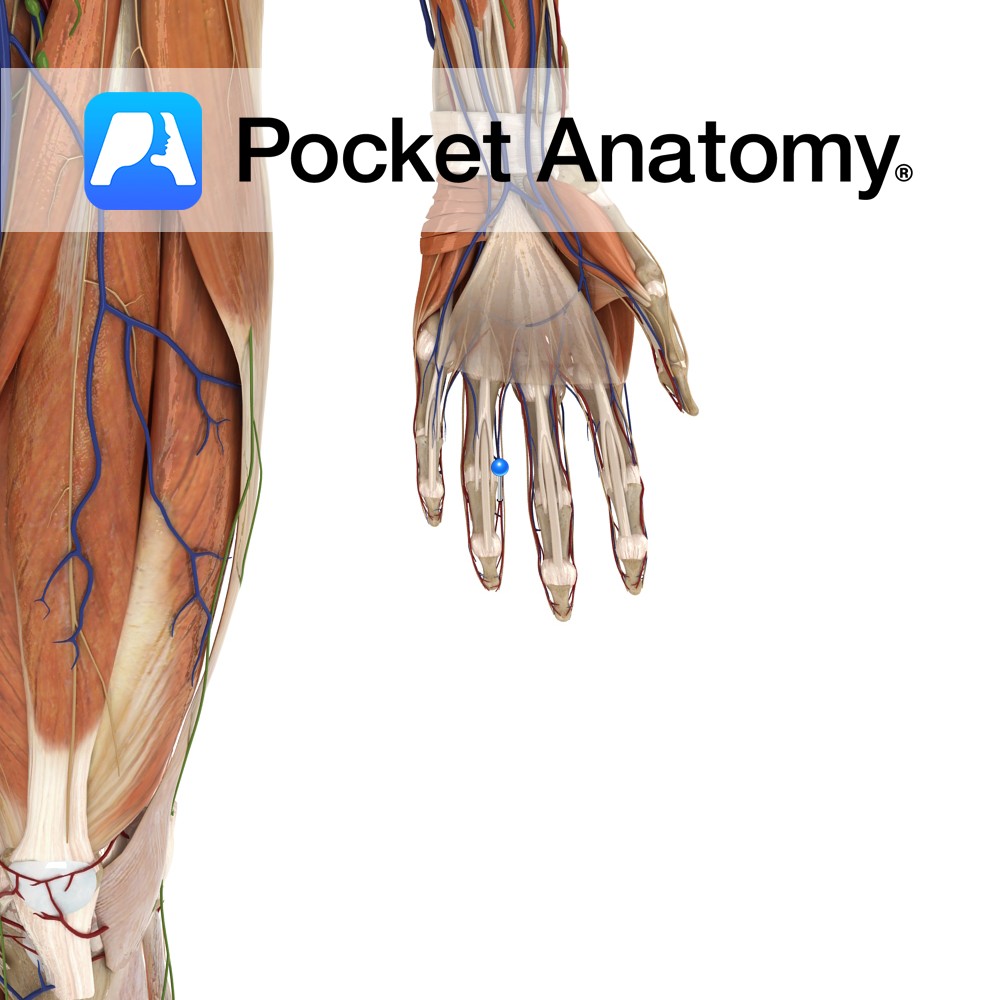
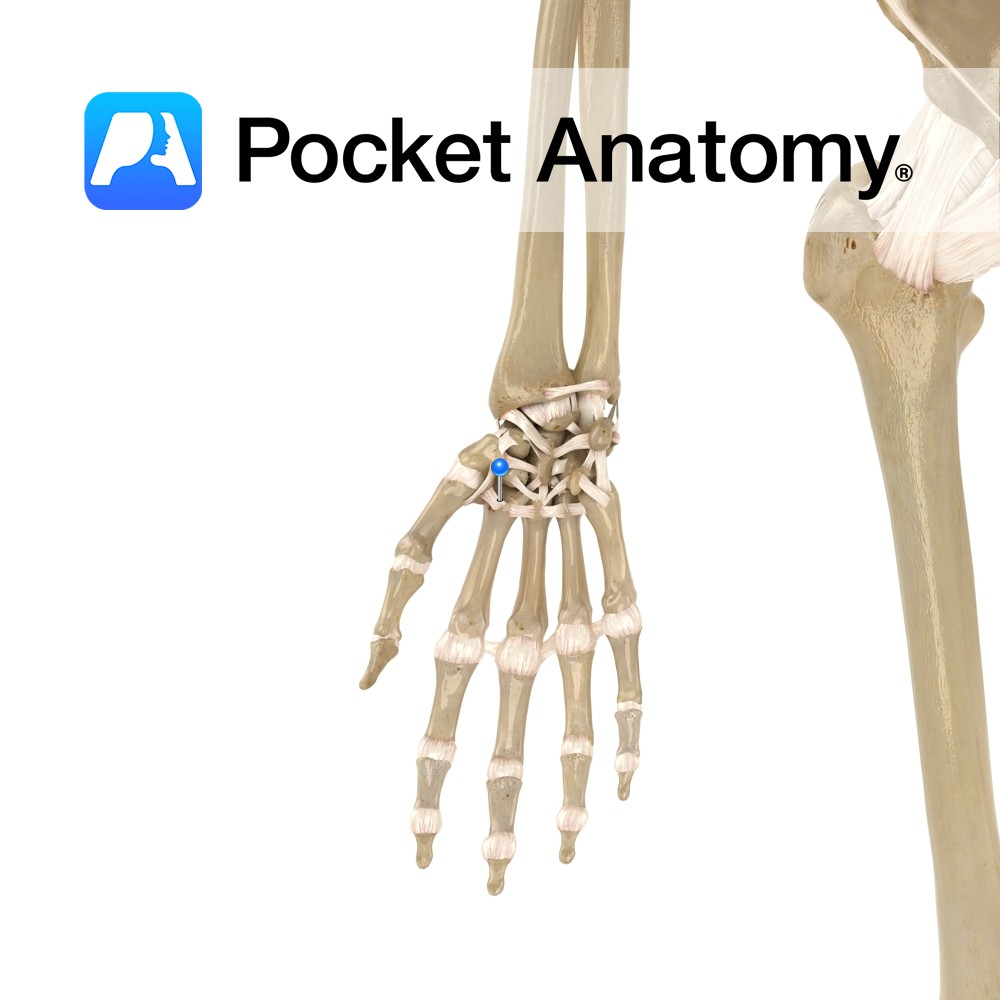
Anatomy A series of transverse ligaments passing from the palmar surface of the base of metacarpals one to five. Functions Provide static stability to the metacarpal joints. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Entire length of side of metacarpal (1st = ulnar aspect, 2nd, 3rd = radial aspect) Insertion: Extensor hood and base of proximal phalanges of the index, middle and ring fingers. Functions Flexion of the index, middle and ring digits at the metacarpophalangeal joint. Adducts the index, middle and ring digits at the metacarpophalangeal
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branches from the superficial palmar arch, just after the deep palmar artery branches from it. It travels medially towards the little finger and runs along the medial side to the tip. The blood it carries is mainly from the ulnar artery. Supply Supplies the medial aspect of the little finger with blood. Interested
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
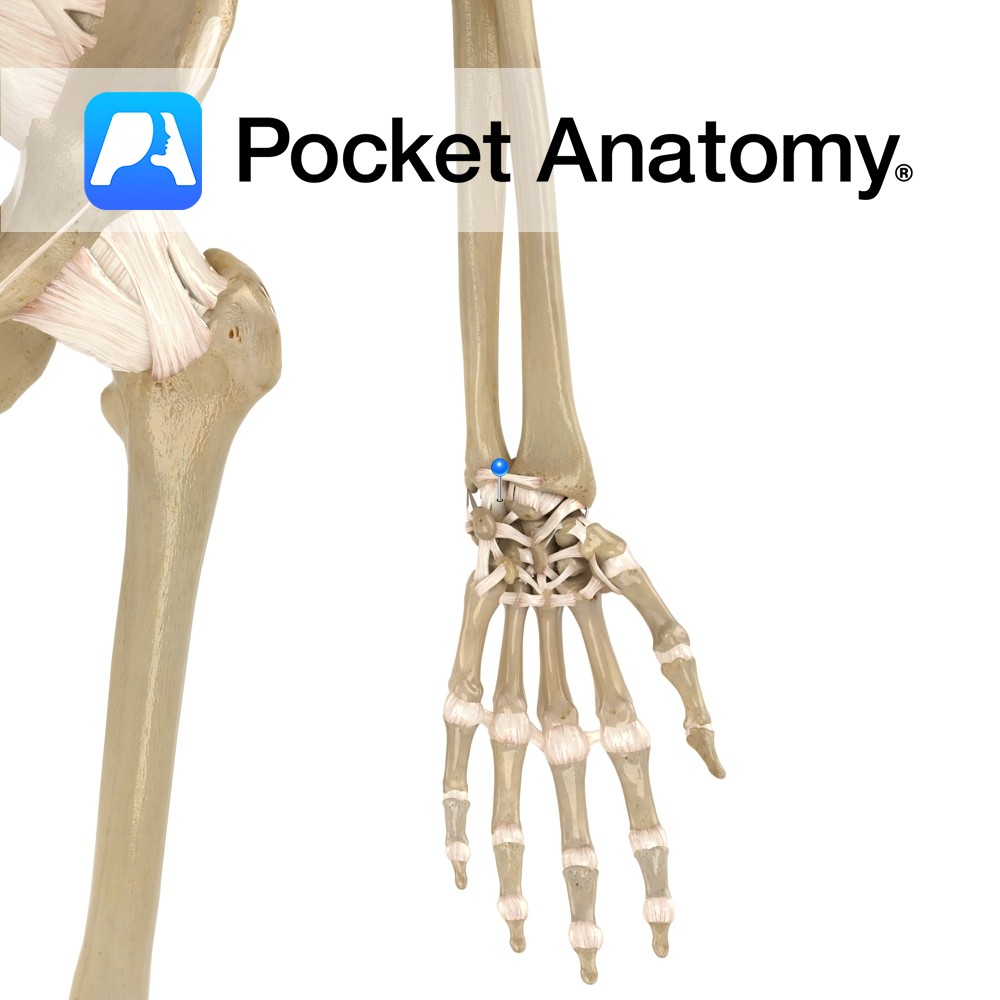
Anatomy Small fibrous bands connecting from the distal row of carpal bones to the proximal end of the metacarpal bones. Functions Provide static stability to the carpometacarpal joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
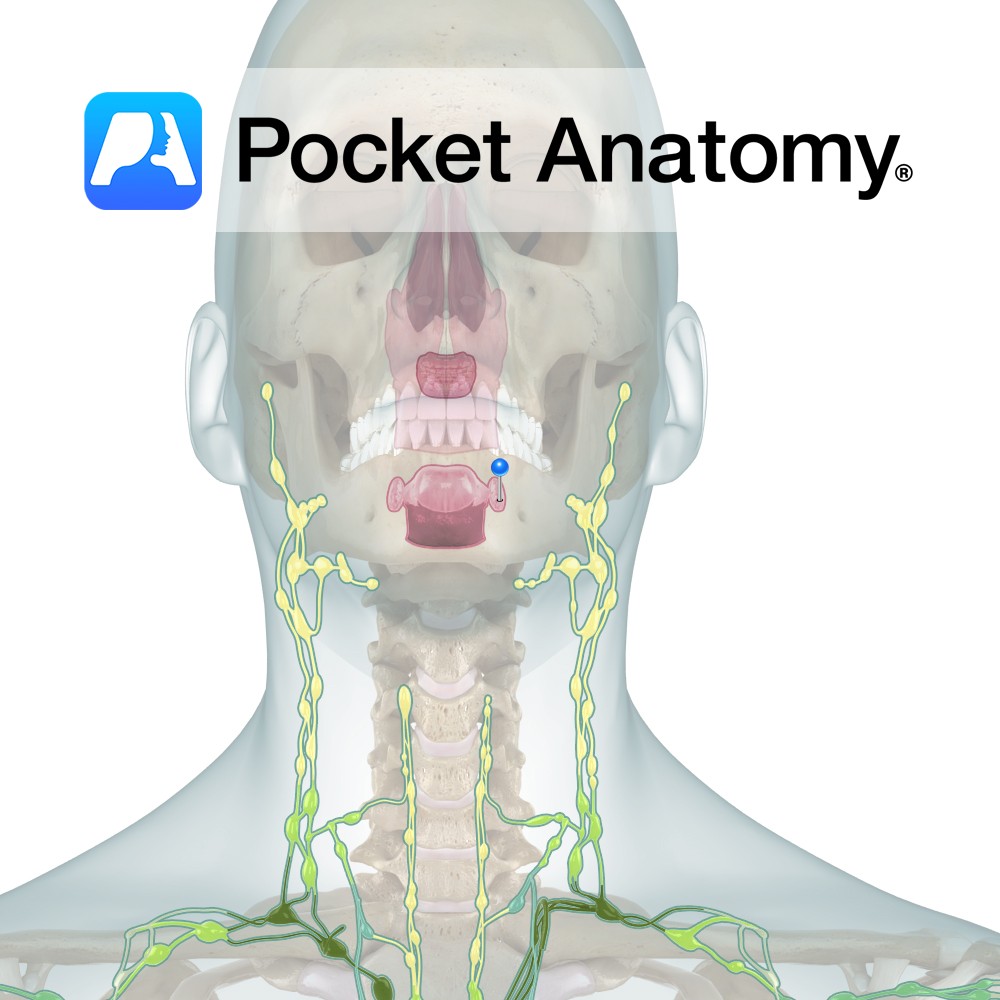
Anatomy The tonsils most commonly referred to, visible either side of the Oropharynx at the back of the tongue. Surface folded on itself, forming 15 or so crypts. Clinical Normal Palatine Tonsils vary considerably in size. Can swell significantly when inflamed/infected, though rarely to the point of blocking the Oropharynx. Tonsillectomy was once very common
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

-ligament.jpg)