PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
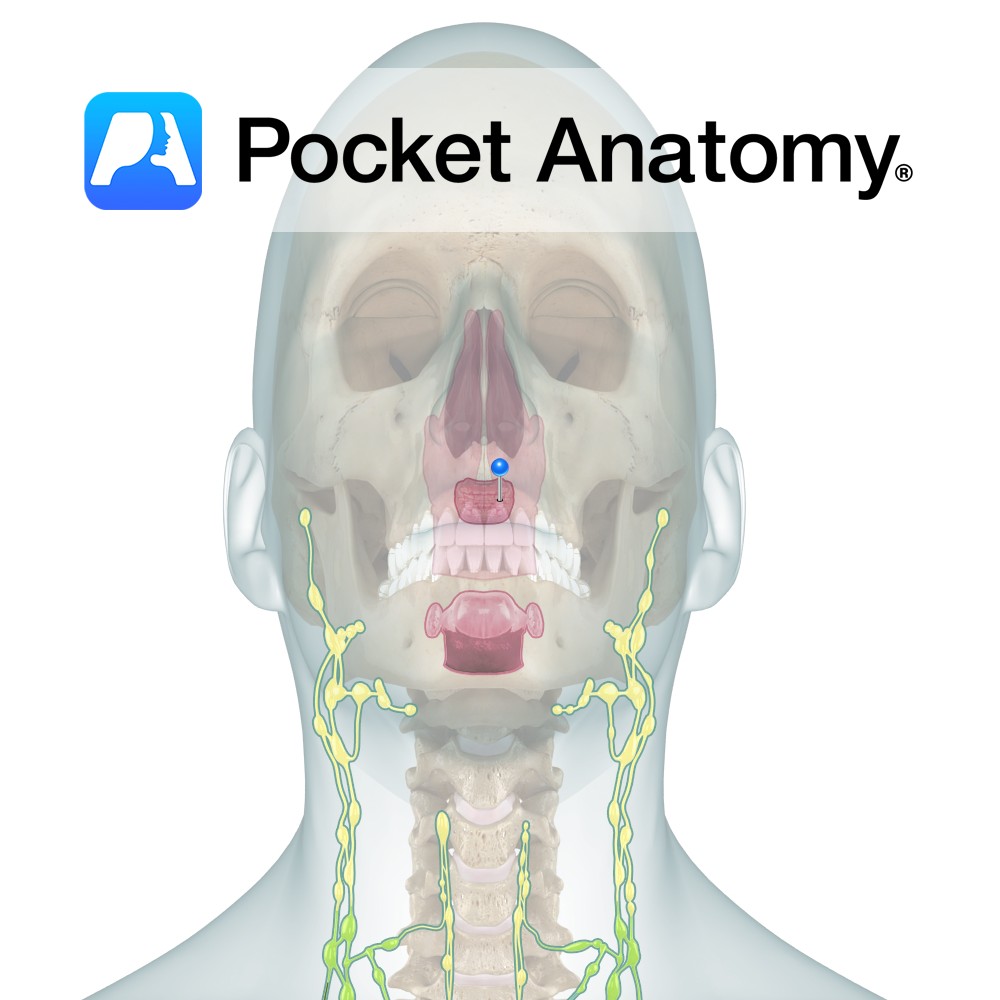
Anatomy Also called Adenoids, located in the back of the throat and up into the nasal cavity (above Palatine Tonsils, behind soft palate and nose) made of folded parts (adenoids), with cilia and mucus which capture coat and dispatch material (allergens/antigens/pathogens) to the stomach for digestion, diverting them from inhalation. Clinical Pharyngeals/Adenoids reach full size
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
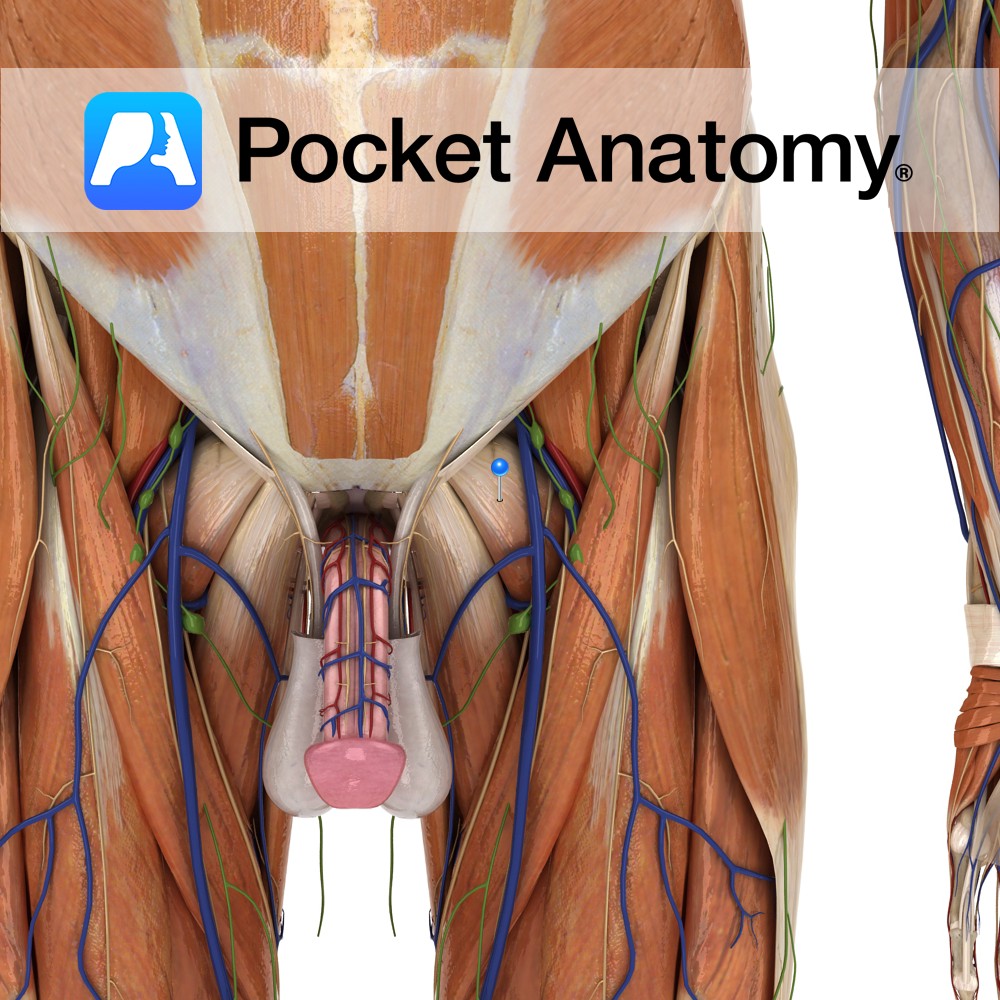
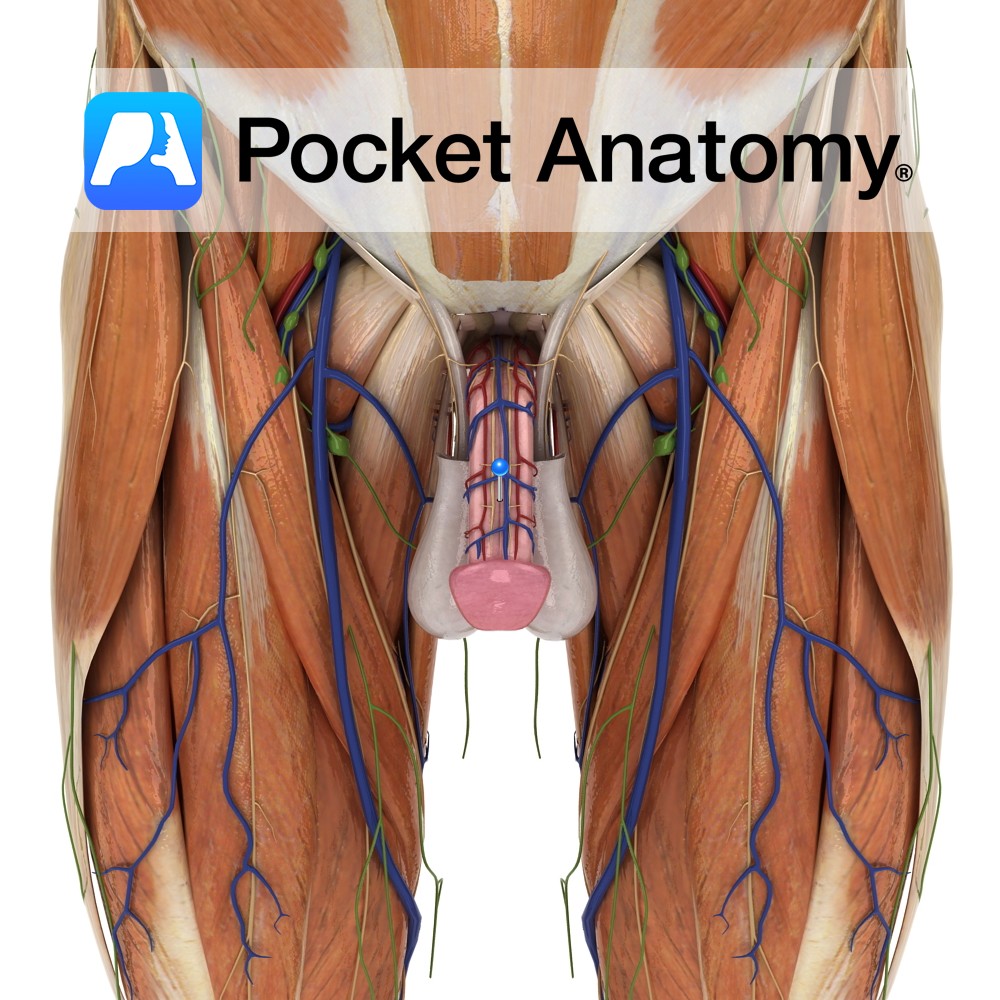
Anatomy Cylindrical male external sexual organ (also serving as a urinal duct) through which sperm are extruded/ejaculated and introduced into the female vagina (during copulation/coitus/intercourse), from where they try (the attrition rate is well over 99.99%) to travel on and seek out an egg to fertilise. Size at any time influenced by factors such as
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
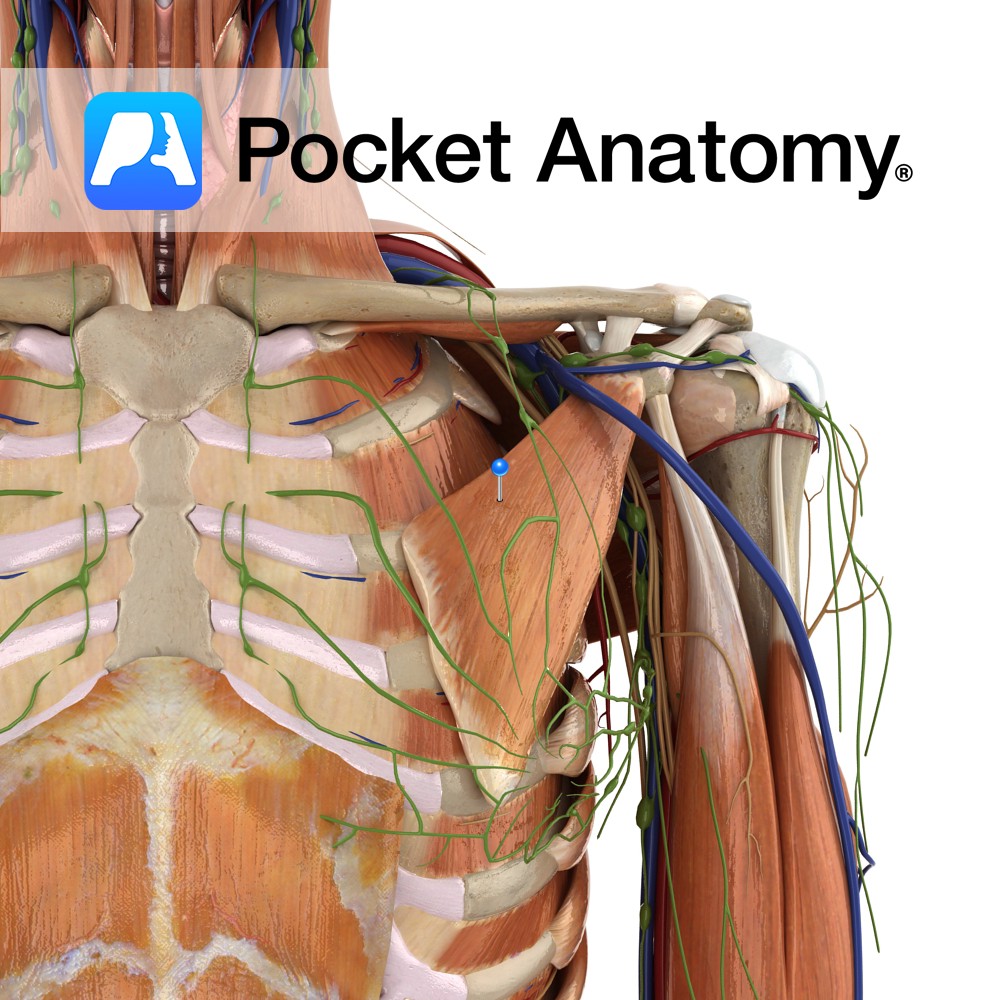
Anatomy Origin: Anterior surface of the 3rd, 4th and 5th ribs near their costal cartilages. Insertion: Medial border and superior surface of coracoid process of scapula. Key Relations: The medial pectoral nerve pierces the muscle and the clavipectoral fascia. Functions -Stabilises the scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly against the thoracic wall. -Protracts the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Clavicular head: Medial half of anterior surface of clavicle. Sternocostal head: Anterior surface of manubrium, sternum, upper six costal cartilages and external oblique aponeurosis. Insertion: Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of humerus. Key Relations: The upper border of the muscle is separated from deltoid by the deltopectoral groove (infraclavicular fossa), in which lies
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Clavicular head: Medial half of anterior surface of clavicle. Sternocostal head: Anterior surface of manubrium, sternum, upper six costal cartilages and external oblique aponeurosis. Insertion: Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of humerus. Key Relations: The upper border of the muscle is separated from deltoid by the deltopectoral groove (infraclavicular fossa), in which lies
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Pecten pubis or pectineal line of the pubic bone. Insertion: Pectineal line of the femur between the lesser trochanter and linea aspera. Key Relations: -One of the six muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh. -Lies anteriorly to adductor brevis, obturator externus and the anterior branch of the obturator nerve. -Forms the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
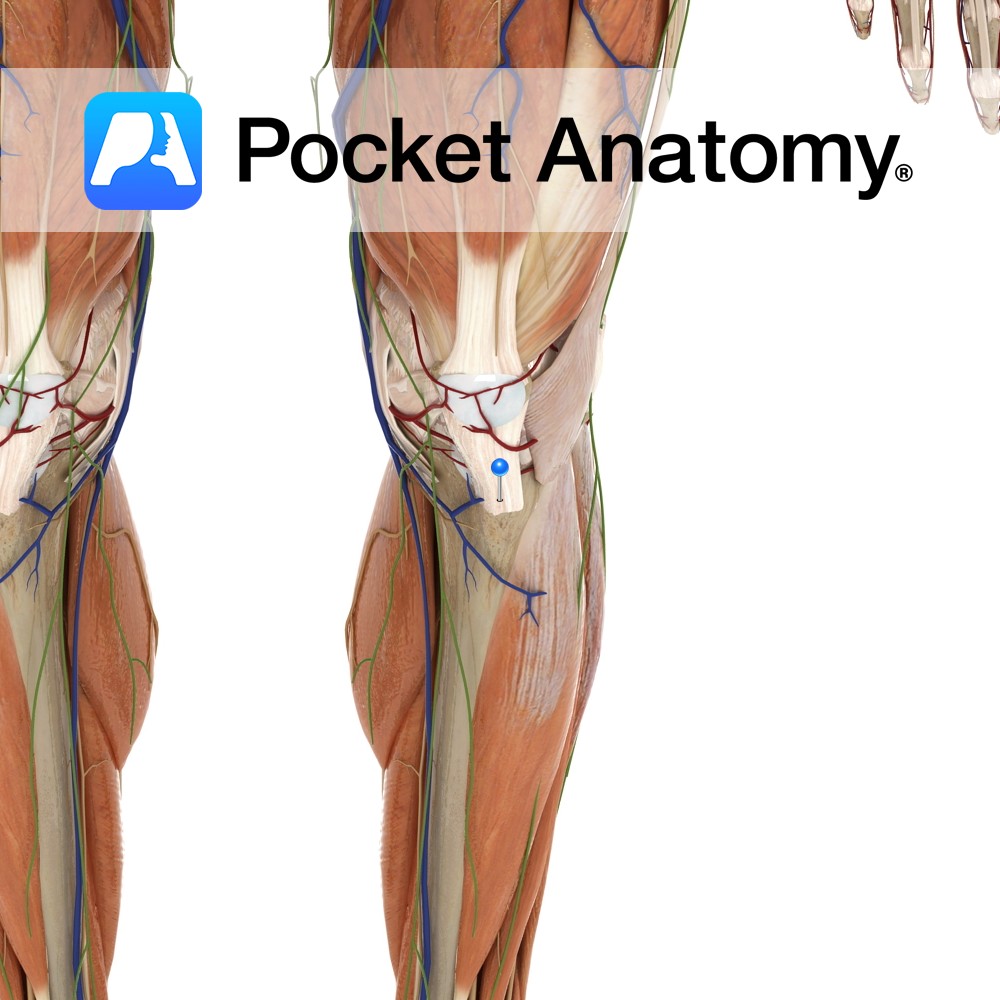
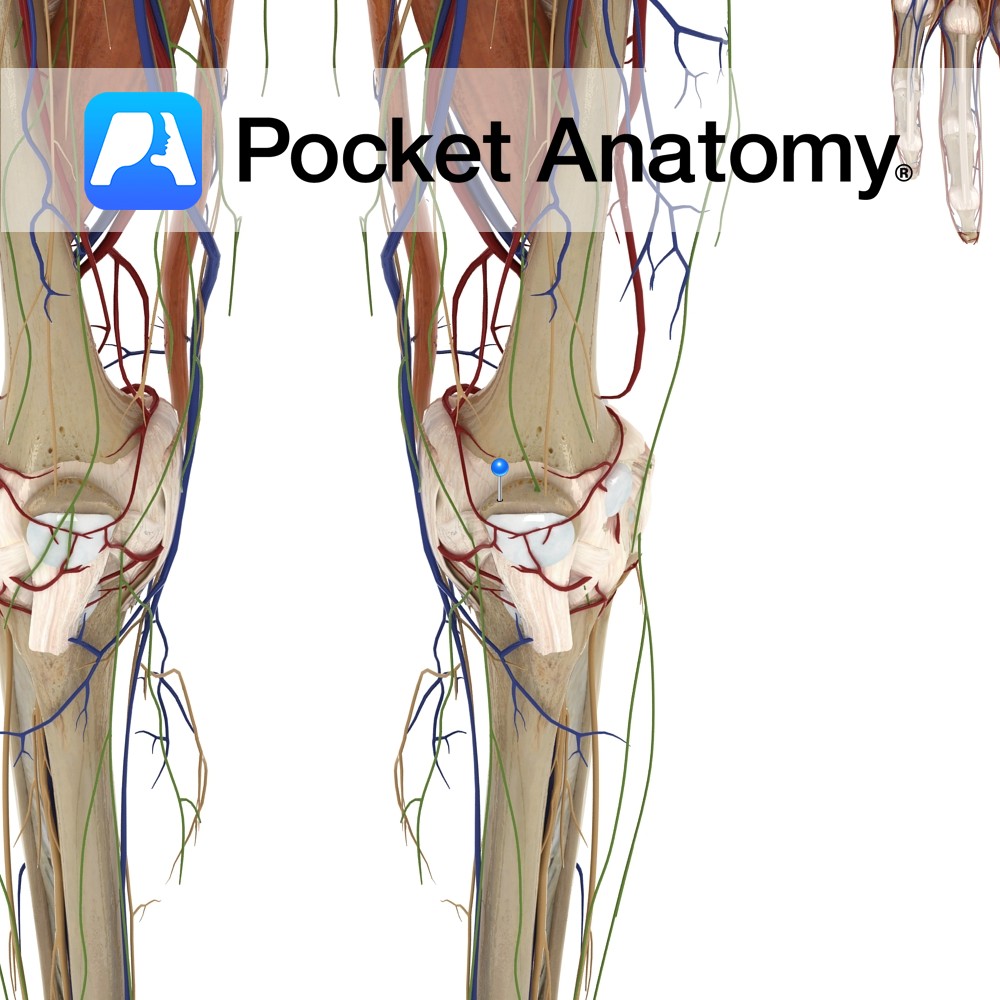
Anatomy Attaches from inferior border of the patellar to the tibial tuberosity. Functions Attaches the patella bone and the quadriceps muscles via their attachment to the tibia. Clinical Tibial tubercle apophyseal traction injury is an inflammation of the patellar ligament at its insertion into the tibial tuberosity. It is generally associated with active children aged
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Kneecap, largest sesamoid (embedded in tendon) bone, triangular (base up, tip down) articulates with femur. Clinical Increases angle and leverage of quads in their extension of knee. Visible, palpable, moveable a little side to side when leg straight and quads relaxed. Patellar dislocation is usually lateral, accompanied by pain and swelling, can often be
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
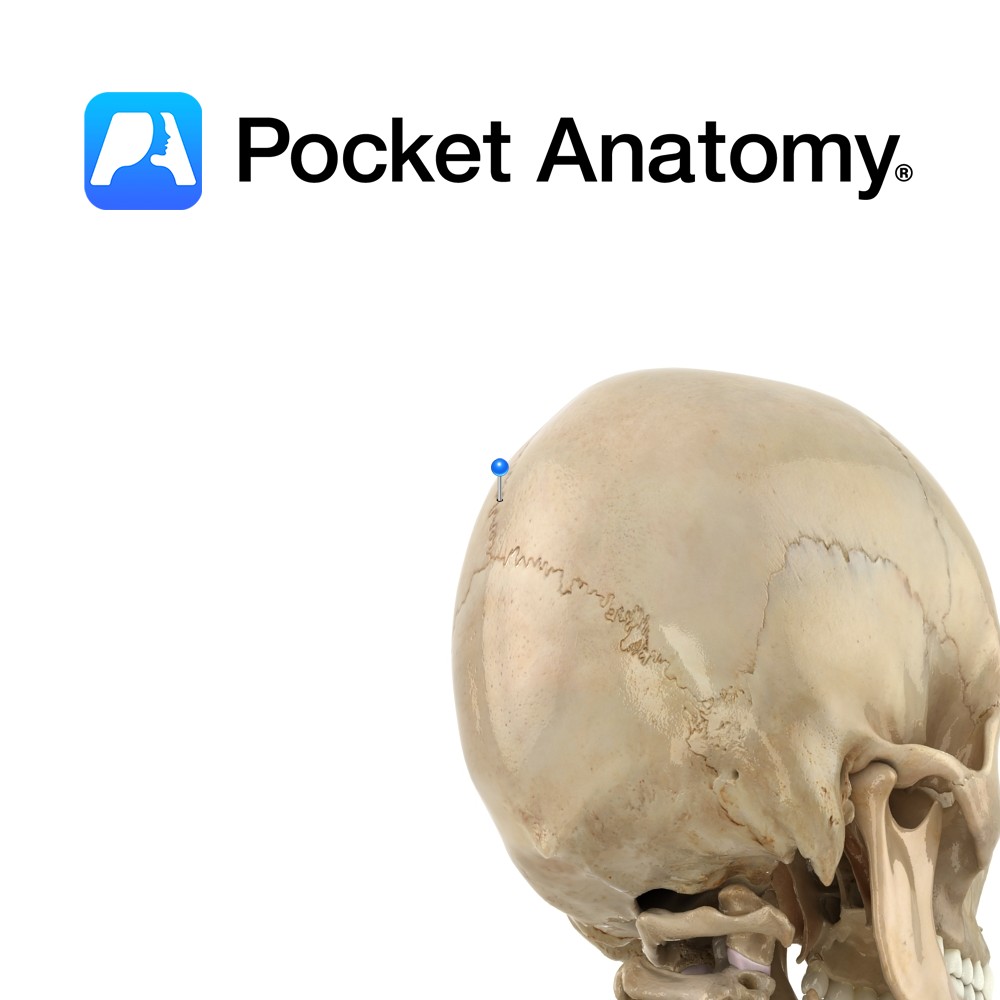
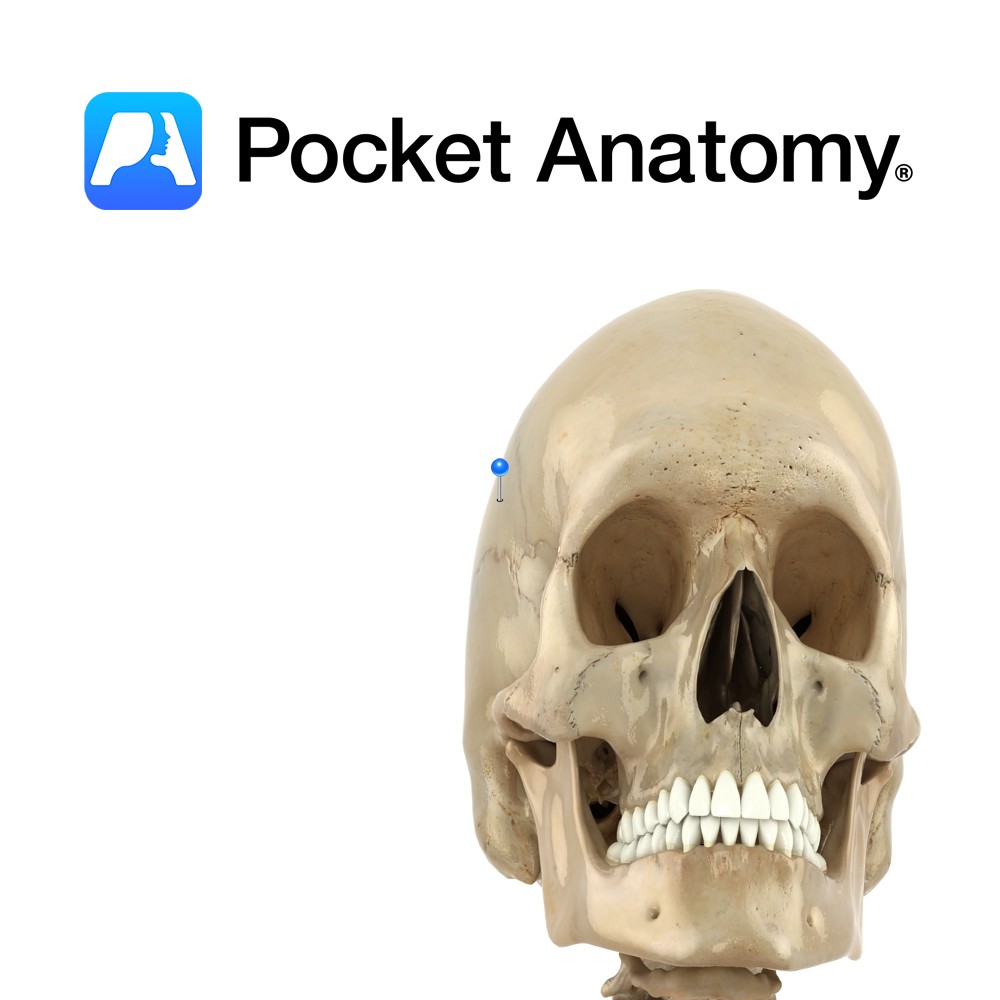
Anatomy Rigid midline joint or seam between paired parietal bones, deeply serrated towards front. Vignette Sagitta (Latin); arrow – With Sagittal suture the shaft and lambdoid suture as the tuft of the arrow. Anterior fontanelle is gap at the junction of sagittal, coronal and frontal sutures which persists until closure in 2nd year; it allows
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Paired bones forming the side-walls and roof of the cranium, meeting each other at the sagittal suture, also articulating with frontal bone, sphenoid anteroinferiorly (below and in front) each side, temporal bones laterally below and occipital below and behind. Vignette Pariet (Latin); wall. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)