PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Origin: Posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of C4 to C7. Insertion: Upper surface of the 2nd rib, posterior to the attachment of serratus anterior. Key Relations: Smallest and deepest of the scalenes. Functions -Elevates the 2nd rib. -Lateral flexes the neck to the same side. -An accessory muscle of inspiration. Supply Nerve Supply:
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
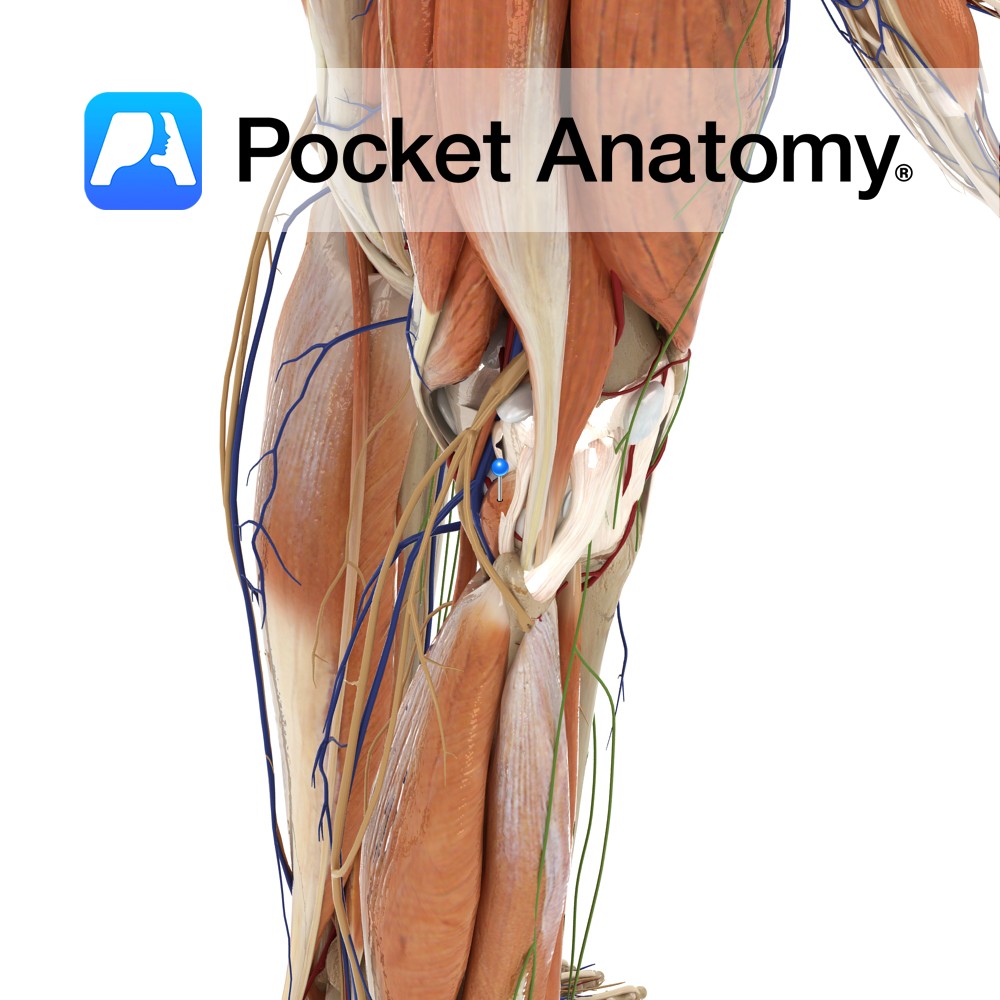
Anatomy Attaches from the head of the fibula, and passes obliquely upwards to attach to the lateral condyle of the tibia. Functions Provides static stability to the proximal tibiofibular joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Originates from the common interosseous artery, which is a branch of the ulnar artery. It branches from the common interosseous artery just above the margin of the interosseous membrane, running dorsally. It then runs distally on the posterior aspect of the forearm, until it reaches the wrist joint where it joins with the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Arises from the sacral plexus in the pelvis. It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle. It passes to the back of the leg and travels distally beneath the gluteus maximus, and then passes over the long head of the biceps femoris muscle, remaining deep to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the ileocolic artery that branches off near the junction of the ileum and the cecum. It can branch off together with the anterior cecal artery as a trunk, or individually. Supply The posterior cecal artery supplies the cecum and the appendix. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins from a plexus on the side of the scalp. It descends behind the ear to join with the posterior facial vein. These both form the external jugular vein. Drain Drains the blood from the region of the scalp behind the ear. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the external carotid artery. It branches from the external carotid just above the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It then ascends posteriorly behind the parotid gland, near the cartilage of the ear. Supply Supplies the auricle of the ear, as well as some of the scalp behind it. Interested
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy A gyrus located posterior to the central sulcus. It extends anteroinferiorly from the great longitudinal fissure and ends just above the lateral sulcus. It forms part of the parietal lobe. Blood supply: Supplied by the middle cerebral artery, and medially by the anterior cerebral artery, to a lesser extent. Functions Is the location of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Formed when the splenic and superior mesenteric veins merge behind the pancreas. It ascends to the liver, passing posterior to the superior duodenum. It divides into right and left branches as it enters the liver. Drain Brings blood for detoxification from the gastrointestinal system to the liver, where it rejoins the systemic circulation.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Lateral surface of the lateral condyle of the femur and the lateral meniscus. Insertion: Medial half of the triangular area above the soleal line on the posterior surface of the tibia. Key Relations: -One of the four muscles of the deep posterior compartment of the leg. -The popliteus forms part of the floor
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins