PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Origin: Humeral head: Medial epicondyle of humerus via the common flexor tendon, and adjacent supraepicondylar ridge. Ulnar head: Medial aspect of the coronoid process of ulna. Insertion: Roughening on lateral surface of radial shaft near its midpoint. Key Relations: -The median nerve courses between the two heads of pronator teres in 80% of people.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
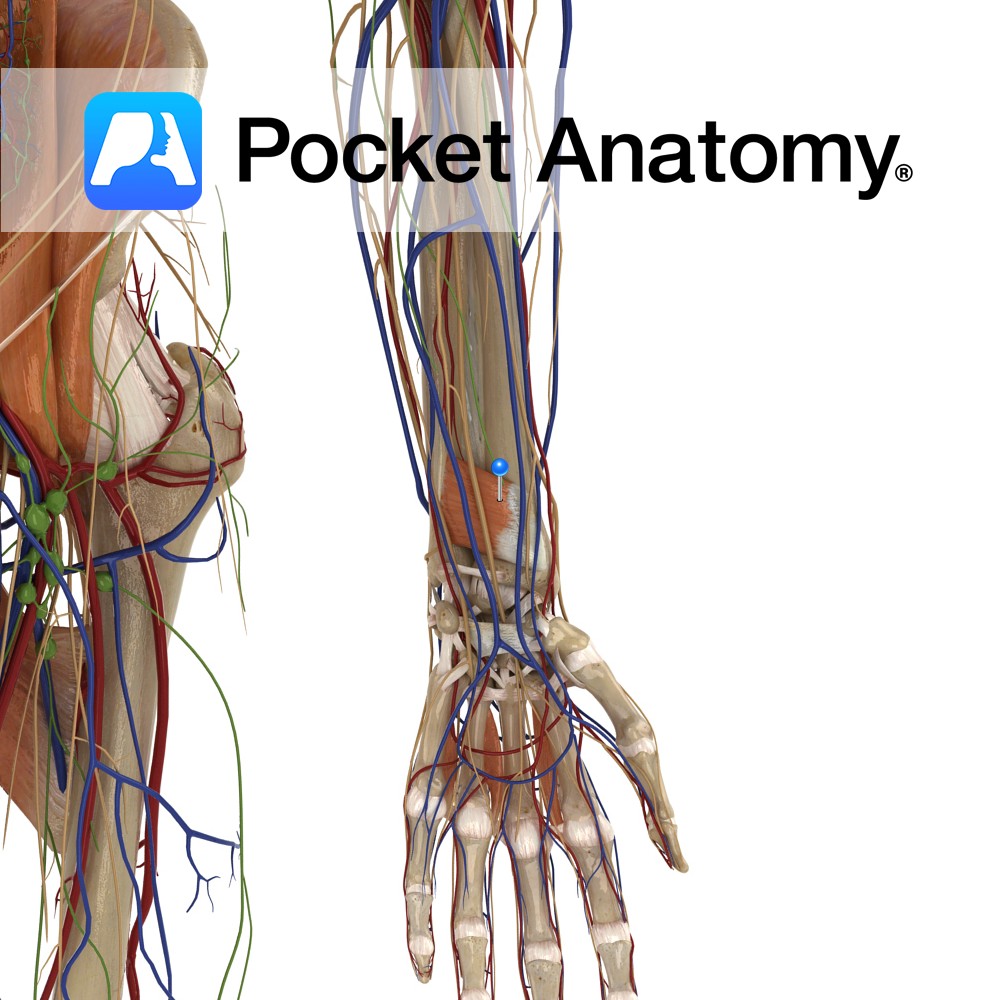
Anatomy Origin: Medial surface of distal ulna. Insertion: Lateral Surface of distal radius. Key Relations: One of the three muscles in the deep anterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Pronates the forearm and hand at the radioulnar joint. -Deep fibres bind the radius and ulna together. e.g.: as in loosening a screw (right hand). Supply
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branches from the brachial artery about a third of the way along the humerus. It enters the posterior compartment of the arm with the radial nerve, passing through the space made by the lateral margin of long head of the triceps, the inferior margin of teres major and the shaft of the humerus.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
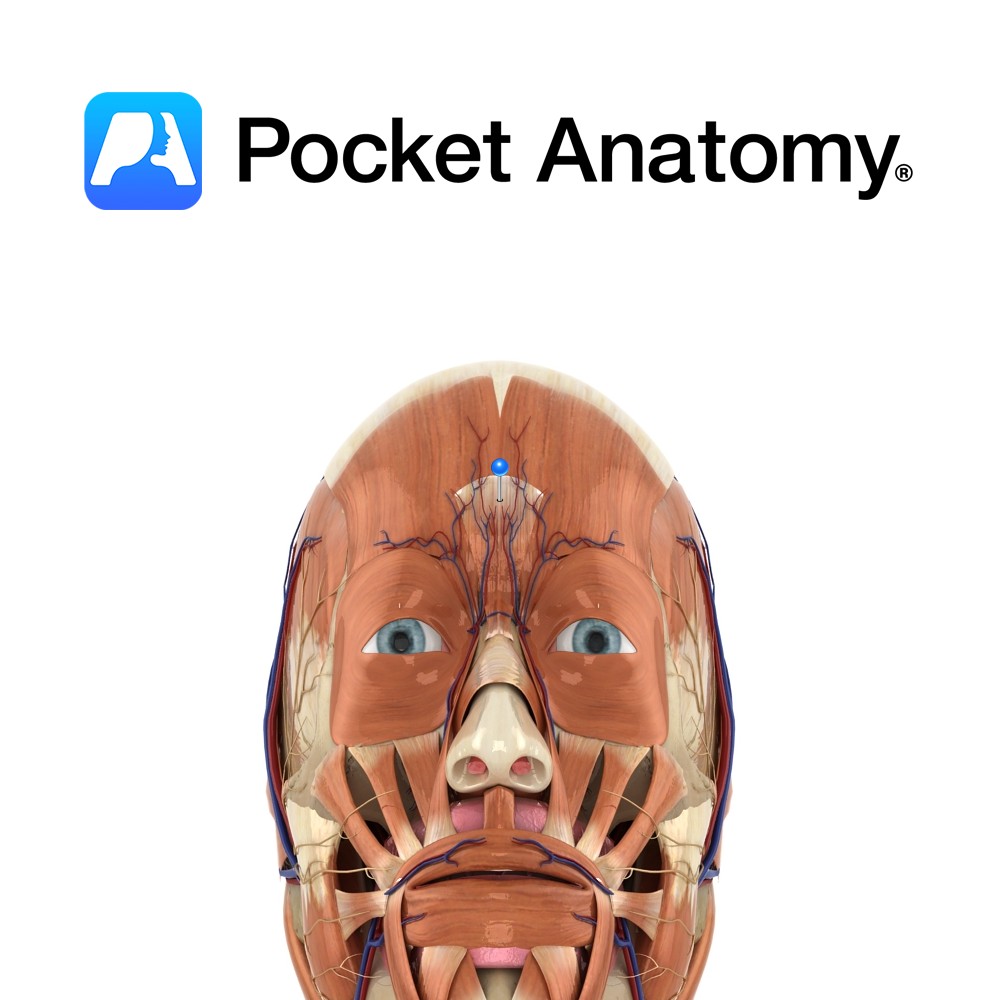
Anatomy Origin: Nasal bone and upper part of the lateral nasal cartilage. Insertion: Skin of lower forehead between the eyebrows. Key Relations: Lies over the nasal bone. Functions Draws medial border of eyebrows inferiorly resulting in transverse wrinkles over the bridge of the nose. e.g. as in an expression of anger.. Supply Nerve Supply: Zygomatic
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
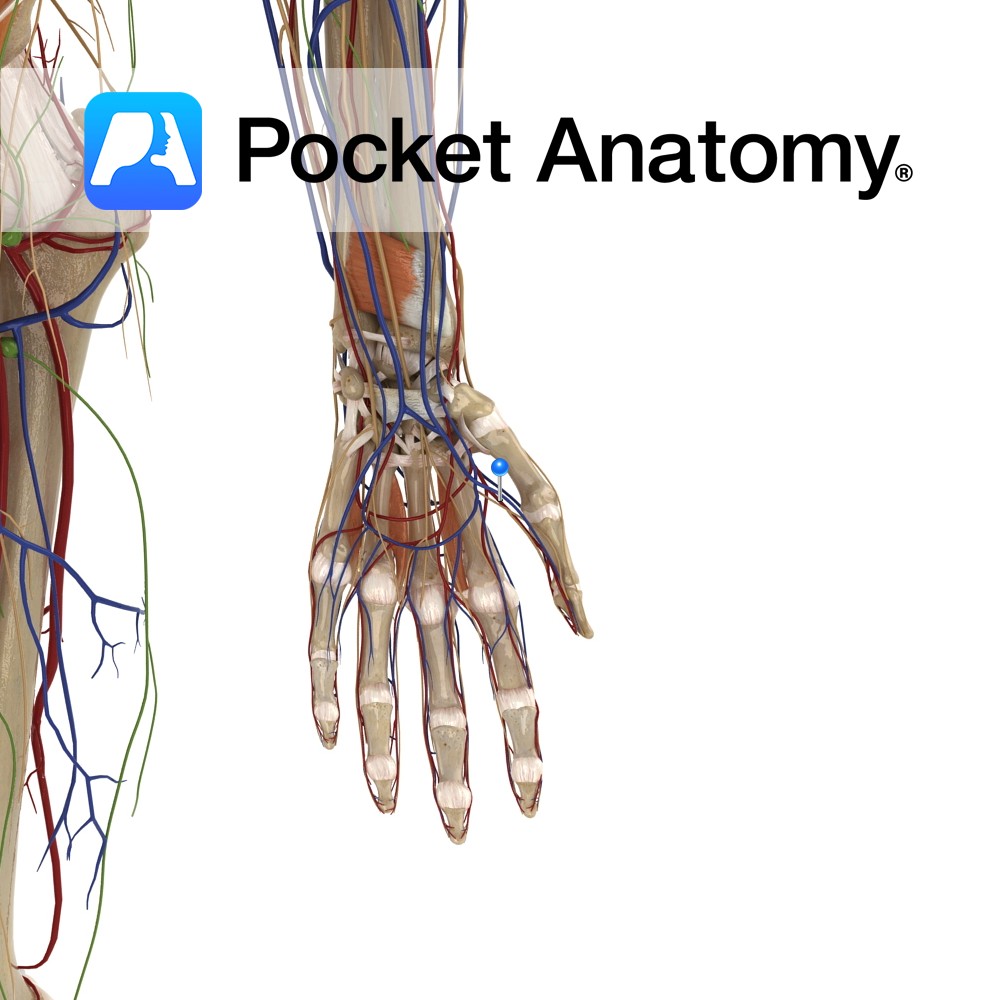
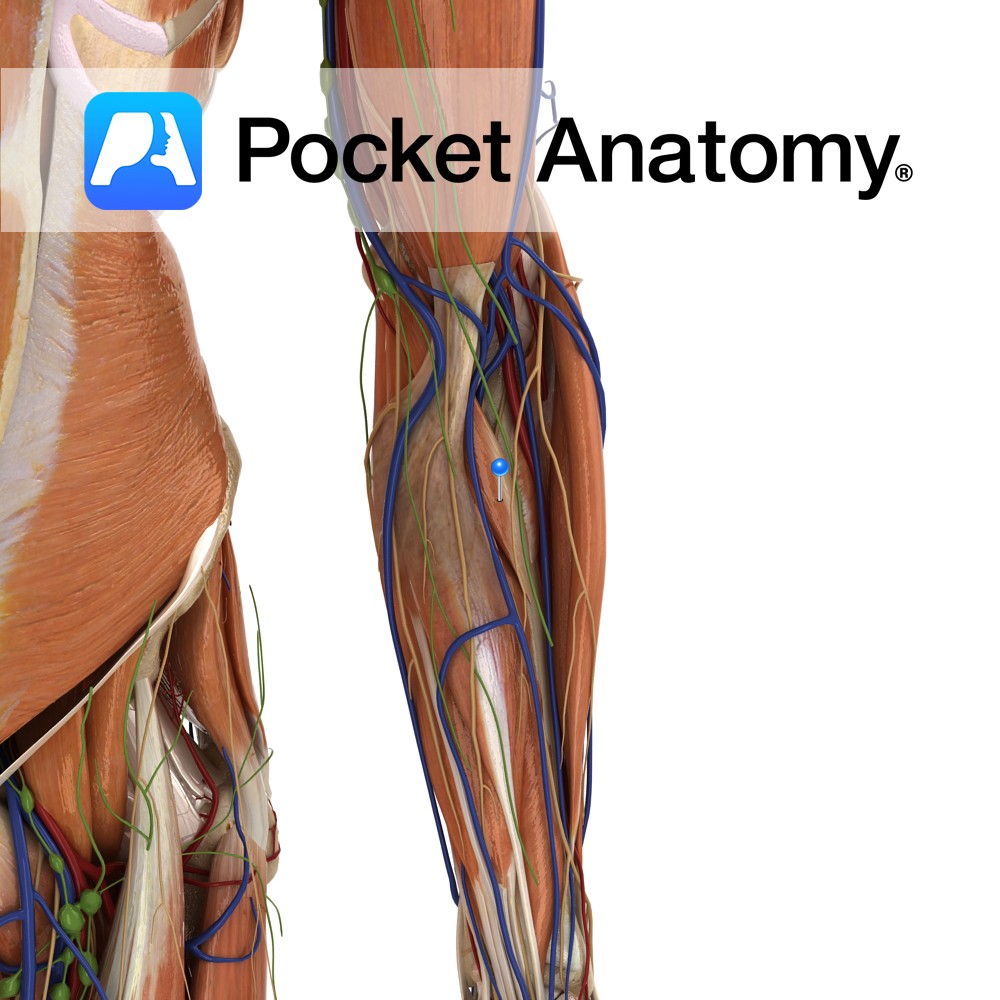
Anatomy Course Branches from the radial artery, just as the radial artery is veering medially to become the deep palmar arterial arch. It travels towards the thumb between the first dorsal interosseous artery and the adductor pollicis muscle. Supply Main blood supply to the thumb. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
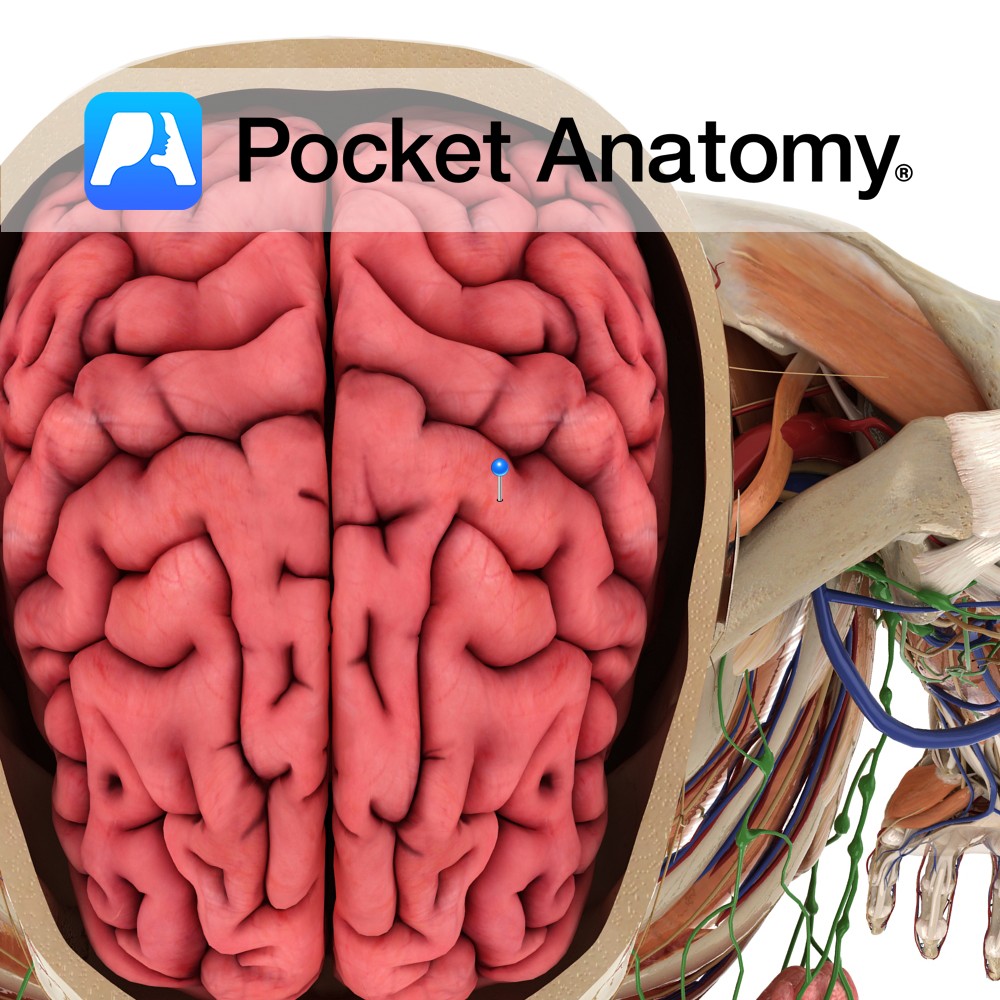
Anatomy A gyrus located anterior to the central sulcus. It extends anteroinferiorly from the great longitudinal fissure and ends just above the lateral sulcus. It forms part of the frontal lobe. Blood supply: Supplied by the middle cerebral artery, and medially by the anterior cerebral artery, to a lesser extent. Functions Is the location of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
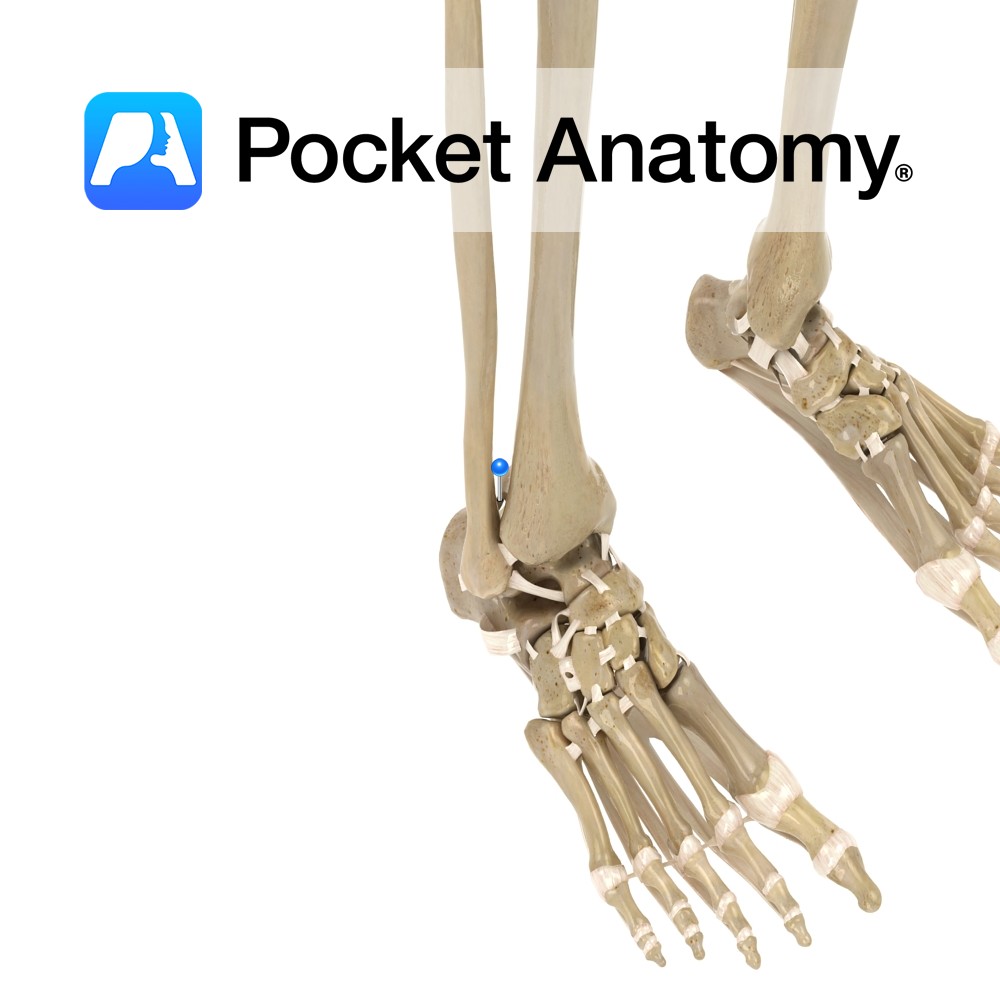
Anatomy Attaches from the posteriolateral surface of the distal tibia to the posterior medial surface of the lateral malleolus. Functions Firmly links the distal ends of the tibia and fibula. This is essential to produce the framework for the articulation of the ankle with the leg. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
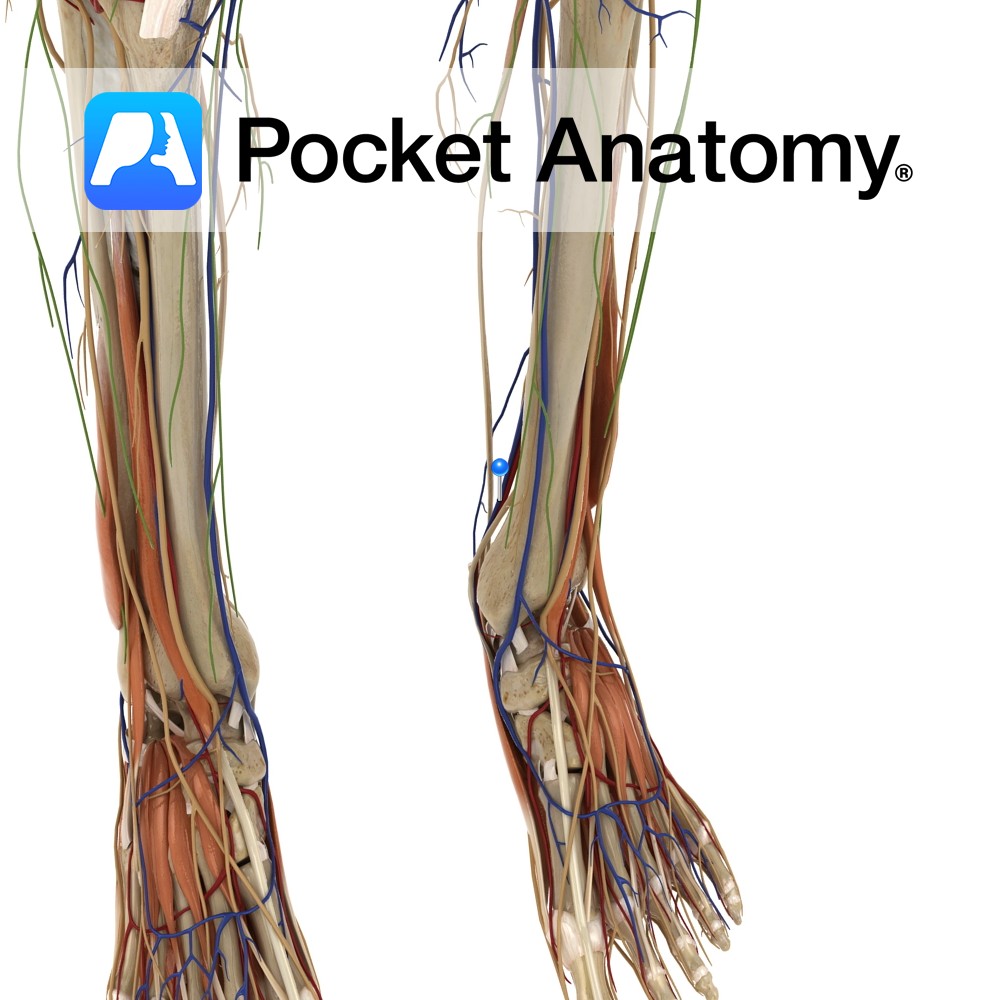
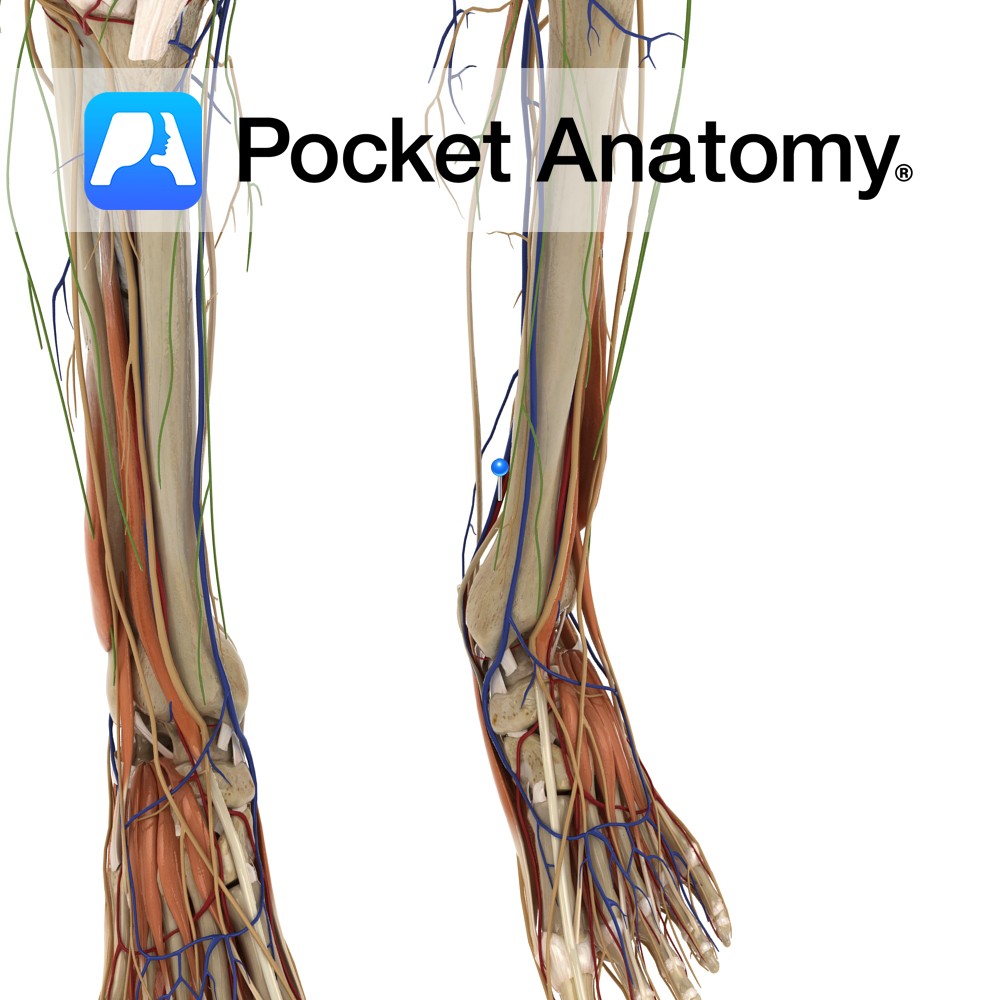
Anatomy Course Begins at the junction of the lateral and medial plantar veins. It ascends to the leg, passing behind the medial malleolus and travels deep in the posterior aspect of the leg. It passes under the tendinous arch formed by the soleus muscle and becomes the popliteal vein in the popliteal fossa. Drain Drains
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the popliteal artery. It originates after the popliteal artery exits the popliteal fossa. It passes under the tendinous arch formed by the soleus muscle and descends in the plane between the solus and the tibialis posterior muscle. It enters the foot by passing behind the medial malleolus, through the tarsal
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
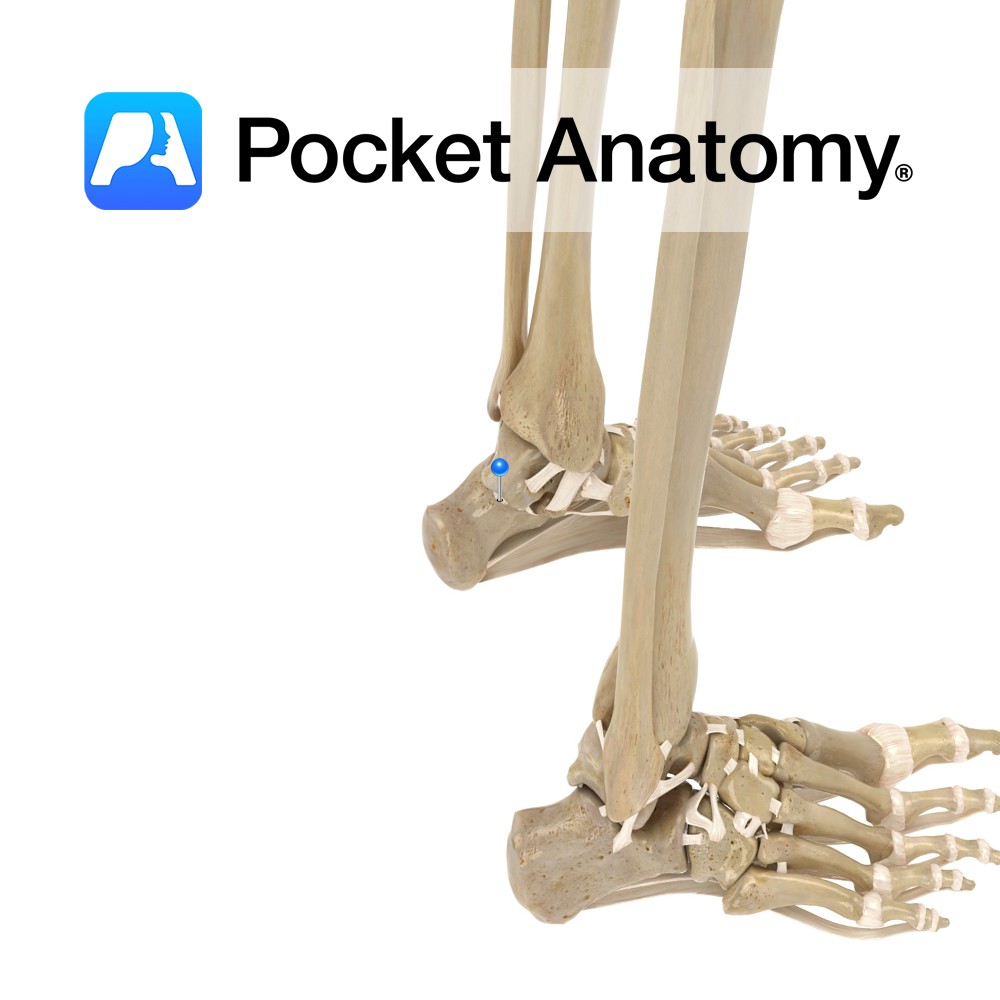
Anatomy Attaches from the lateral tubercle of the talus to the upper and medial aspect of the calcaneus. Functions Provides static stability to the talocalcaneonavicular. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

-artery.jpg)