PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
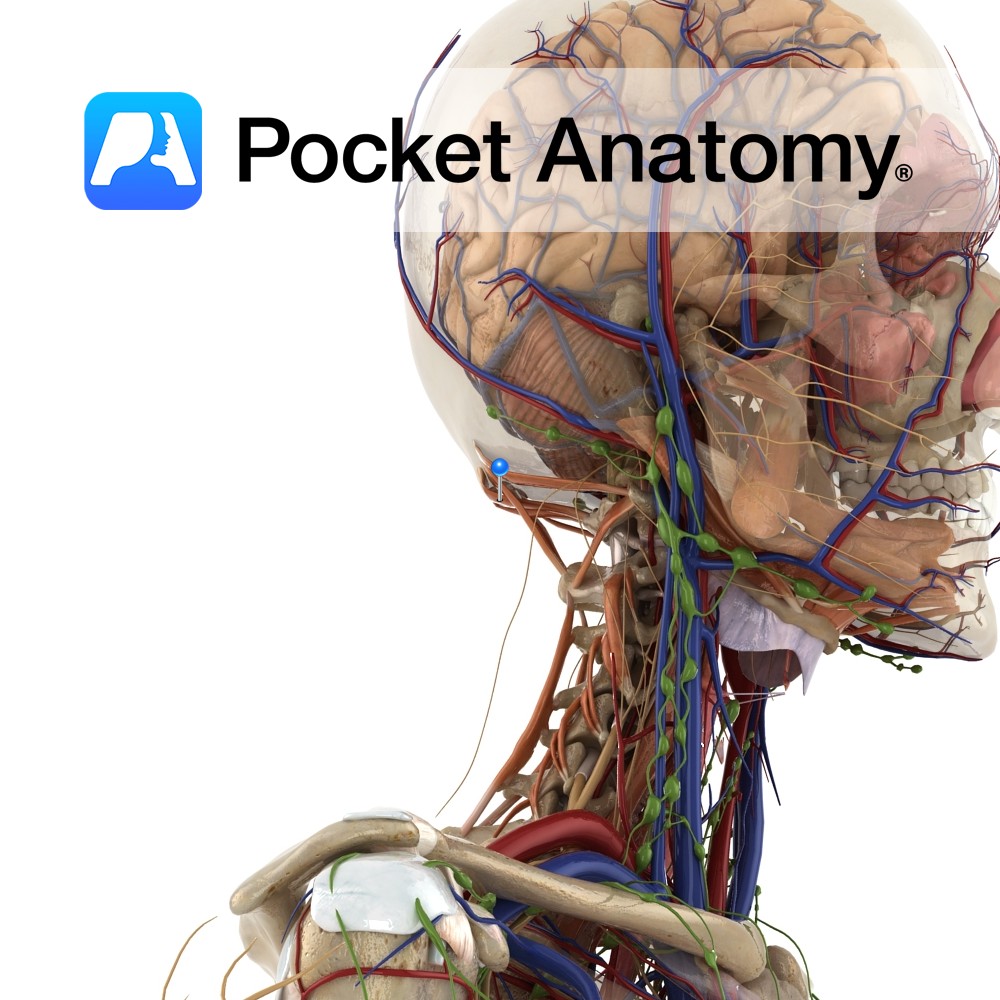
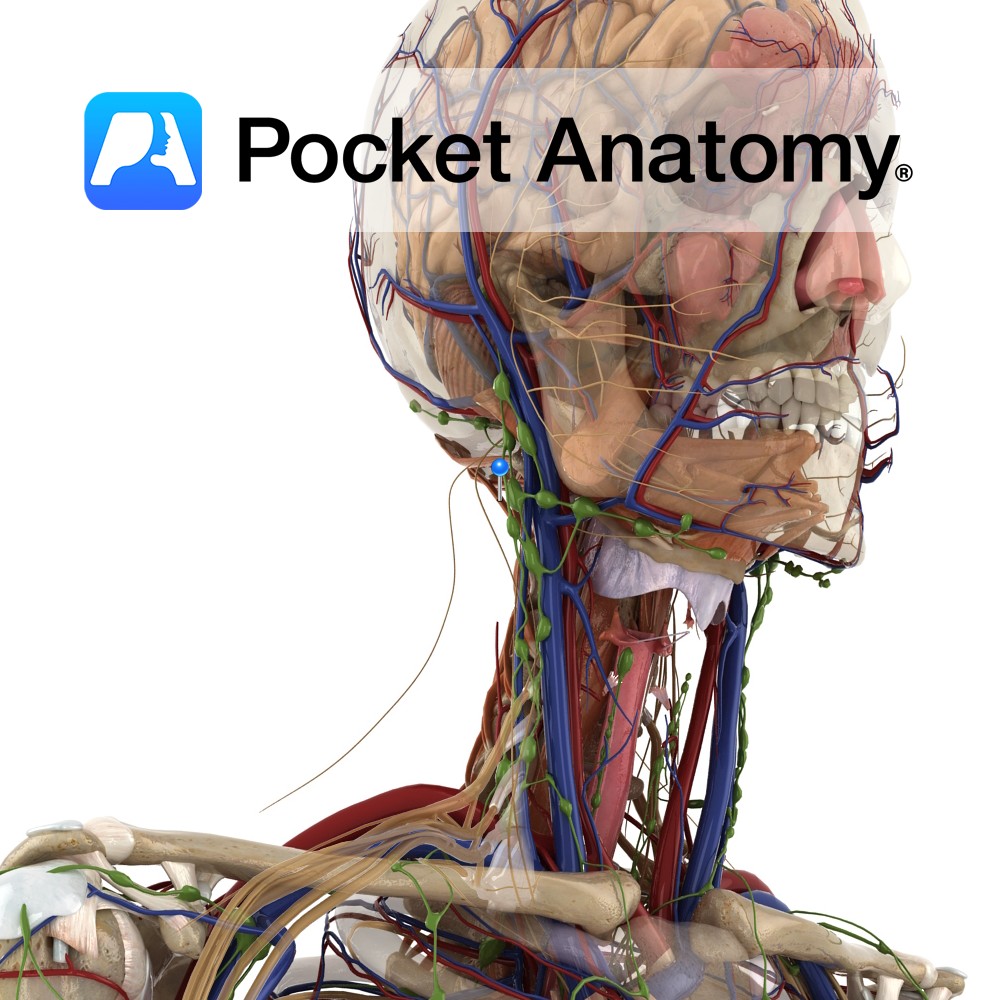
Anatomy Origin: posterior tubercle of atlas. Insertion: From foramen magnum to medial third of inferior nuchal line. Functions Acts bilaterally to extend the head at the atlanto-occipital joint. Supply Innervation: Suboccipital nerve (C1). Blood supply: Muscular branches of vertebral artery. Clinical Slips of the muscle attach to the spinal dura and may be involved in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Spinous process of axis. Insertion: Middle third of inferior nuchal line. Key Relations: Forms the superior and medial border of the suboccipital triangle. Functions -Acts bilaterally to extend the head at the atlanto-occipital joint. -Acts unilaterally to rotate the head to the same side at the atlanto-occipital joint. Supply Innervation: Suboccipital nerve (C1).
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
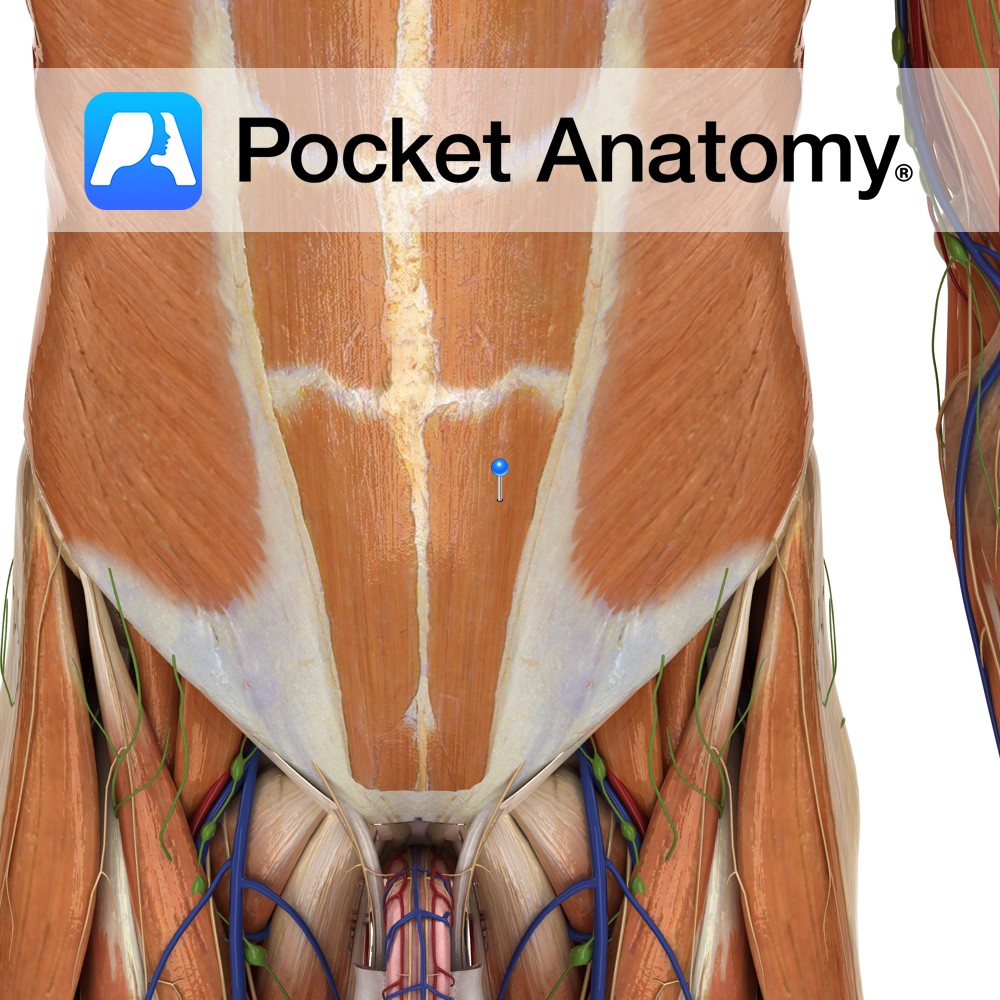
Anatomy Origin: Pubic crest, pubic tubercle and pubic symphysis. Insertion: Xiphoid process and lower costal cartilages (of 5th to 7th ribs). Key relations: Contained within the rectus sheath and separated from the rectus abdominis muscle on the opposite side by the linea alba. Functions -Compresses abdominal cavity. -Tenses abdominal wall. -Flexes vertebral column (trunk) e.g.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
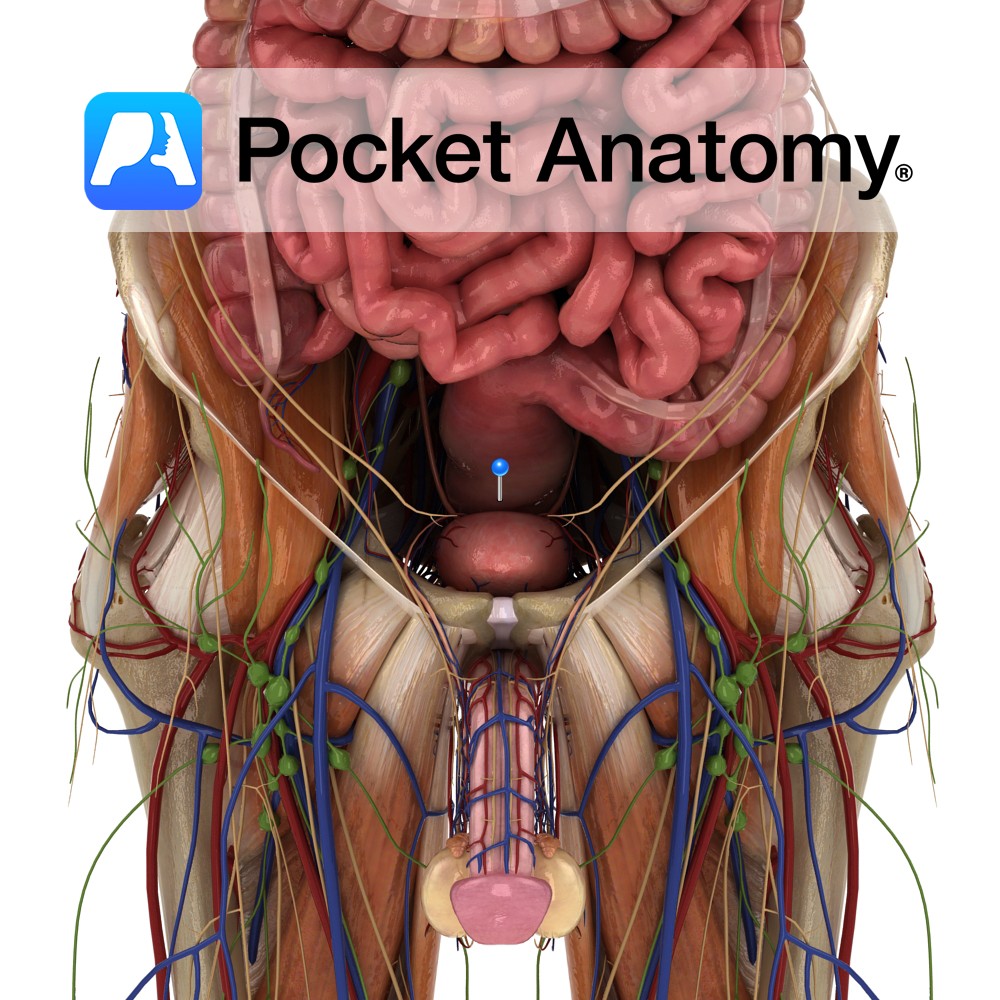
Anatomy Continuous with sigmoid colon above and anal canal below, sitting in and following sacrococcygeal curve and on to c 2.5 cms below coccyx, to level of apex prostate, then turning back abruptly and dilating (rectal ampulla) to anal canal. 3 or 4 transverse folds (Houston’s valves) overlap when rectum empty and both support weight
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
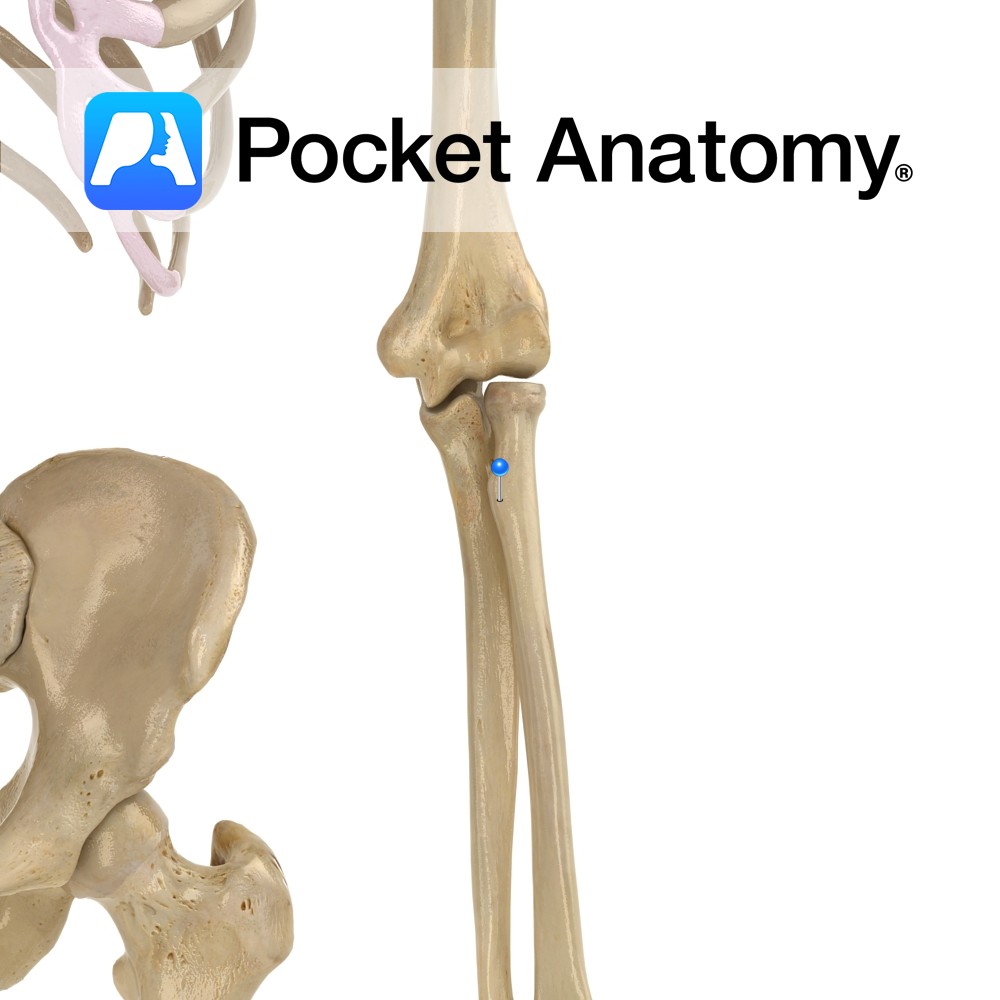
Anatomy Almost cylindrical head of ulna articulates with ulnar notch of radius, distal radioulnar joint. A pivot joint; movement is rotation of radius (and hand; ulna main contributor to elbow joint, radius to wrist joint) around the ulnar head. Clinical Radial head is proximal and articulates with a notch on the ulna (proximal radioulnar joint
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Bulge down from lateral side (thumb-side) lower extremity, conical in shape, giving attachment to tendons of brachoradialis, abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, and radial collateral ligament of wrist. Bigger, more inferior/distal than ulnar styloid. Vignette Chauffeur’s fracture; pressure of scaphoid on styloid. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Broader towards the bottom, slightly curved convex laterally. Radius and ulna joined (syndesmosis joint – allows slight movement) by interosseous membrane along their lengths. Clinical Dinnerfork or bayonet deformity in Colles’ (commonest wrist) fracture; a fall on the outstretched hand). Radial pulse felt against thumb-side anterior/palmar aspect, lower quarter. Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
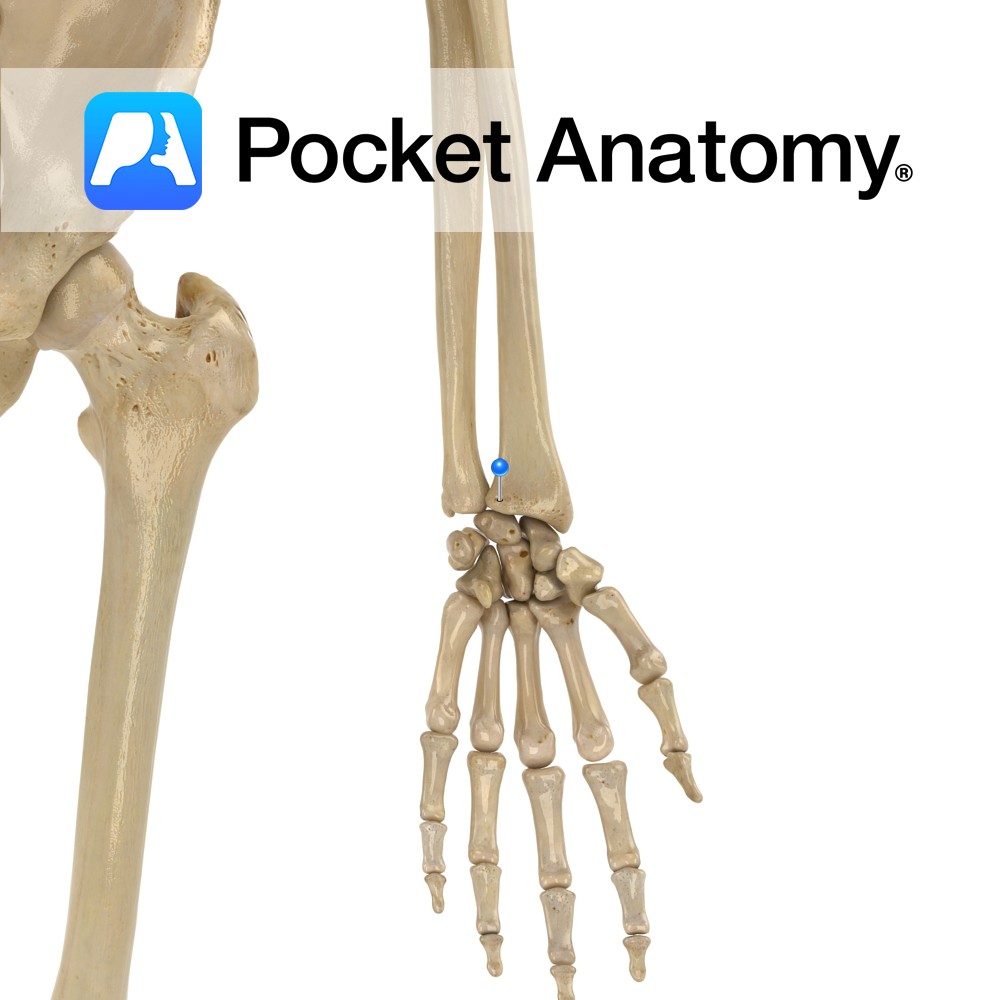
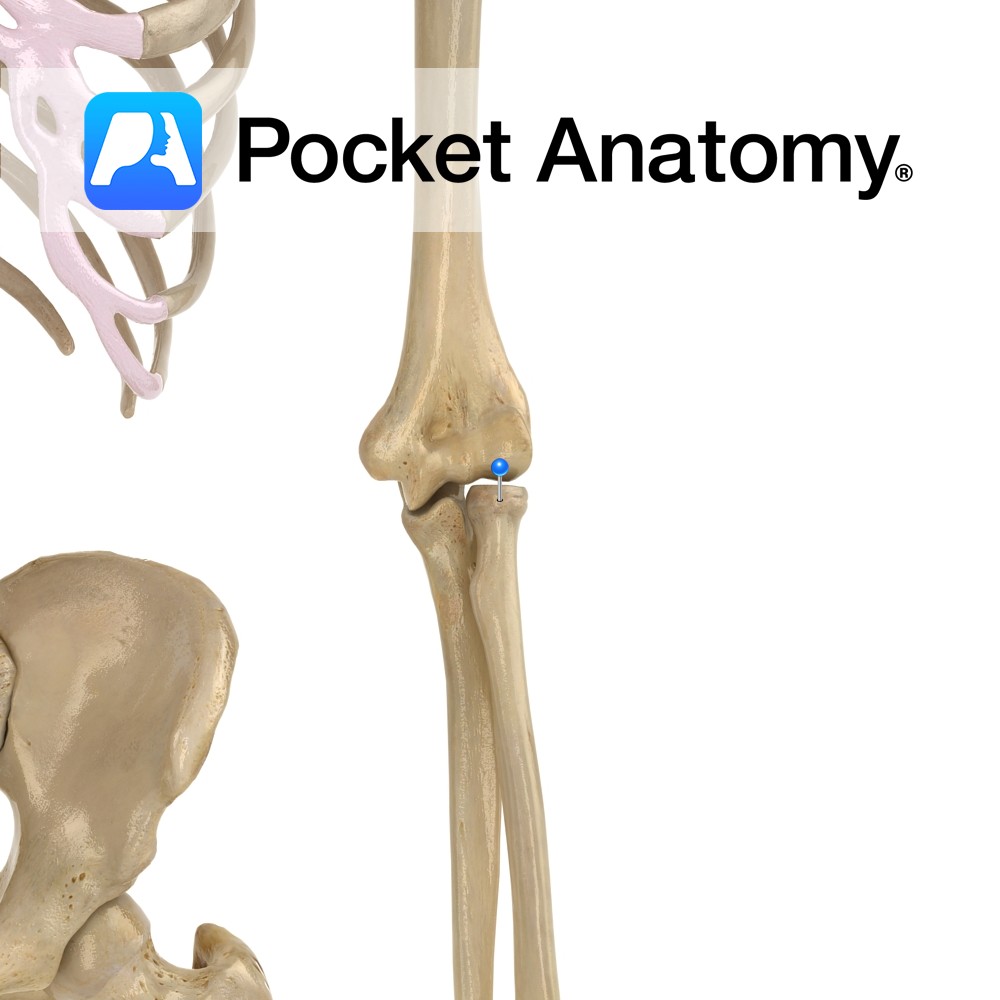
Anatomy A bulge medially, just below radial neck, for insertion of tendon biceps brachii. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
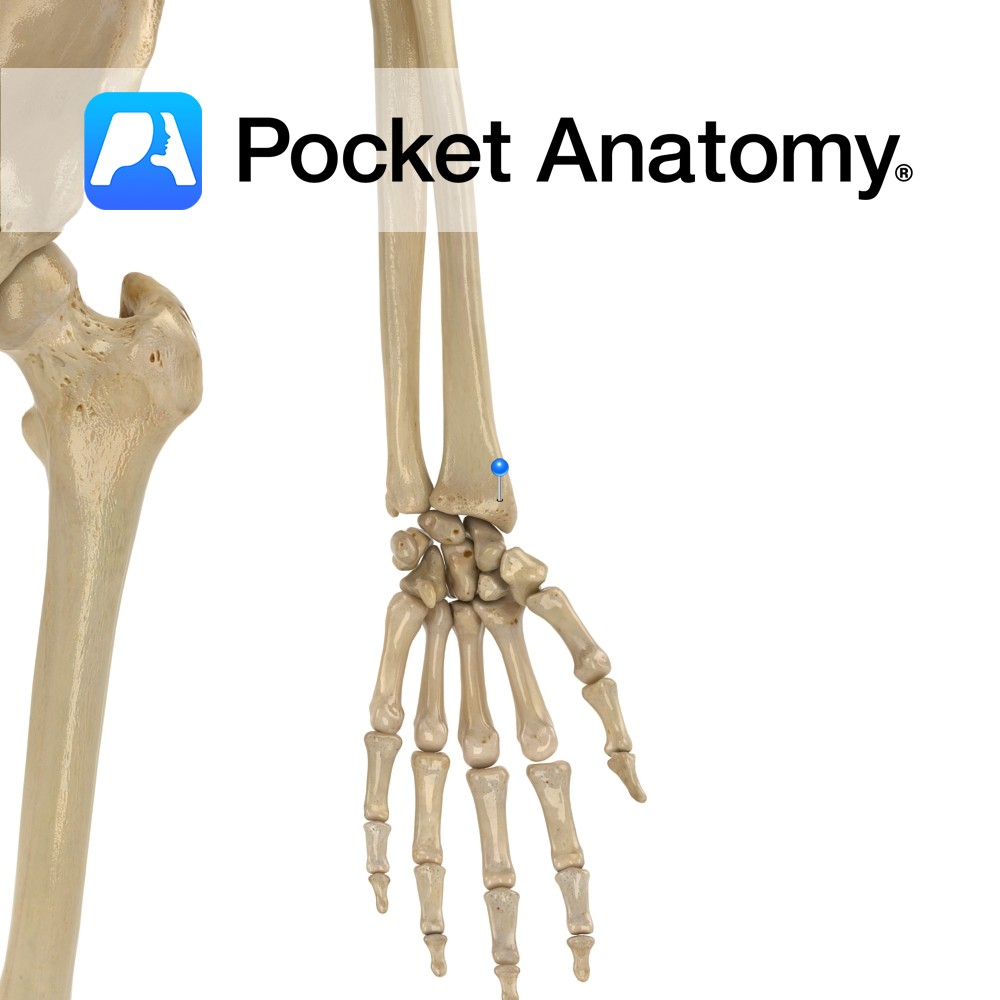
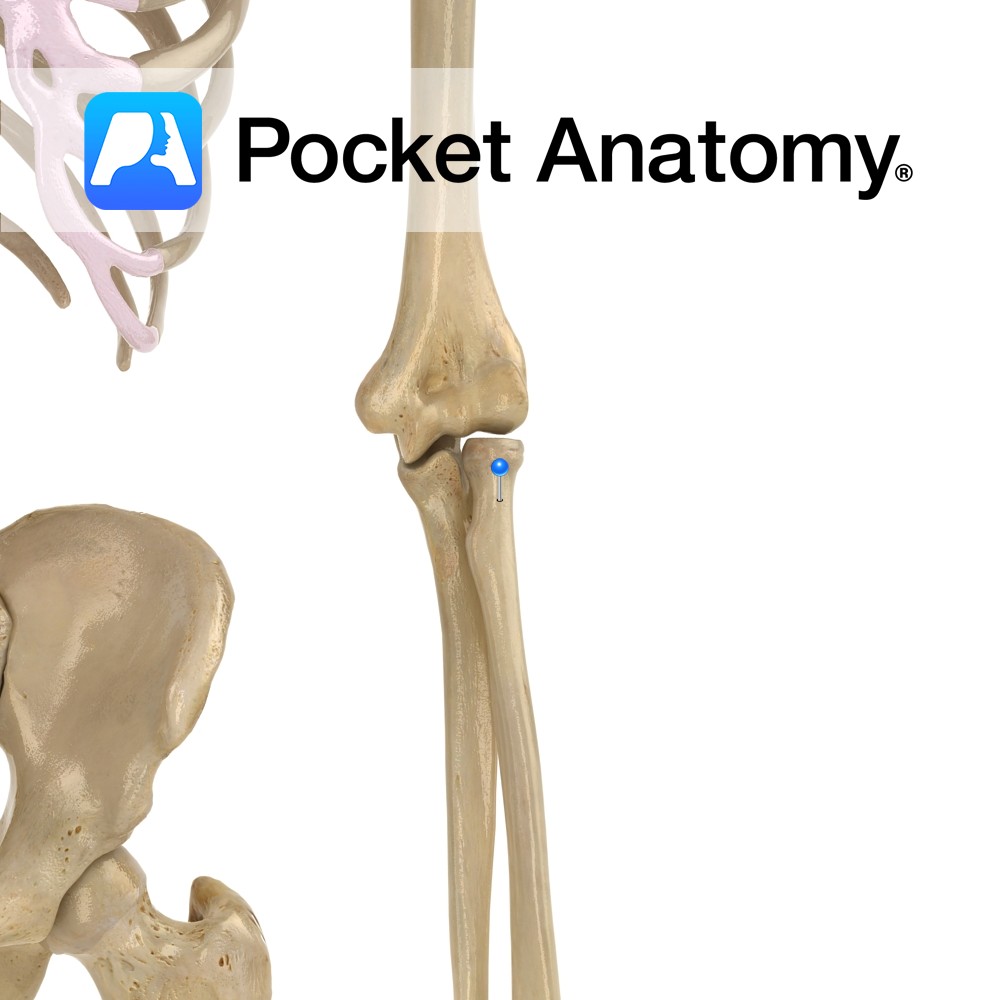
Anatomy A narrowing below the radial head; part of supinator inserts behind. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
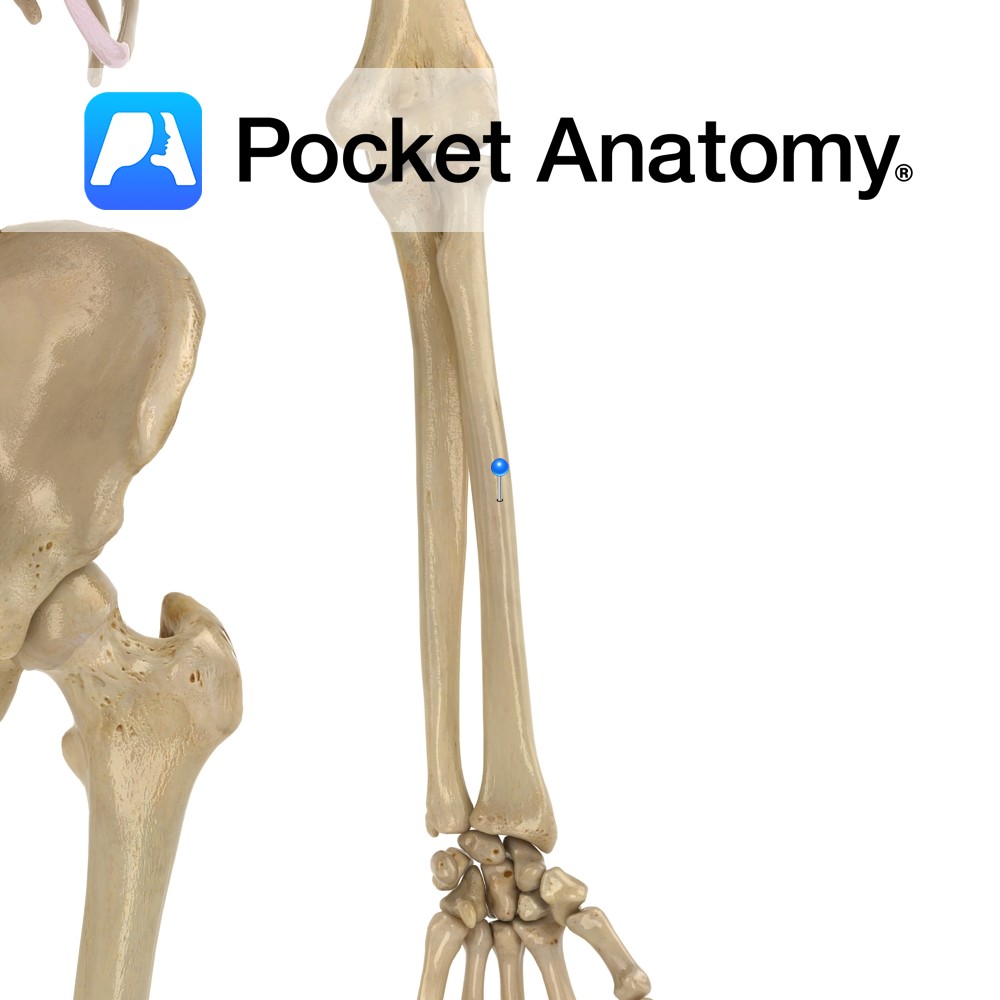
Anatomy Almost cylindrical, articulates with humerus at capitulum, and ulna at radial notch (proximal radioulnar joint). Radiohumeral joint is hinge; movement is flexion-extension. Proximal radioulnar joint is pivot; movement is rotation of radial head inside ring formed by radial notch of ulna and annular ligament. Clinical Radial head is proximal and articulates with a notch
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins