PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Only rib with sternal articulation that straddles manubrium and body. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Most curved, usually shortest (sometimes 12th shorter). Only rib whose posterior/vertebral articulation is with only 1 vertebra (T1). Only rib whose anterior/sternal articulation is entirely with manubrium (lateral extremity of the arm of the cruciform – ross-shaped – manubrium. Clinical Ordinarily there are 12 ribs, sometimes 11, this number added to if there are
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy False rib, i.e. articulates posteriorly but not anteriorly. Tapers to a pointed costal cartilage that ends in abdominal wall. Head articulates with only 1 vertebra (T12); no neck or tubercle. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy False rib, i.e.articulates posteriorly but not anteriorly. Tapers to a pointed costal cartilage that ends in abdominal wall. Head articulates with only 1 vertebra (T11); no neck or tubercle. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
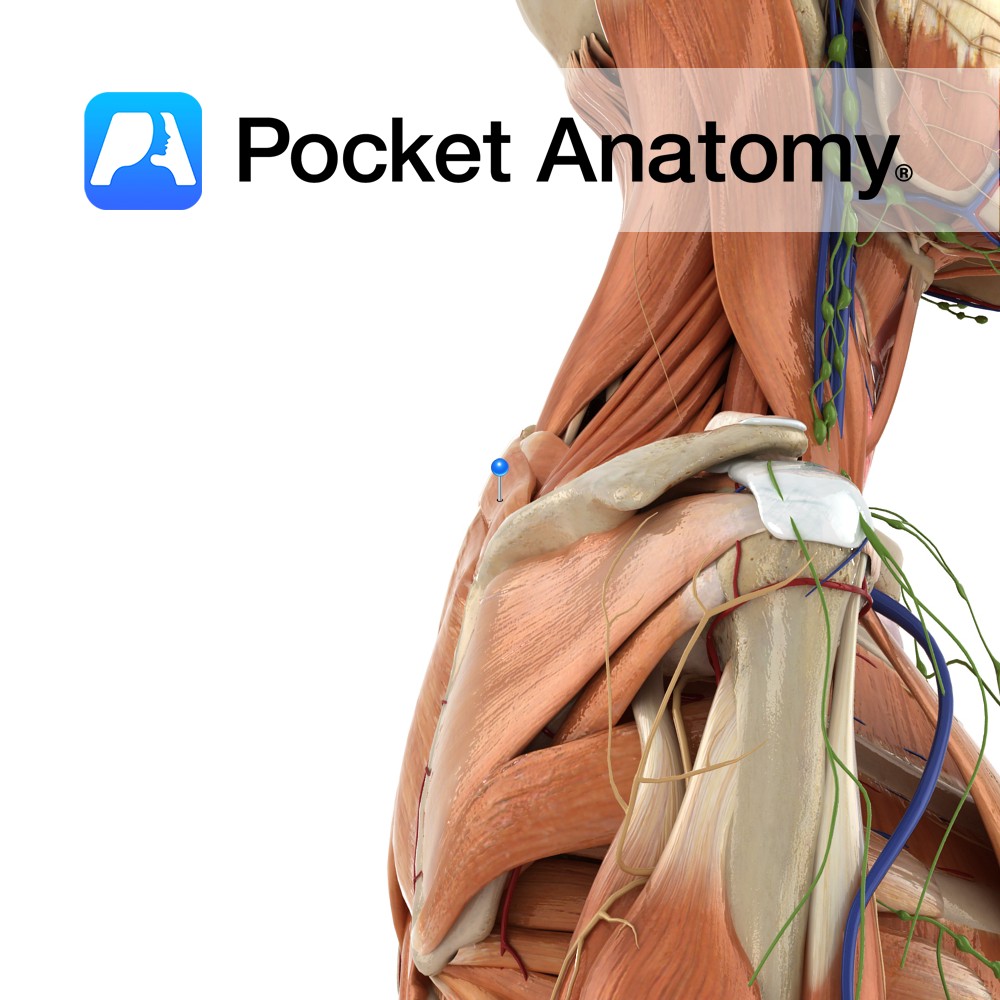
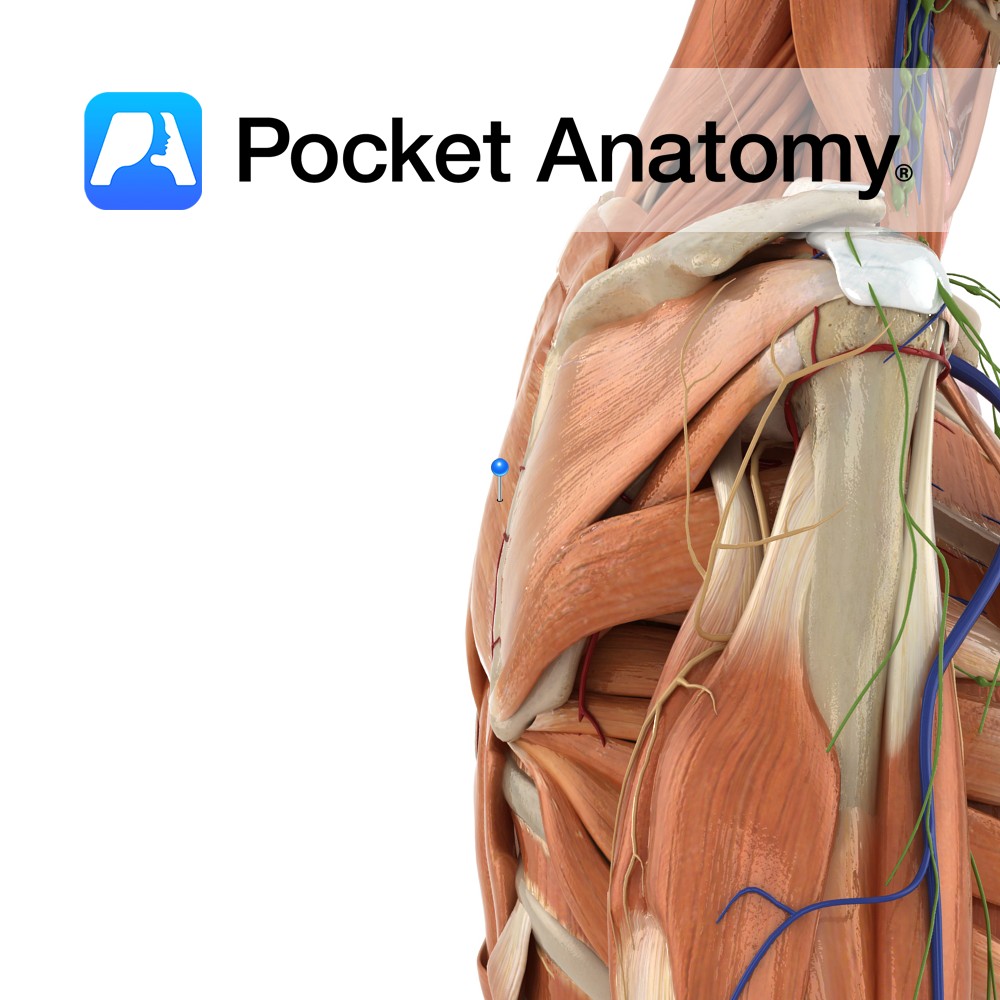
Anatomy Origin: Lower ligamentum nuchae and the spinous processes of C7 to T1. Insertion: Medial border of the scapula at the level of the spine, superior to the attachment of rhomboid major. Key Relations: -Superior to rhomboid major. -Posterior to trapezius. -Fascia of rhomboid minor and serratus anterior are tightly fused. Functions Retracts e.g. pulling
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Spinous processes of T2 to T5. Insertion: Medial border of the scapula between the spine and the inferior angle, inferior to the attachment of rhomboid minor. Key Relations: -Inferior to rhomboid minor. -Posterior to trapezius except at the triangle of auscultation. Functions -Retracts the scapula e.g. pulling open a drawer. -Working with the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
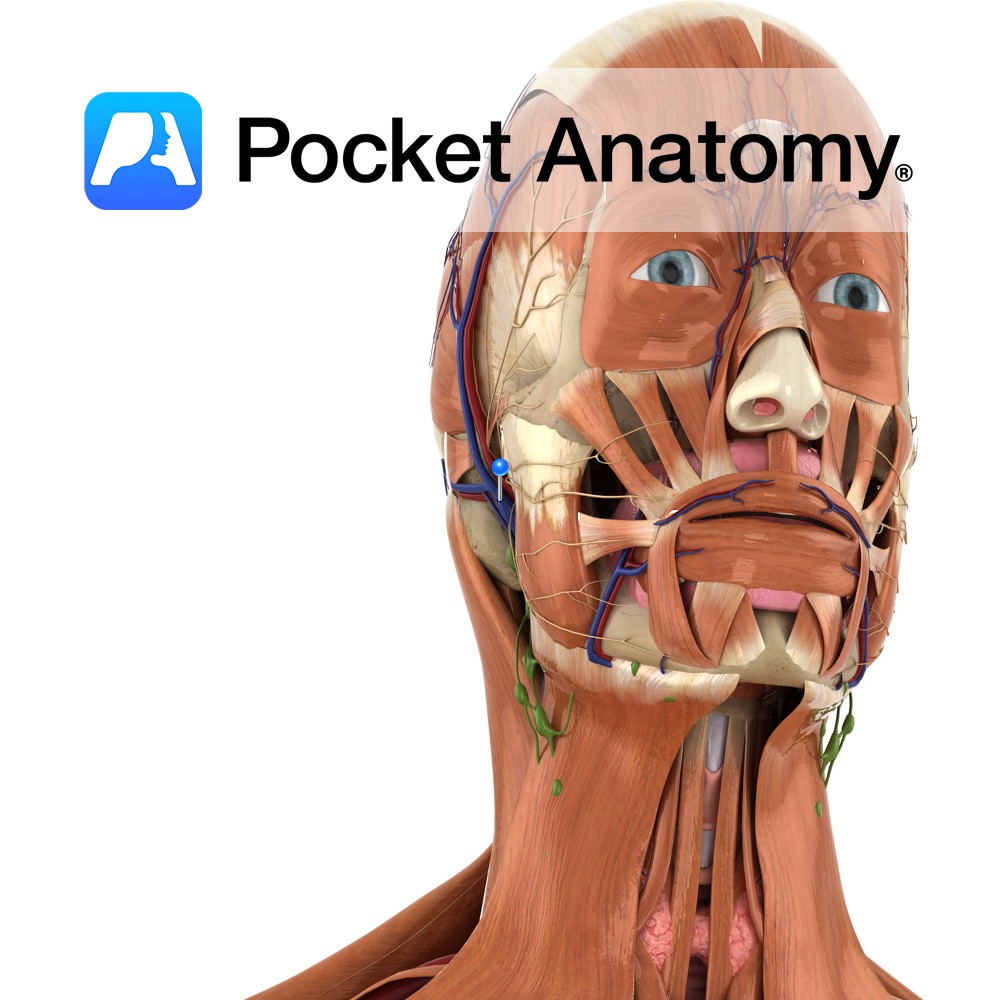
Anatomy Course Formed when the superficial temporal vein and the maxillary vein unite, just superior to the parotid gland. It descends through the parotid gland before dividing into an anterior and posterior branch. Drain The retromandibular vein contributes to the drainage of the deep facial structures and the temporal region of the scalp. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
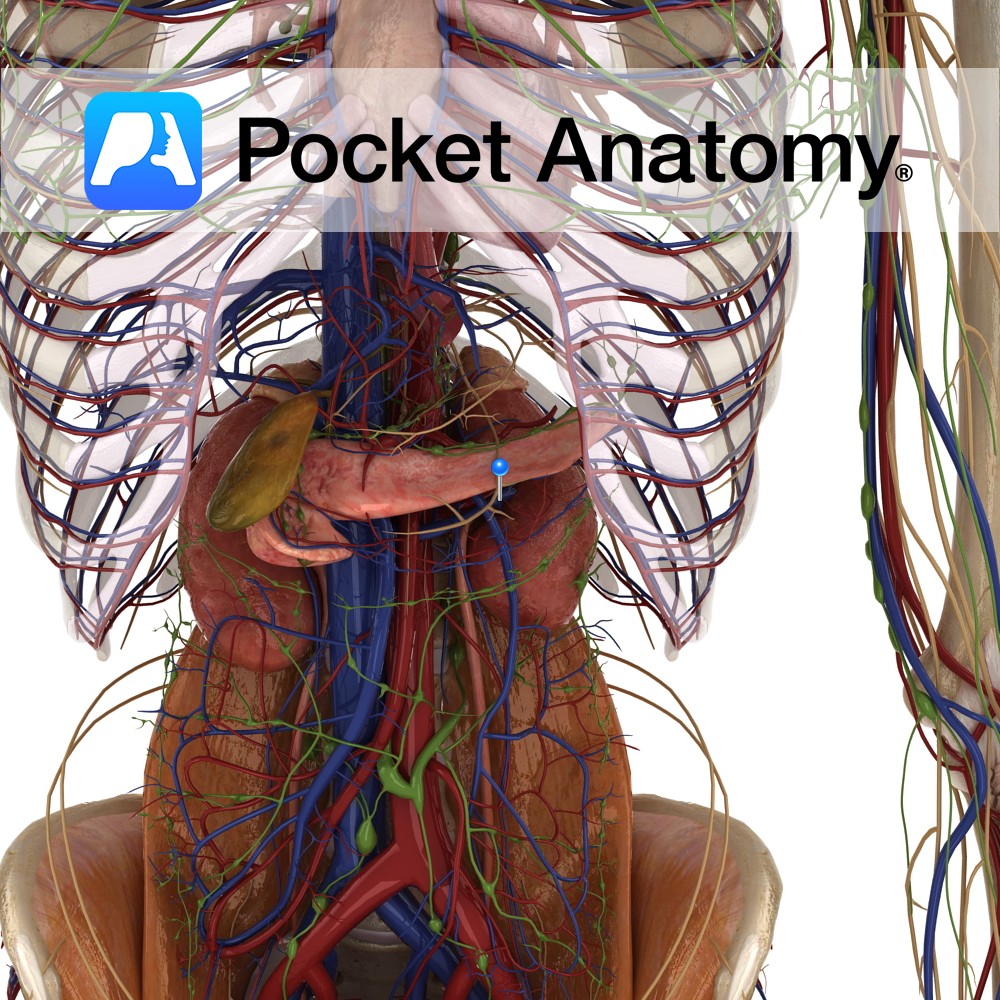
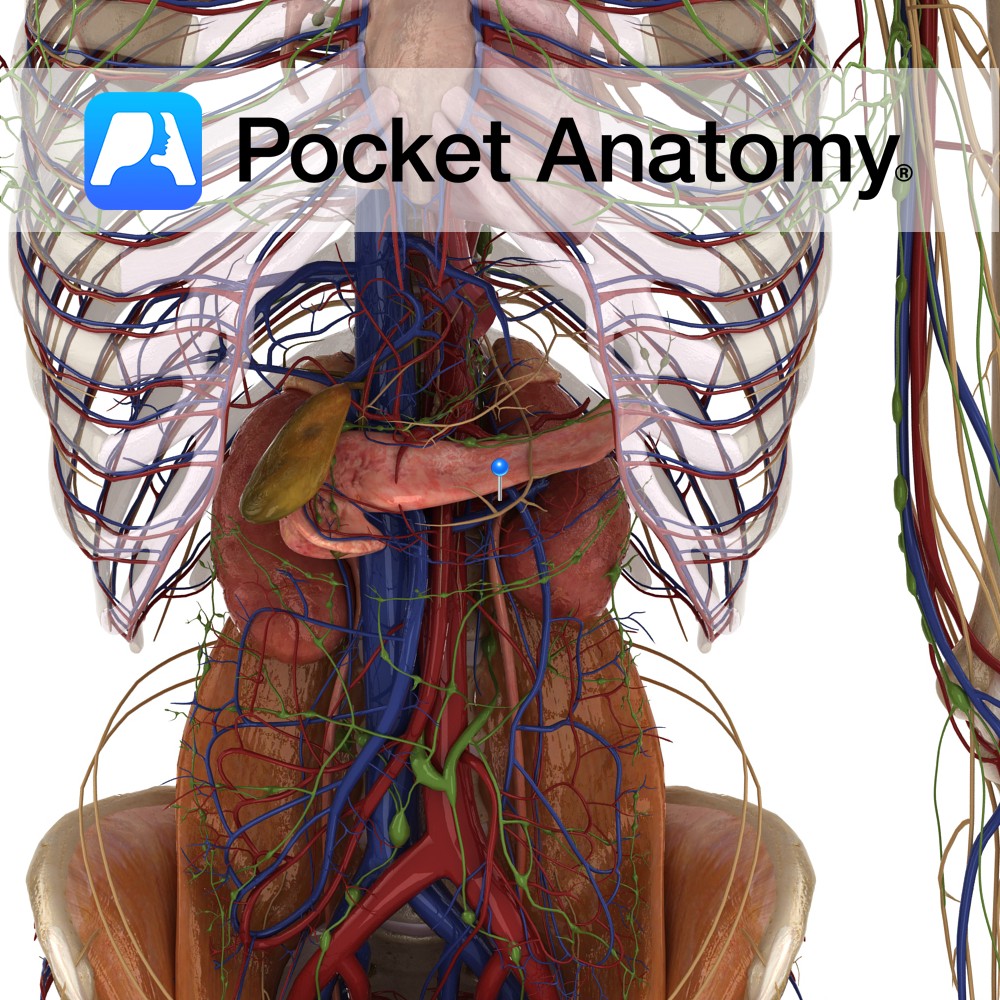
Anatomy Course Begin at the hilums of the kidneys, running horizontally and retroperitoneally to the inferior vena cava. They drain into the inferior vena cava at the approximate vertebral level of L2. Because the left renal vein is longer, and must cross the aorta, it receives a number of tributaries, such as the left phrenic
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course The renal arteries branch directly from the abdominal aorta at approximately vertebral level L1-L2. The right renal artery is longer and must pass behind the inferior vena cava to reach the right kidney. The left renal artery usually originates slightly higher. Both travel horizontally and retroperitoneally to their respective kidneys. Supply Supply blood
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Straight head: anterior inferior iliac spine. Reflected head: a groove on the upper surface of the acetabulum and from the fibrous capsule of the hip joint. Insertion: Base of the patella via the quadriceps femoris tendon. The quadriceps femoris tendon is functionally continuous with the patellar ligament which runs from the apex of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

-%5Btrue-rib%5D.jpg)
-%5Btrue-rib%5D.jpg)
-%5Bfloating-rib%5D.jpg)
-%5Bfloating-rib%5D.jpg)