PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
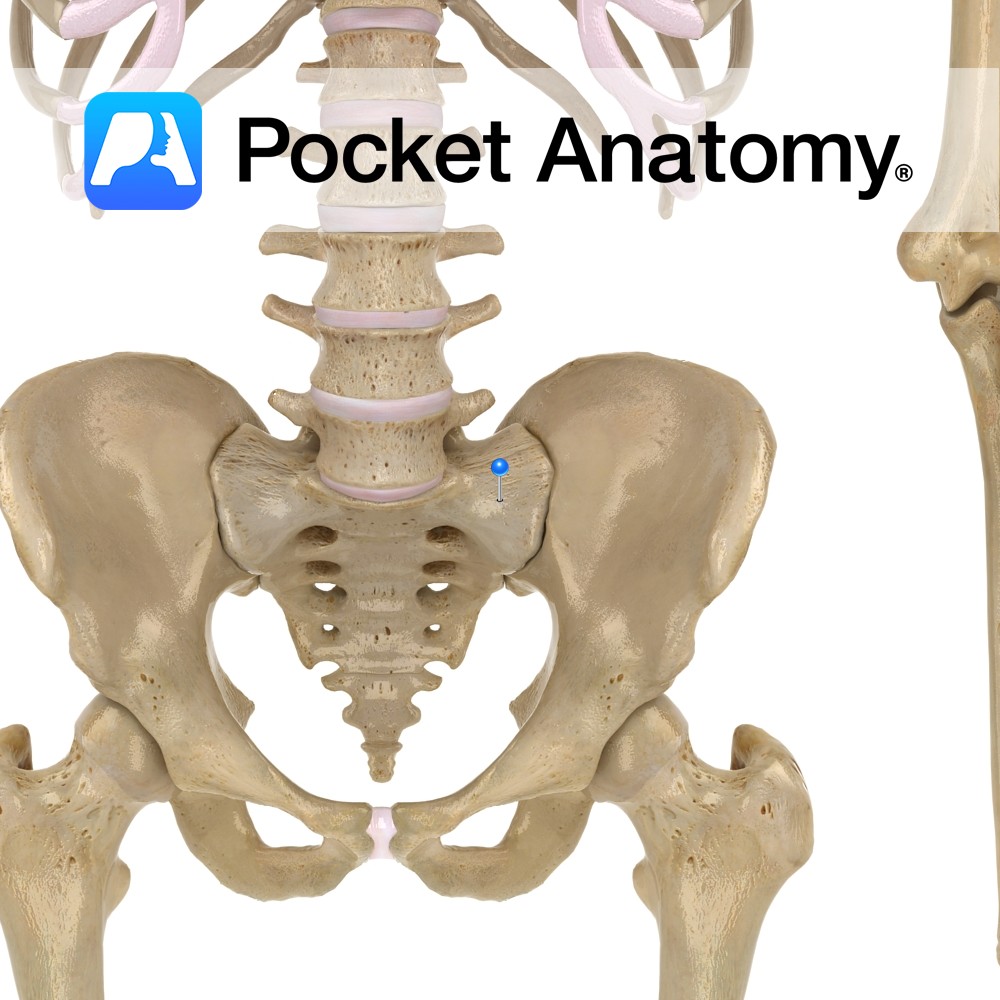
Anatomy Large triangular surface either side of sacral base, continuous with iliac fossa (akin to adapted and joined transverse and costal processes elsewhere spine). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
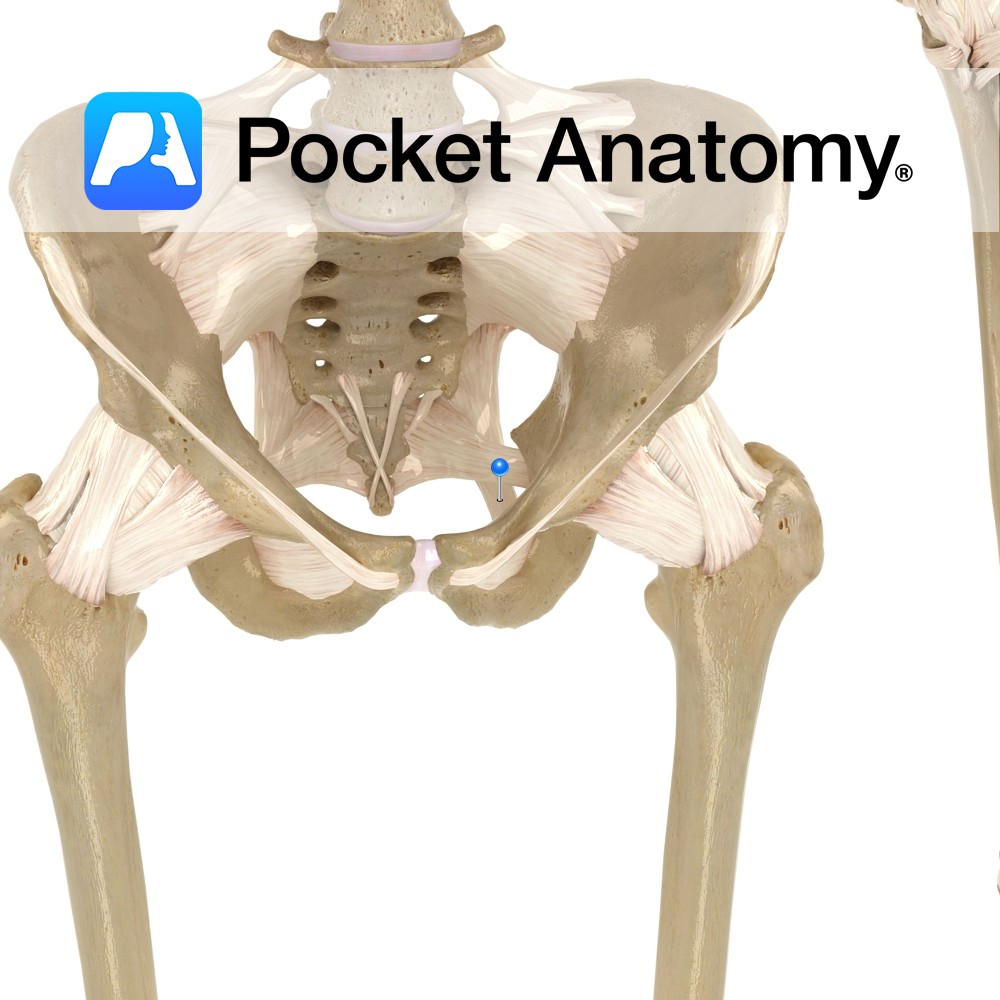
Anatomy Attaches from the posterior border of the ilium, the transverse tubercles of the sacrum, and the superior part of the coccyx, passing downwards to the ischial spine. Functions Provides static stability to the sacroiliac joint. Also, the ligament is important in forming the pelvic wall along with the sacrospinous ligament as they attach all
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
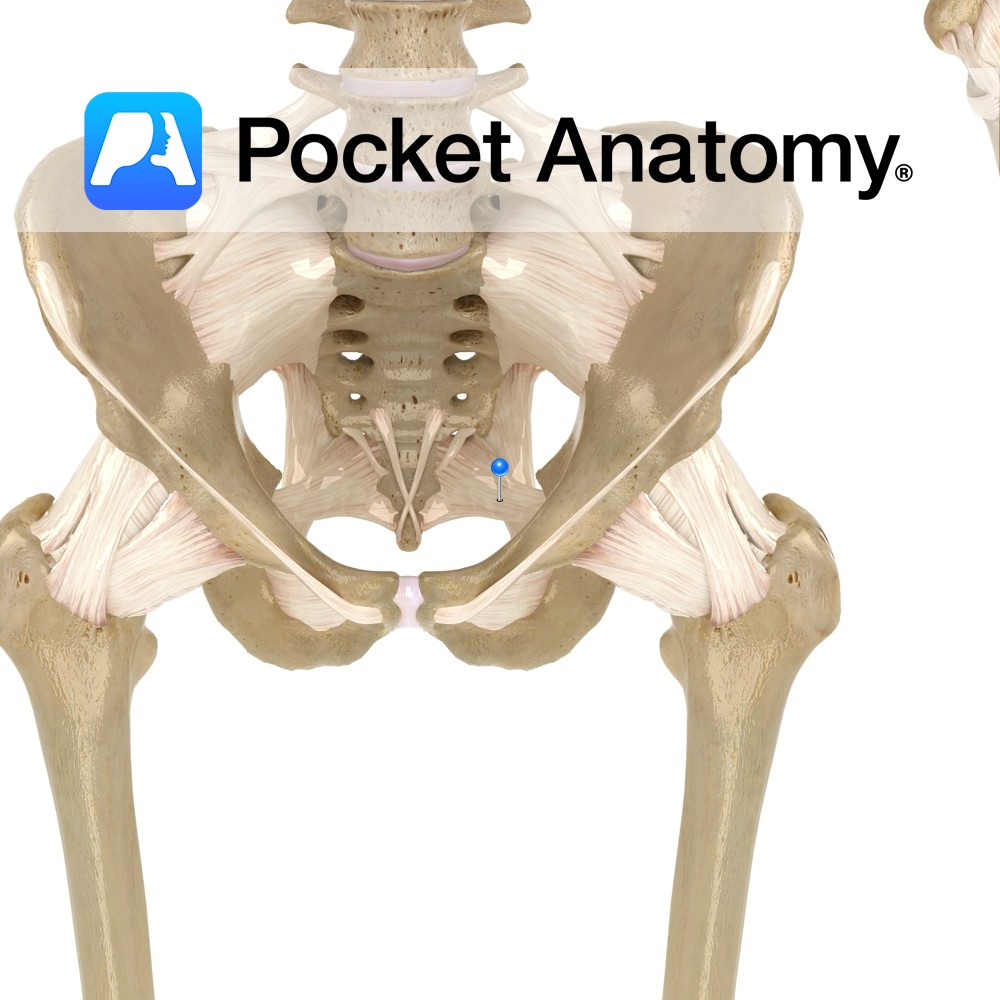
Anatomy Attaches bilaterally from the side of the inferior part of the sacrum and superior part of the coccyx, passing to the ischial spine. Functions Provides static stability to the sacroiliac joint. Also, the ligament is important in forming the pelvic wall along with the sacrotuberous ligament as they attach all the pelvic bones to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
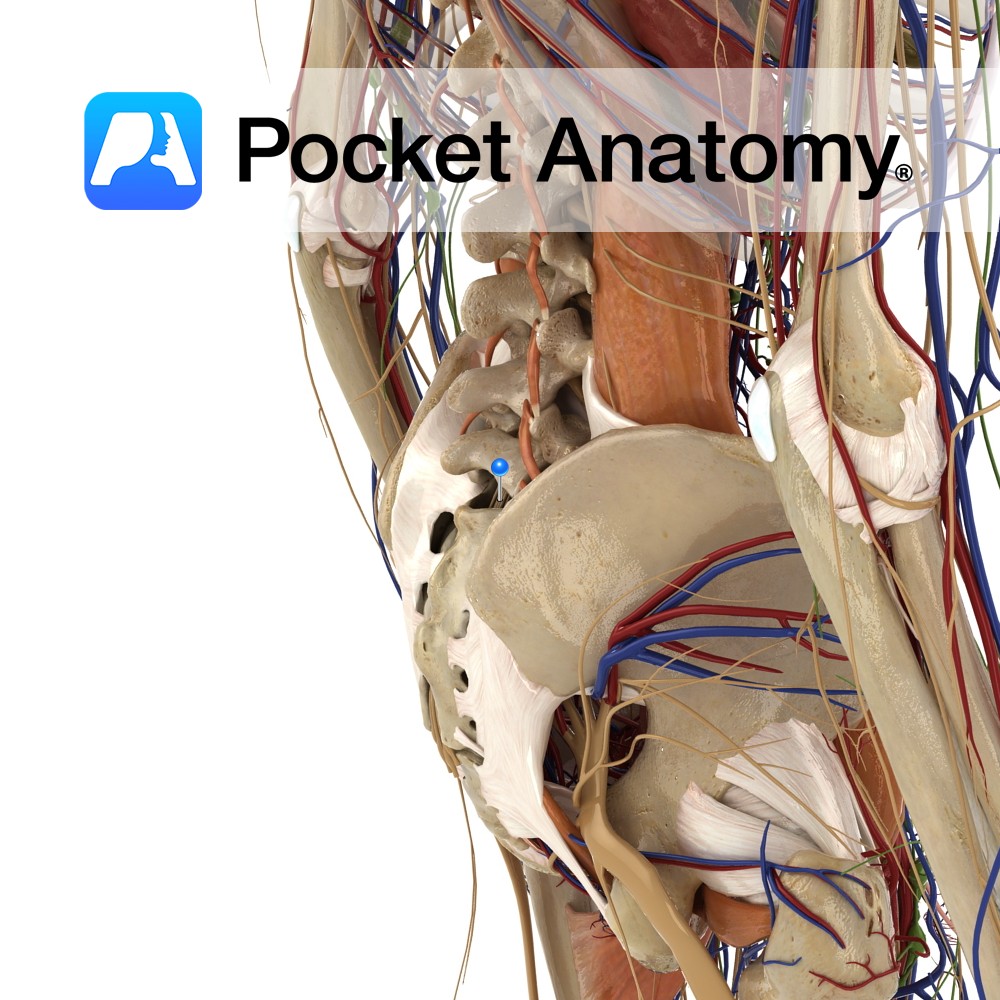
Anatomy Course Made up of the anterior rami of S1 – S4 and the lumbosacral trunk, which is made up of L4 and L5. It is a part of the lumbosacral plexus. It is in the pelvis, located just by the posterior pelvic wall, anterior to the piriformis muscle. The anterior rami of spinal nerves
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy One of the intrinsic muscles of the back. Consists of rotatores cervicus, thoracis and lumborum. Rotatores cervicis: Origin: Articular processes of cervical vertebrae. Insertion: Spinous processes of cervical vertebrae. Rotatores thoracis: Origin: Transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae. Insertion:Spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae. Rotatores lumborum: Origin: Mammillary processes of lumbar vertebrae. Insertion: Spinous processes of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
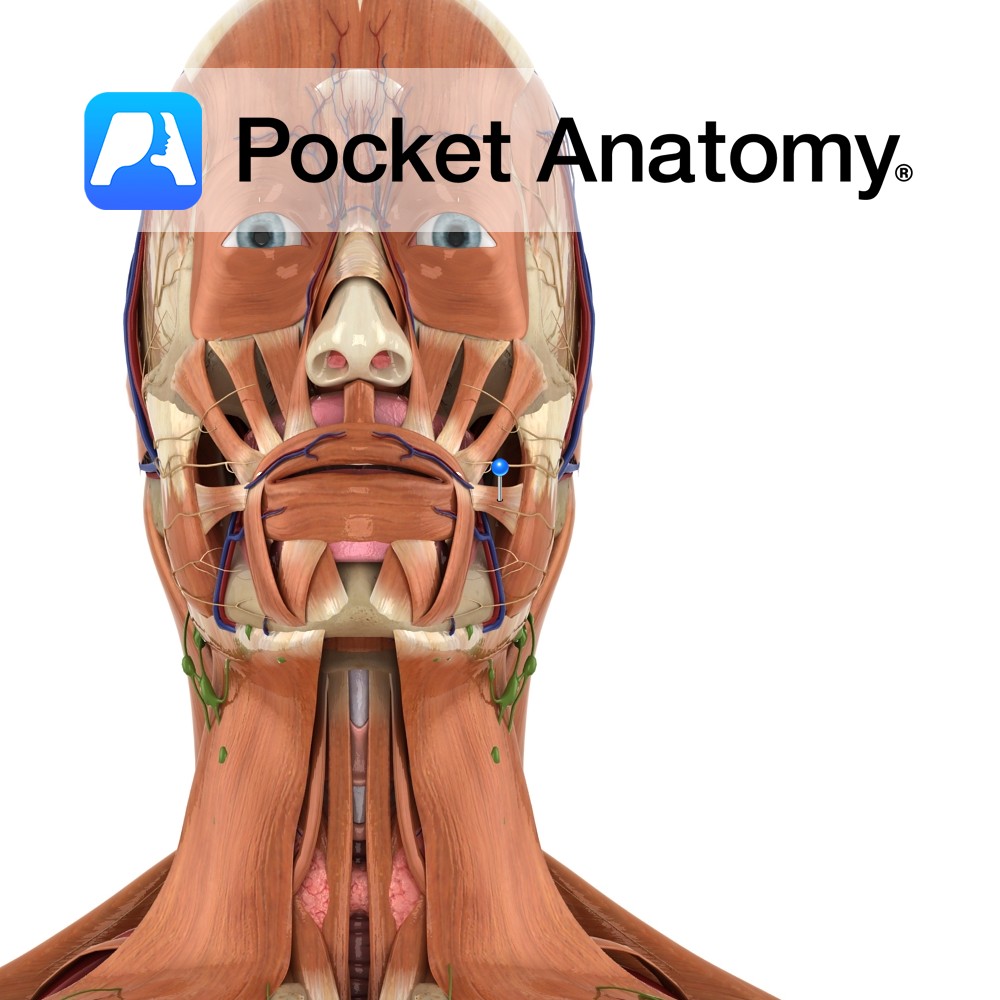
Anatomy Origin: Fascia over the masseter muscle. Insertion: Skin at the corner of the mouth. Key Relations: Thin superficial muscle in the upper group of oral muscles. Functions Pulls the corner of the mouth laterally and upwards. e.g. when grinning.. Supply Nerve Supply: Buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN 7). Blood Supply: Superior labial
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins from a series of veins that drain the ascending colon. It travels through the mesentery to drain into the superior mesenteric vein. Drain Drains the ascending colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
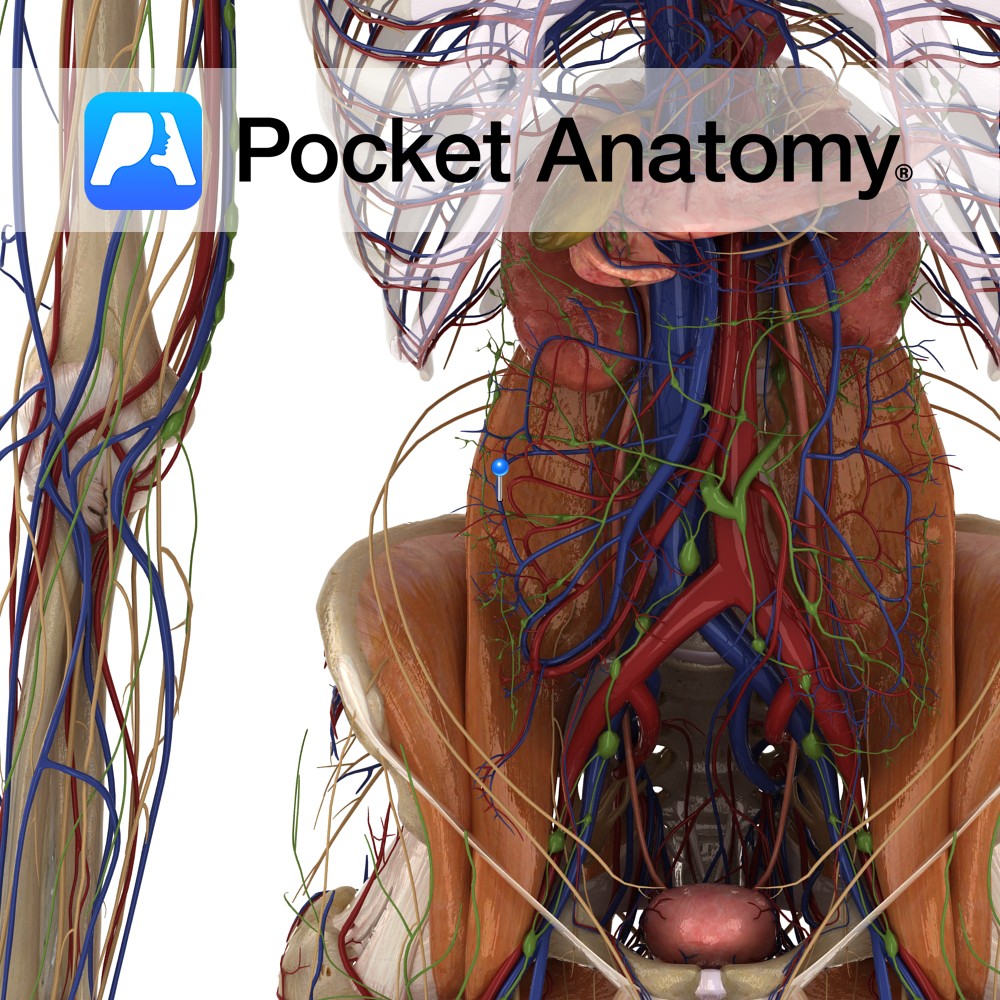
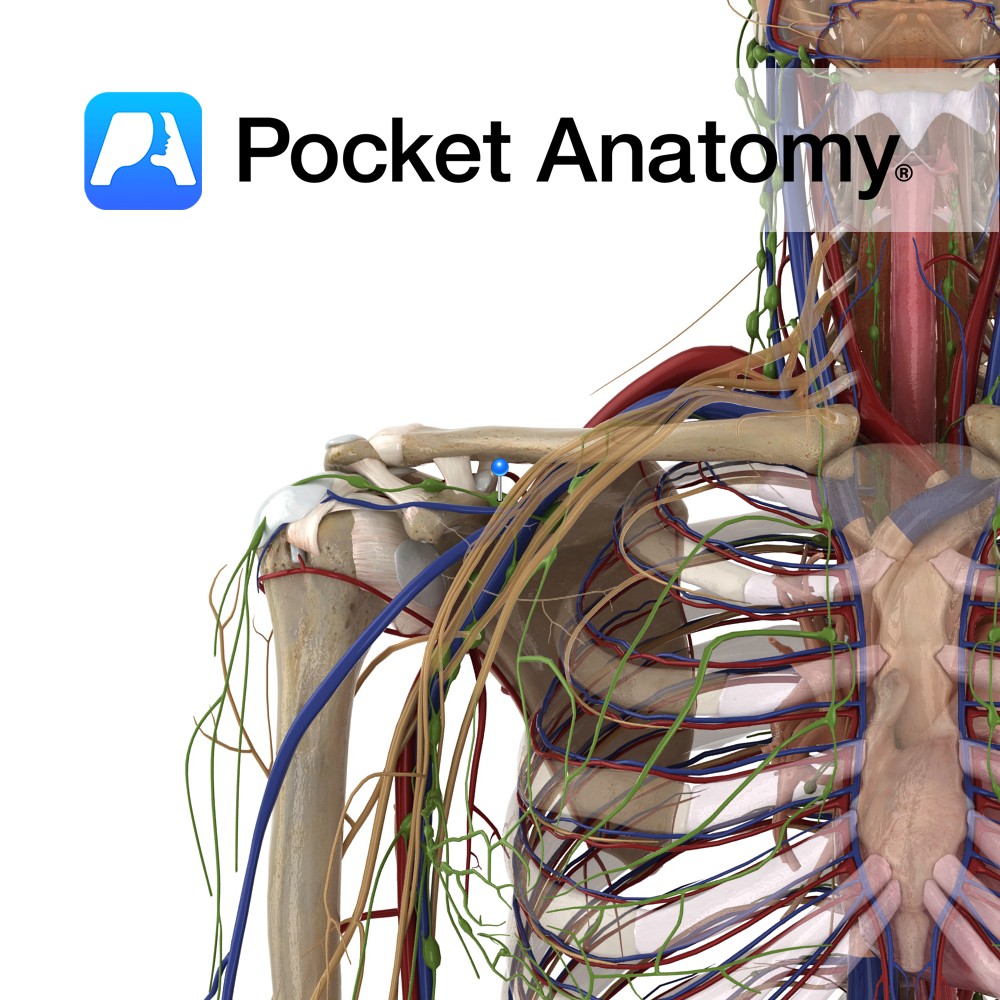
Anatomy Drains R Upper Limb, R side of head and neck and R side of Thorax/chest (and sometimes L lung lower lobe), formed by union of 3 Trunks (R Jugular, R Bronchomediastinal and R Subclavian), about 1/2 inch in length, empties into R Subclavian Vein. Clinical 85% of what leaves through the arteriolar end of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
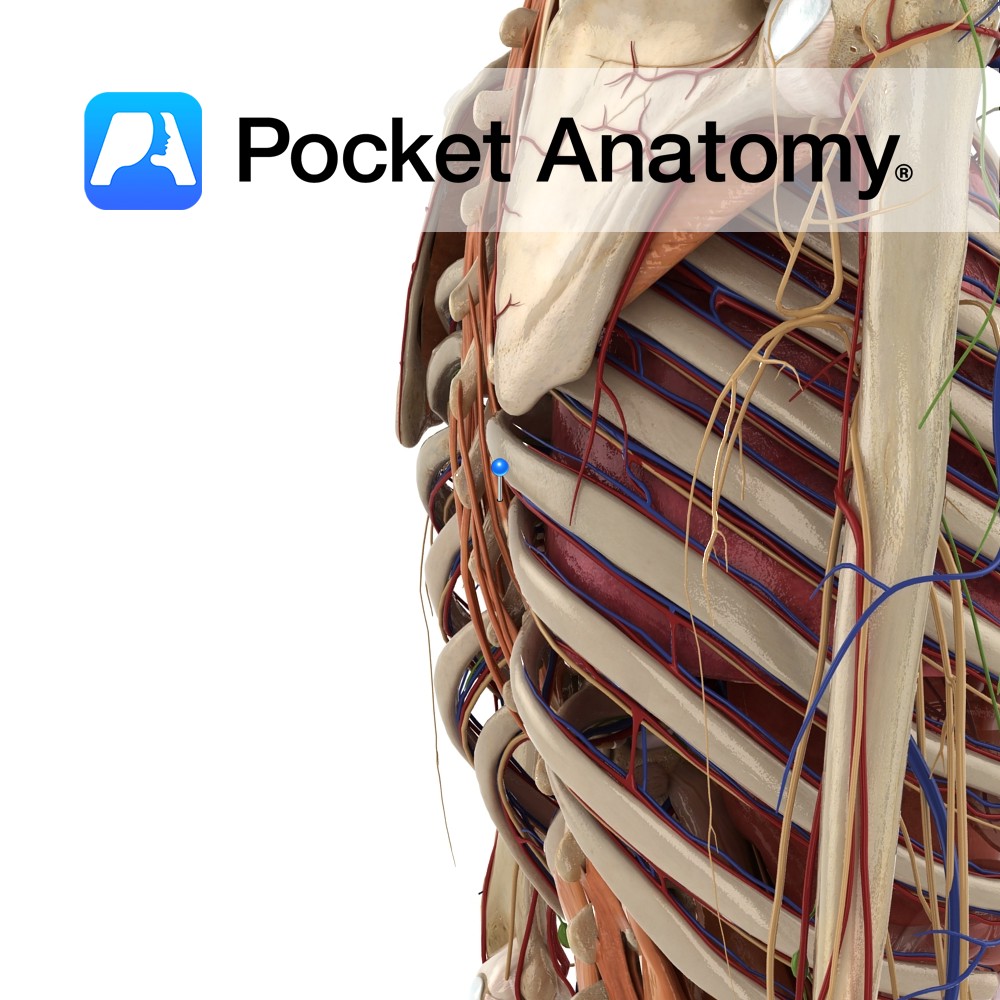
Anatomy False rib, i.e. articulates posteriorly but not directly anteriorly. Its costal cartilages (CC) merges with CC of 7th rib above. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy From 6th rib down, the costal cartilages (CC) above receive contribution from CC below. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

-%5Bfalse-rib%5D.jpg)
-%5Btrue-rib%5D.jpg)