Anatomy
Course
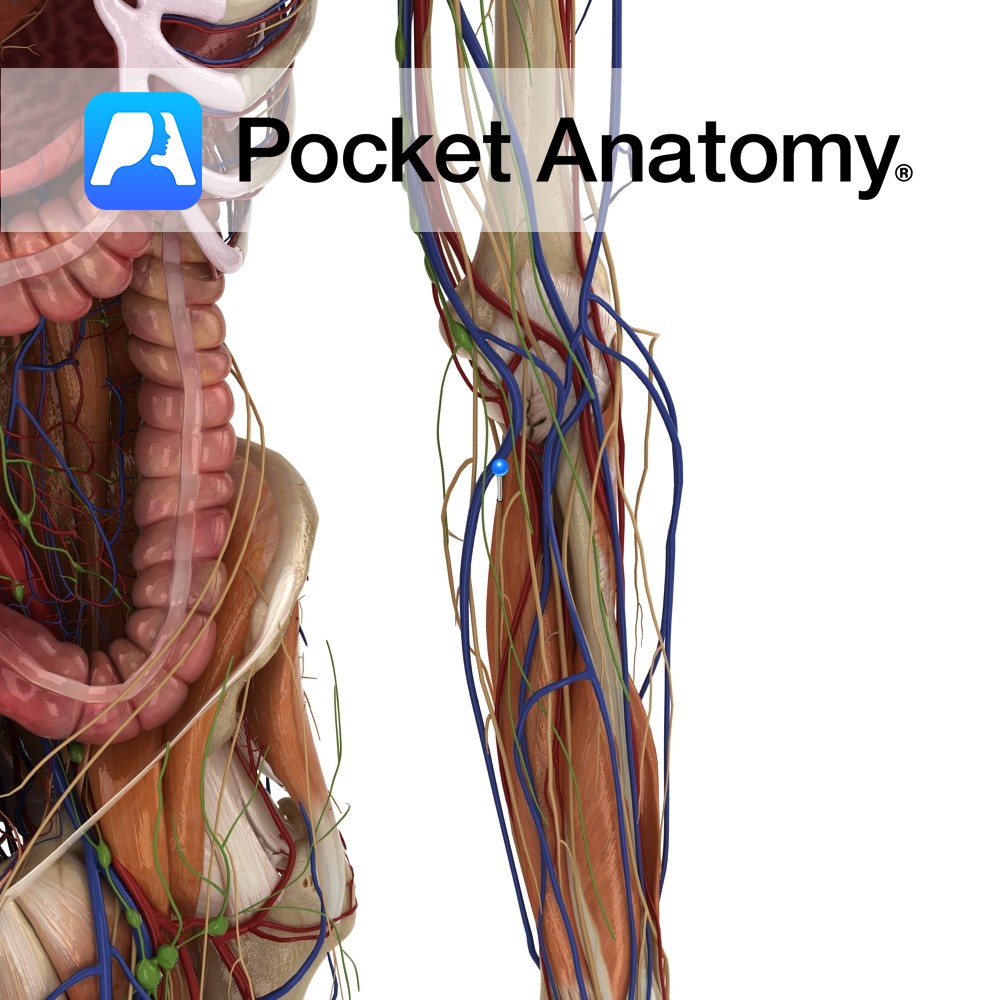
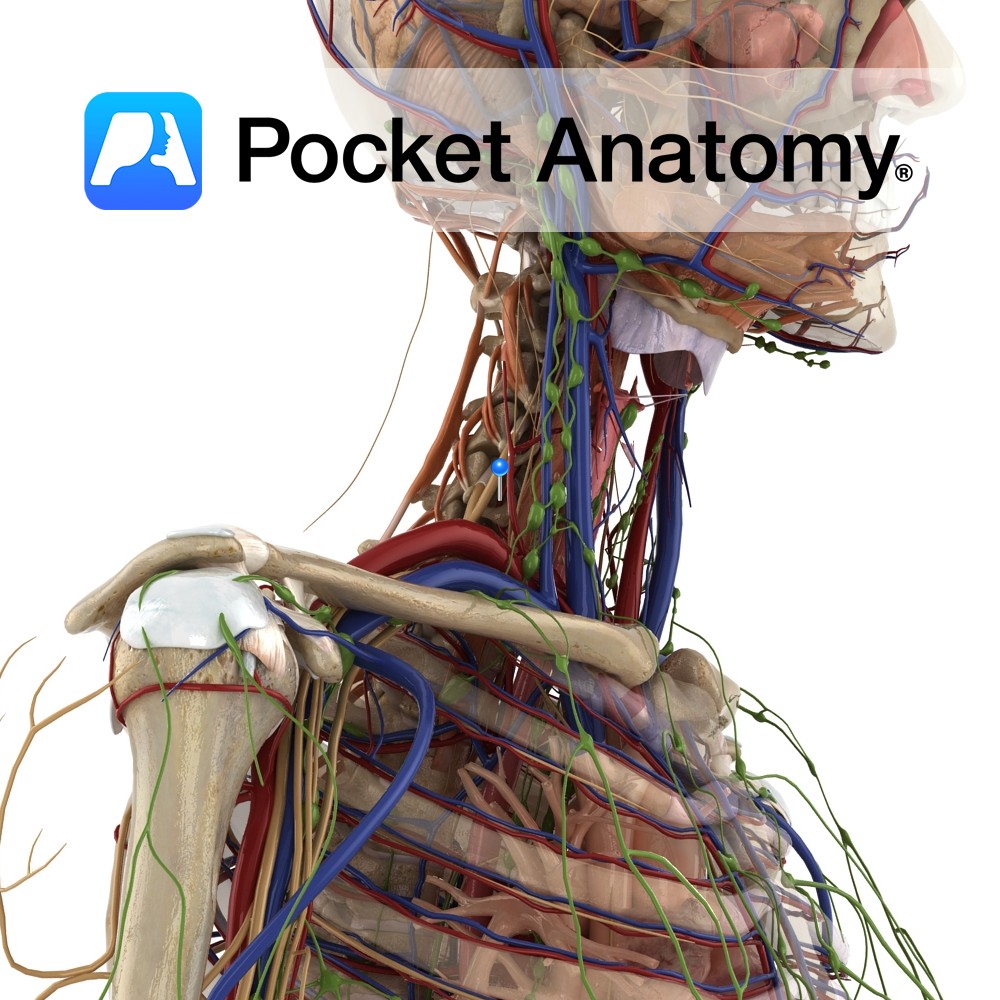
A terminal branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. It enters the arm with the median nerve and then travels on the medial side, until about halfway down the arm, when it pierces the intermuscular septum.
Once it pierces the septum it is in the posterior compartment of the arm, and it passes over the medial head of the triceps brachii. It continues to descend medially, passing beneath the medial epicondyle of the humerus, and then coursing anteriorly to enter the anterior compartment of the forearm, passing between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris.
It continues to descend towards the hand between the flexor carpi ulnaris and the flexor digitorum profundus muscles. It enters the hand superficially to the flexor retinaculum. In the hand it divides into deep and superficial branches.
Supply
Provides motor innervation to two muscles in the forearm – flexor carpi ulnaris and half of flexor digitorum profundus. In the hand, the ulnar nerve provides motor innervation to some muscles on the side of the little finger, as well as sensory innervation here.
Clinical
Easily injured when passing beneath the medial epicondyle, it is responsible for the sensation you get when you hit your ‘funny bone’. Injury to the ulnar nerve results in a clawed hand in a patient. The patient is unable to fully extend the fingers on the medial side, resulting in the little finger and ring finger having a clawed appearance.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?


.jpg)