Anatomy
Origin:
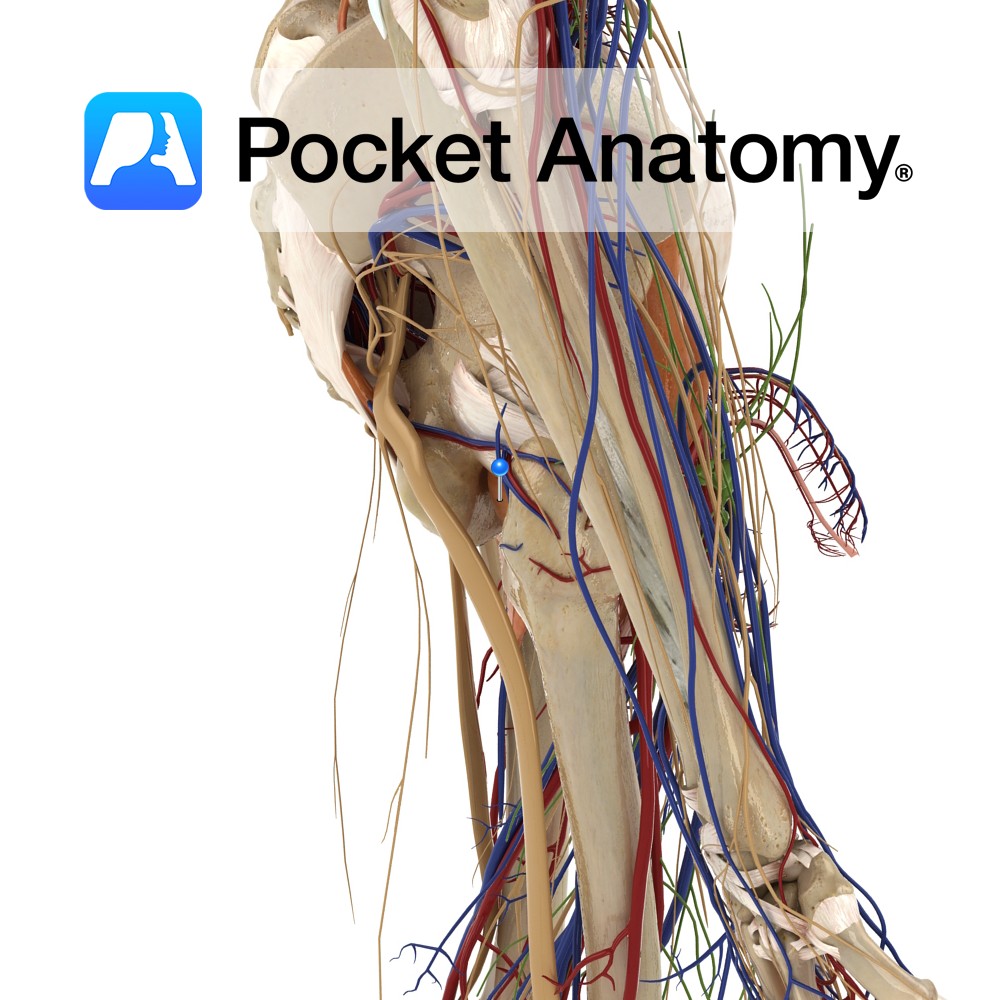
Outer margins of the obturator foramen, the medial two thirds of the obturator membrane and the pubic and ischial rami.
Insertion:
Trochanteric fossa on the medial aspect of the greater trochanter of the femur.
Key Relations:
-One of the six muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh.
-The obturator vessels lie between the obturator externus muscle and the obturator membrane in the obturator canal.
-The anterior branch of the obturator nerve passes in front of the obturator externus muscle while the posterior branch pierces through it.
Functions
-Due to inaccessibility of obturator externus there is little information on its actions. It has been speculated due to its attachment that it laterally rotates the extended thigh and abducts the flexed thigh at the hip joint.
-It is also thought to have a role in stability of the hip joint and is also therefore a postural muscle.
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Posterior branch of the obturator nerve (L3 and L4).
Blood Supply:
–Obturator artery
-Medial circumflex femoral artery.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?