Anatomy
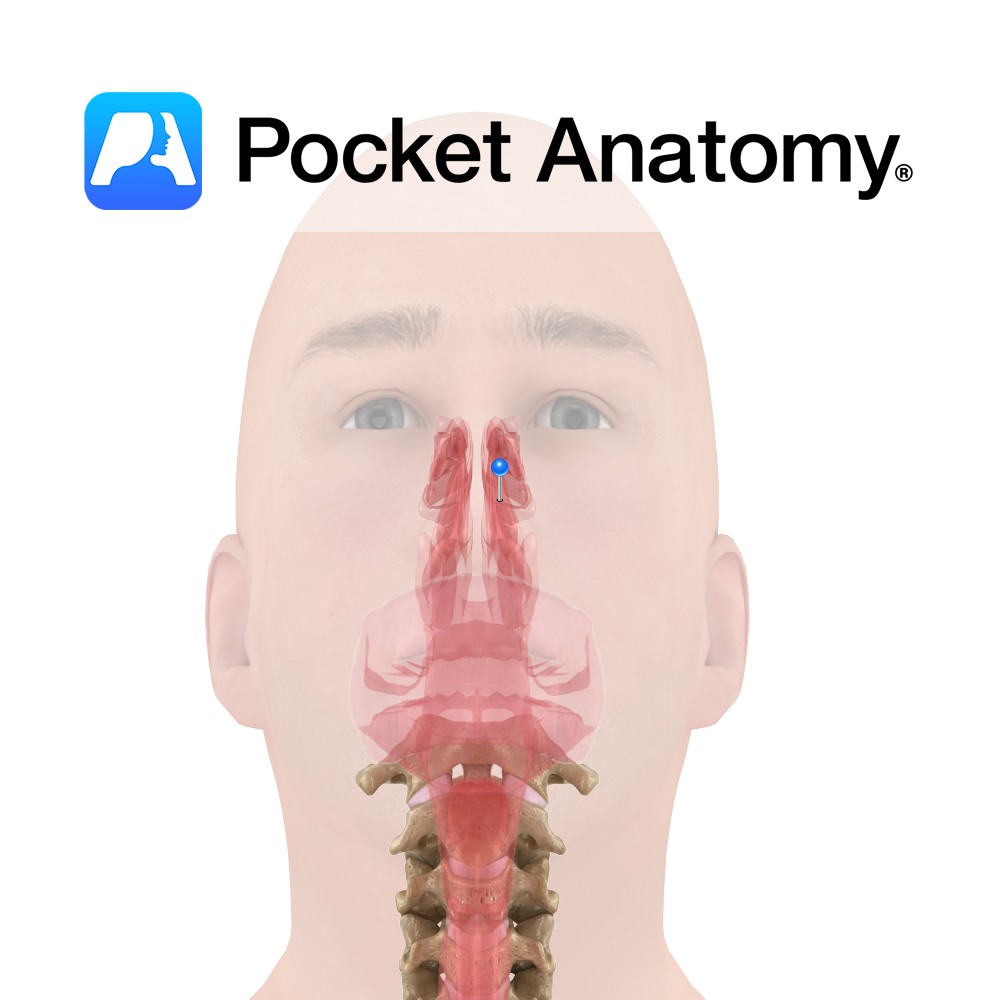
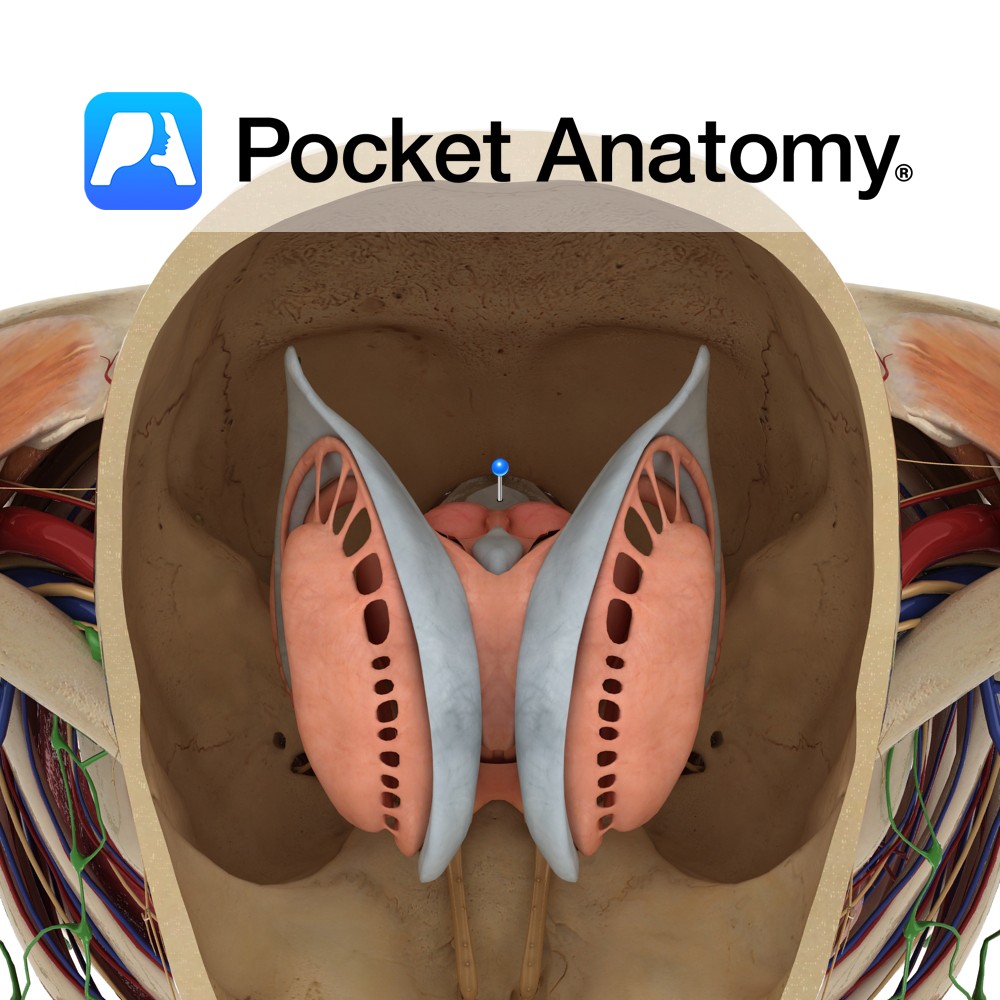
Extends from the nostrils to the posterior nasal apertures where the nasopharynx begins. The cavity is pear shaped on the coronal section and divided by a median septum. The borders are as follows:
The roof is very narrow (2cm) and forms the floor of the anterior cranial fossa. It is formed by the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone centrally, the body of the sphenoid posteriorly and the frontal and nasal bones anteriorly.
The floor is broad and forms the roof of the oral cavity. It is made up of the palatine process of the maxilla anteriorly and the horizontal plate of the palatine maxilla bone posteriorly.
The lateral wall is formed by the ethmoid bone superiorly and the nasal and frontal bones anteriorly and superiorly, the maxilla and lacrimal bones anteriorly, the vertical plate of the palatine bone posteriorly and the sphenoid posterosuperiorly. The lateral walls approach the septum from inferior to superior.
The medial wall is formed by the perpendicular of the ethmoid, the vomer and the septal cartilage.
Functions
Smell.
Warming and humidifying inhaled air.
Trapping particles in secreted mucous.
Modifying sounds produced by the larynx.
Supply
Nerve: anterior ethmoidal nerve – nasopalatine nerve – medial and lateral posterior superior nasal branch of the pterygopalatine ganglon – superior alveolar branch of the maxillary nerve – posterior inferior branch of the greater palatine nerve – olfactory nerve – infraorbital nerve.
Blood: maxillary artery – opthalmic artery
Lymph: submandibular nodes – retropharyngeal nodes.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?