Anatomy
Origin:
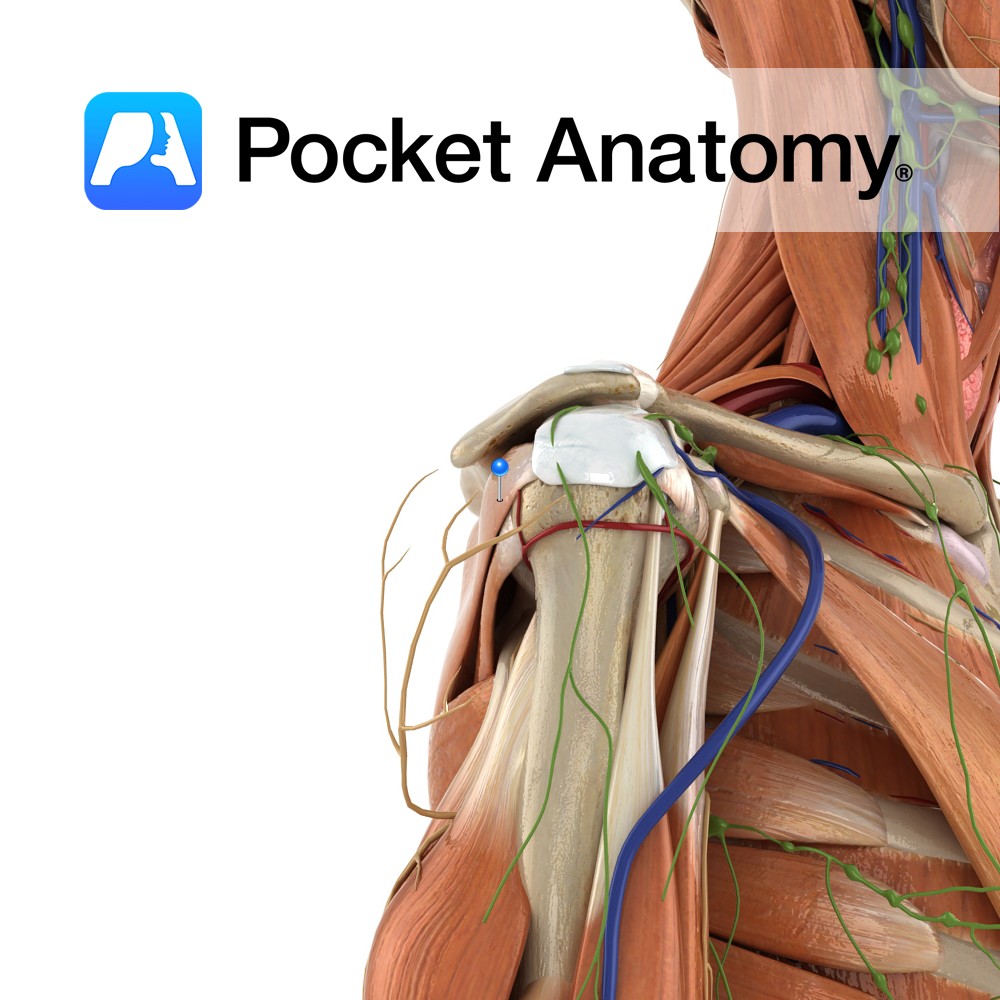
Medial two-thirds of infraspinous fossa of scapula and infraspinous fascia that covers the muscle.
Insertion:
Middle facet of greater tubercle of humerus.
Key Relations:
-The tendon of infraspinatus is sometimes separated from the capsule of the shoulder joint by a bursa, which may communicate with the joint cavity.
-One of the four muscles of the rotator cuff muscle group.
Functions
-Lateral rotation of the arm at the glenohumeral joint (with Teres minor).
-Abducts the arm at the glenohumeral joint e.g as in brushing your hair.
-Contributes to the stability of the shoulder joint with the other rotator cuff muscles.
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6).
Blood Supply:
-Suprascapular artery
-Circumflex scapular artery.
Clinical
Shoulder pain may be caused by infraspinatus tendinitis although this is not the most common cause of shoulder pain. Tenderness mostly occurs at the point of insertion.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?