Motion
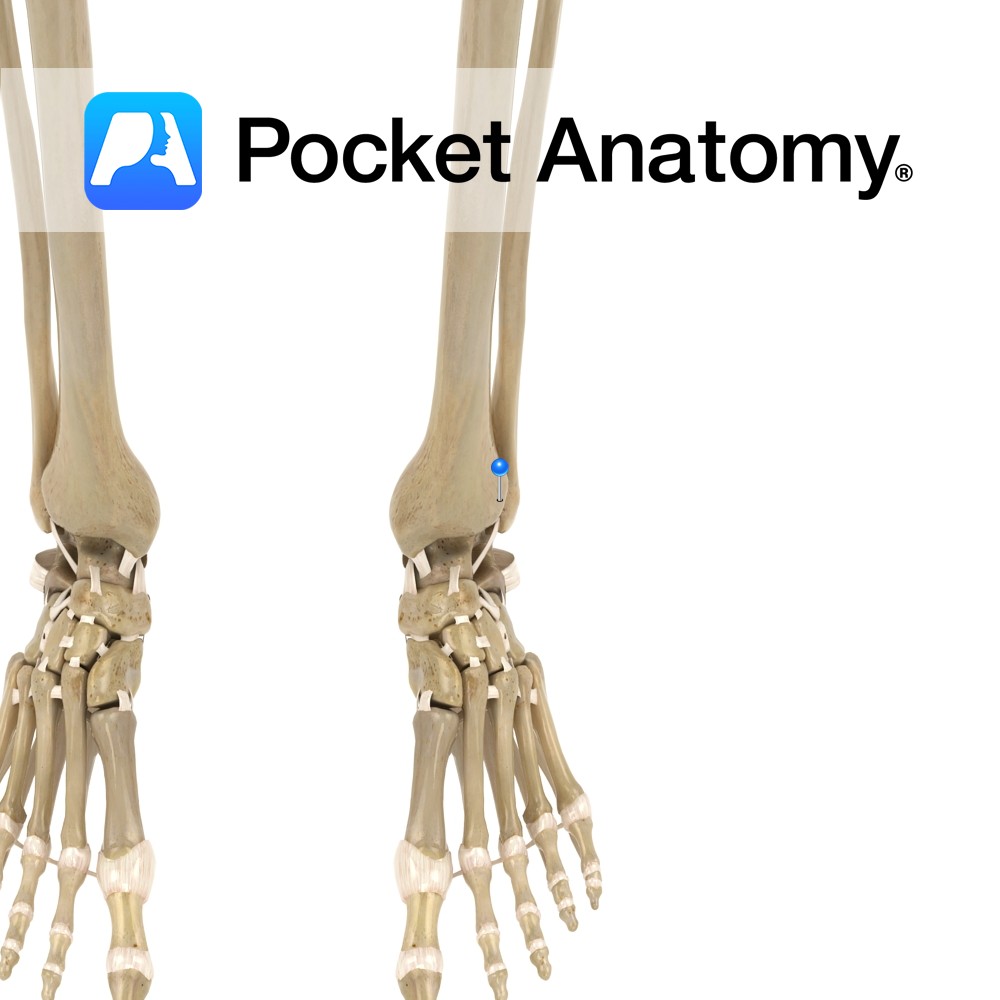
The distal tibiofibular joint is a syndemosis type fibrous joint. The medial surface of the inferior end of the fibula articulates with the fibular notch on the lateral side of the tibia. It allows very little movement but slight movement accommodates the talus during dorsiflexion of the foot.
Stability
Ligaments stabilizing the joint include:
– Interosseous tibiofibular ligament
–Anterior tibiofibular ligament
–Posterior tibiofibular ligament
-Transverse tibiofibular ligament
The strength of this joint contributes to the stability of the ankle joint.
Muscles
The anterior tibiofibular ligament is weaker than the posterior tibiofibular ligament. The anterior tibiofibular ligament is commonly torn, often as a result of supination/external rotation ankle injuries.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?


.jpg)