Anatomy
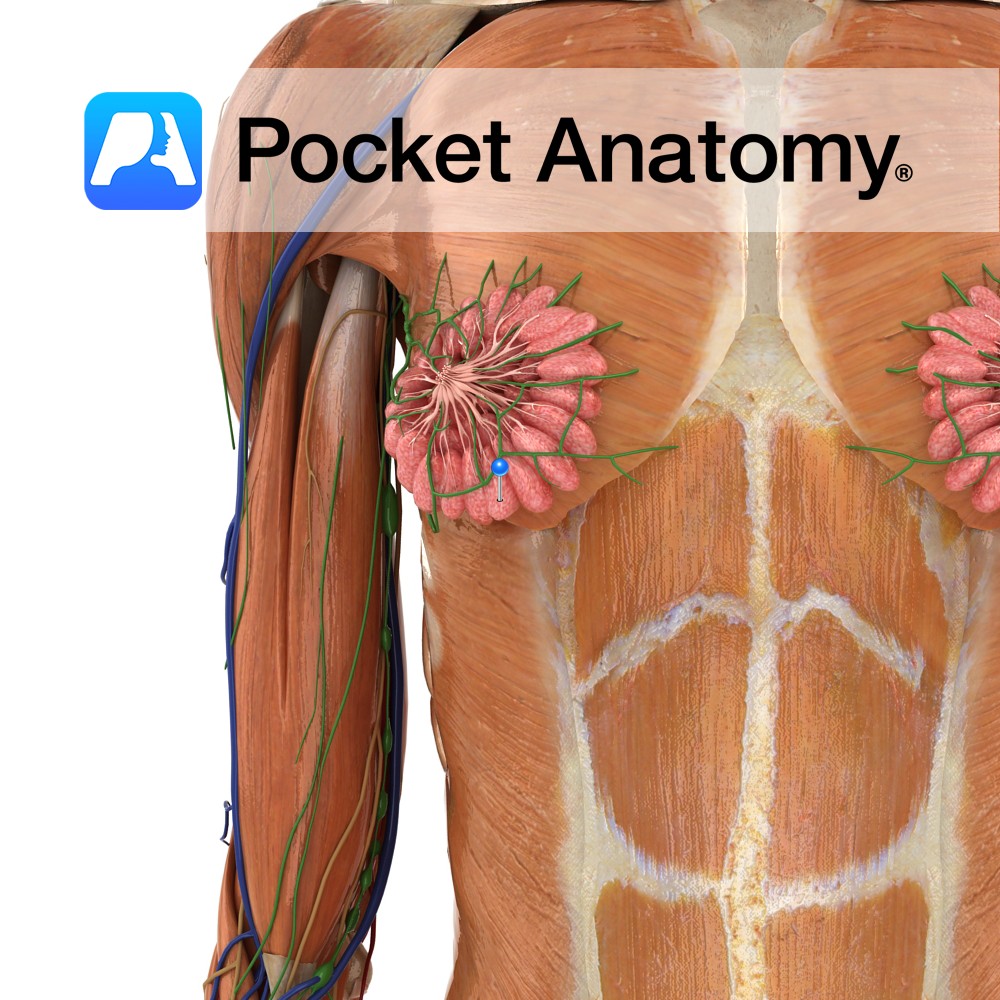
Milk-producing component of breast (15-20 in each breast, 10-100 acini/clusters of milk-producing cells each lobe/lobule), drained to the nipple by a duct (breast is modified sweat/apocrine gland, ie an exocrine gland, its secretion being milk), irregularly arranged around the nipple, subcutaneous, composed of fatty tissue in a stroma and supported by ligaments (Cooper’s).
Physiology
Hormonal influences (estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, oxytocin) throughout life cause/influence/stimulate development (puberty/menarche), monthly/cyclical change and preparation for potential pregnancy (menstruation), preparation for childbirth (pregnancy), breastfeeding (lactation) and eventual involution/shrinkage (menopause).
Clinical
Benign breast disease is common (30-60%), presenting as benign (non-cancerous) lumps/cysts with/out associated symptoms of pain/discomfort, often waxing/waning with monthly hormonal menstrual variation. Imaging (including mammography/ultrasound) can assist in outruling cancer, as can biopsy (sa fine-needle aspiration of cystic lumps, core needle biopsy of solid lumps).
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?


.jpg)